
Does current flow through the capacitor?
Answer
540.6k+ views
Hint: As we know, there are two types of currents, AC and DC. In the case of a capacitor, it blocks the DC signal while allowing the AC signal to pass through it. Only the signals with frequencies pass through the capacitor and not the current.
Complete answer:
The capacitor only allows the AC signal to pass through it, whereas, the DC signal gets blocked. The diagram representing the same is given as follows.
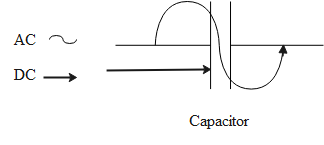
The reactance of the capacitor, that is, the capacitive reactance.
\[{{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{\omega C}\]
Where \[\omega \]is the angular frequency and C is the capacitance of the capacitor.
\[{{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{2\pi fC}\]
Where f is the frequency of the signal.
The direct current (DC) signal does not have frequency. So, the capacitive reactance is,
\[\begin{align}
& {{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{2\pi \times 0\times C} \\
& \Rightarrow {{X}_{C}}=\infty \\
\end{align}\]
Thus, as the reactance (resistance of the capacitor is high) is infinite, the current will not be allowed to pass through it.
The alternate current (AC) signal have frequency. So, the capacitive reactance is,
\[\begin{align}
& {{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{2\pi \times f\ne 0\times C} \\
& \Rightarrow {{X}_{C}}\ne \infty \\
\end{align}\]
Thus, as the reactance (resistance of the capacitor is not high) is not infinity, a small amount of current will be allowed to pass through it.
\[\therefore \]The capacitor does not allow the current to flow through it, instead, it allows the AC signal to pass through it.
Additional information:
The capacitor stores energy in the form of an electric field. Up to a certain potential, the capacitor allows the current to charge it, and after, that, it starts discharging through a load.
Thus charging and discharging happens alternatively, i.e. in alternate positive and negative cycles of AC signal. As the DC signal doesn't have any alternating cycles, so a capacitor can only charge.
Note:
In the case of DC circuits, a capacitor connected in a circuit charges and discharges when the current flows into and out of the circuit. In the case of AC circuits, a capacitor connected in a circuit acts resistance, called reactance when the current flows through the circuit.
Complete answer:
The capacitor only allows the AC signal to pass through it, whereas, the DC signal gets blocked. The diagram representing the same is given as follows.

The reactance of the capacitor, that is, the capacitive reactance.
\[{{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{\omega C}\]
Where \[\omega \]is the angular frequency and C is the capacitance of the capacitor.
\[{{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{2\pi fC}\]
Where f is the frequency of the signal.
The direct current (DC) signal does not have frequency. So, the capacitive reactance is,
\[\begin{align}
& {{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{2\pi \times 0\times C} \\
& \Rightarrow {{X}_{C}}=\infty \\
\end{align}\]
Thus, as the reactance (resistance of the capacitor is high) is infinite, the current will not be allowed to pass through it.
The alternate current (AC) signal have frequency. So, the capacitive reactance is,
\[\begin{align}
& {{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{2\pi \times f\ne 0\times C} \\
& \Rightarrow {{X}_{C}}\ne \infty \\
\end{align}\]
Thus, as the reactance (resistance of the capacitor is not high) is not infinity, a small amount of current will be allowed to pass through it.
\[\therefore \]The capacitor does not allow the current to flow through it, instead, it allows the AC signal to pass through it.
Additional information:
The capacitor stores energy in the form of an electric field. Up to a certain potential, the capacitor allows the current to charge it, and after, that, it starts discharging through a load.
Thus charging and discharging happens alternatively, i.e. in alternate positive and negative cycles of AC signal. As the DC signal doesn't have any alternating cycles, so a capacitor can only charge.
Note:
In the case of DC circuits, a capacitor connected in a circuit charges and discharges when the current flows into and out of the circuit. In the case of AC circuits, a capacitor connected in a circuit acts resistance, called reactance when the current flows through the circuit.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




