
How does blood clot in human beings?
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: Blood clotting helps to heal a wound. It is a semi-solid mass formed when the blood at some area of our tissue gets thickened. Heparin is an anticoagulant which prevents the clotting of blood.
Complete answer: Stepwise solution: Blood clotting or coagulation is an important process in our body that prevents excessive bleeding. Platelets and proteins in the plasma work together to stop the formation of clot thereby stopping the bleeding.
After the injury is healed, the clot will naturally be dissolved but sometimes clots formed inside the vessels do not dissolve naturally. These situations become dangerous and require accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Blood clot occurs through a series of chemical interactions:
1. Platelets forming a plug- platelets get turned on when a blood vessel is damaged. They stick to the walls in the area changing their shape to form a plug that fills the affected part to stop the blood from oozing out.
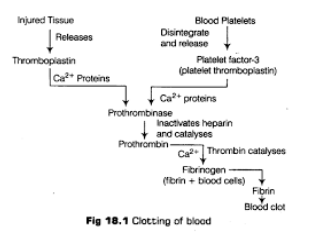
2. The clot grows- Proteins in the blood called clotting factors signal each other to cause a cascade of reactions. Thromboplastin (TF) in the presence of calcium ions converts inactive prothrombin into active prothrombin. This in turn activates fibrinogen to fibrin. Fibrin with platelets forms a homeostatic plug or clot over the wounded site.
3. Other proteins offset extra clotting factors to stop the spread of the clot farther.
4. As the damaged tissue heals, the body does not need the clot anymore. The tough fibrin strands dissolve and the blood takes back the platelets and cells of the clot.
Blood clots are treated differently depending upon their location. Some current treatments include Anticoagulants, Thrombolytics, Thrombectomy and Catheter-directed thrombolysis.
Note: Some drugs taken to stop the platelets from signalling each other so that they won’t stick together are Aspirin, Clopidogrel, Dipyridamole. Some medicines called blood thinners to make it hard for the body to make clotting factors are Heparin, Apixaban, Warfarin etc.
Complete answer: Stepwise solution: Blood clotting or coagulation is an important process in our body that prevents excessive bleeding. Platelets and proteins in the plasma work together to stop the formation of clot thereby stopping the bleeding.
After the injury is healed, the clot will naturally be dissolved but sometimes clots formed inside the vessels do not dissolve naturally. These situations become dangerous and require accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Blood clot occurs through a series of chemical interactions:
1. Platelets forming a plug- platelets get turned on when a blood vessel is damaged. They stick to the walls in the area changing their shape to form a plug that fills the affected part to stop the blood from oozing out.
2. The clot grows- Proteins in the blood called clotting factors signal each other to cause a cascade of reactions. Thromboplastin (TF) in the presence of calcium ions converts inactive prothrombin into active prothrombin. This in turn activates fibrinogen to fibrin. Fibrin with platelets forms a homeostatic plug or clot over the wounded site.
3. Other proteins offset extra clotting factors to stop the spread of the clot farther.
4. As the damaged tissue heals, the body does not need the clot anymore. The tough fibrin strands dissolve and the blood takes back the platelets and cells of the clot.
Blood clots are treated differently depending upon their location. Some current treatments include Anticoagulants, Thrombolytics, Thrombectomy and Catheter-directed thrombolysis.

Note: Some drugs taken to stop the platelets from signalling each other so that they won’t stick together are Aspirin, Clopidogrel, Dipyridamole. Some medicines called blood thinners to make it hard for the body to make clotting factors are Heparin, Apixaban, Warfarin etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




