
How does dehydration synthesis relate to lipids?
Answer
557.1k+ views
Hint: Parchedness amalgamation responses in lipids structure an ester linkage between the carboxyl gathering of an unsaturated fat and the hydroxyl gathering of a liquor monomer, for example, glycerol. Lipids are the macromolecules that are delivered by sort of buildup response i.e. lack of hydration blend.
Complete step by step answer:
Dehydration Synthesis being a kind of buildup response is generally engaged with union of macromolecules. It includes the joining of the two more modest atoms of low sub-atomic weight i.e. monomers with the expulsion of water (\[{H_2}O\] ) particles to frame bigger particles having high subatomic loads for example macromolecules.
Lipids are orchestrated by this technique.
Formation of Triglyceride (lipid) by Dehydration synthesis:
Lipids likewise called as fats are composed of glycerol and fatty acids monomers. Lipids that comprise the significant part of our body are fatty substances. Fatty oils consist of one glycerol and three unsaturated fats.
A glycerol particle is an alcohol that comprises three carbon bonds with five hydrogen molecules and three hydroxyl groups.
The fatty acid being Carboxylic acids comprises one carboxyl group toward the finish of a straight hydrocarbon containing at least four carbon atoms.
The picture below shows structure of lauric Acid which is an immersed unsaturated fat.
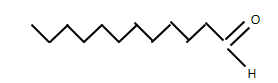
Note:
The hydroxyl groups (\[OH\] ) of glycerol atoms and carboxyl groups (\[COOH\] ) of three fatty acids associate with one another. Because of which three water particles are delivered and glycerol atoms become covalently connected with three unsaturated fats by means of 3 ester securities framing fatty oil (lipid). This reaction is known as a drying out combination.
Complete step by step answer:
Dehydration Synthesis being a kind of buildup response is generally engaged with union of macromolecules. It includes the joining of the two more modest atoms of low sub-atomic weight i.e. monomers with the expulsion of water (\[{H_2}O\] ) particles to frame bigger particles having high subatomic loads for example macromolecules.
Lipids are orchestrated by this technique.
Formation of Triglyceride (lipid) by Dehydration synthesis:
Lipids likewise called as fats are composed of glycerol and fatty acids monomers. Lipids that comprise the significant part of our body are fatty substances. Fatty oils consist of one glycerol and three unsaturated fats.
A glycerol particle is an alcohol that comprises three carbon bonds with five hydrogen molecules and three hydroxyl groups.
The fatty acid being Carboxylic acids comprises one carboxyl group toward the finish of a straight hydrocarbon containing at least four carbon atoms.
The picture below shows structure of lauric Acid which is an immersed unsaturated fat.

Note:
The hydroxyl groups (\[OH\] ) of glycerol atoms and carboxyl groups (\[COOH\] ) of three fatty acids associate with one another. Because of which three water particles are delivered and glycerol atoms become covalently connected with three unsaturated fats by means of 3 ester securities framing fatty oil (lipid). This reaction is known as a drying out combination.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




