
How does DNA replication relate to mitosis?
Answer
552.3k+ views
Hint: DNA replication is a biological process in which the DNA (genetic information) makes its copy during the division of cells from the parental DNA which is important for cell division.
The cell division is of two types i.e. meiosis and mitosis.
Complete answer:
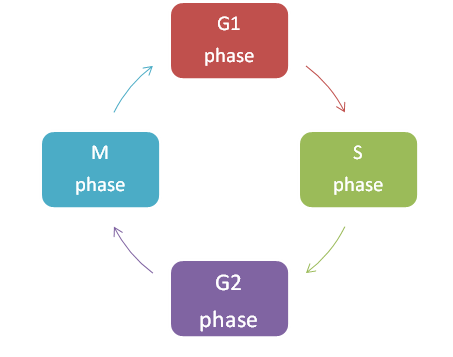
The cell undergoes a 4 stage process to divide itself. The four stages are the G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase, and M phase. G1, S, and G2 stages are collectively called Interphase. It is during the G1 and G2 phase the cell prepares itself and accumulates protein necessary for cell division or M phase while in S phase the DNA replicates itself. All these stages are in order.
which the cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Since the process is identical it means the daughter cells contain the same genetic information i.e. DNA and chromosomes as the parental cell. To divide the genetic material equally between two daughter cells the genetic material replicates itself by the DNA replication without increasing the chromosome number. All this occurs during the highly regulated and conserved S phase.
Additional information:
Mitosis is further divided into Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, and Cytokinesis.
The DNA is a double helix molecule that replicates in a semi-conservative fashion. The DNA unwinds itself using the helicase enzyme. The parental strand then acts as a template for the enzyme DNA polymerase which then helps to form two identical DNA helices each containing one parental and one daughter strand.
Note: During Mitosis the chromosome number remains the same in parental and daughter cells i.e. 2n. So the DNA replication only increases genetic material or DNA, not the chromosome number to maintain ploidy (sets of chromosomes)of the cell.
The cell division is of two types i.e. meiosis and mitosis.
Complete answer:
The cell undergoes a 4 stage process to divide itself. The four stages are the G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase, and M phase. G1, S, and G2 stages are collectively called Interphase. It is during the G1 and G2 phase the cell prepares itself and accumulates protein necessary for cell division or M phase while in S phase the DNA replicates itself. All these stages are in order.
which the cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Since the process is identical it means the daughter cells contain the same genetic information i.e. DNA and chromosomes as the parental cell. To divide the genetic material equally between two daughter cells the genetic material replicates itself by the DNA replication without increasing the chromosome number. All this occurs during the highly regulated and conserved S phase.

Additional information:
Mitosis is further divided into Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, and Cytokinesis.
The DNA is a double helix molecule that replicates in a semi-conservative fashion. The DNA unwinds itself using the helicase enzyme. The parental strand then acts as a template for the enzyme DNA polymerase which then helps to form two identical DNA helices each containing one parental and one daughter strand.
Note: During Mitosis the chromosome number remains the same in parental and daughter cells i.e. 2n. So the DNA replication only increases genetic material or DNA, not the chromosome number to maintain ploidy (sets of chromosomes)of the cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




