
Why does an iron nail float on mercury but sinks in water?
A. Density of nail is less than mercury but more than water.
B. Density of nail is more than mercury but less than water.
C. Density of nails is less than both mercury and water.
D. Density of nails is more than both mercury and water.
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: When we place something in a liquid, either it sinks or it floats. Every fluid exerts an upward force on objects lying inside it. This upward force is known as buoyant force or the force of buoyancy. If this force is more than the weight of the object, it will float and if the force is less than the weight of the object, it will sink.
Formula Used:
$F_{Buoyancy} = \sigma Vg, \quad \rho = \dfrac{m}{V} , \ where \ \sigma$ is the density of the liquid and $\rho$is the density of the object of volume ‘V‘ and mass ‘m’.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Whenever a body is immersed in a liquid, the two forces acting on the body is its weight and the force of buoyancy. Hence the net force acting on the body is:
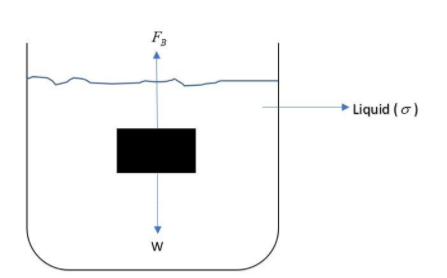
Net Force = Weight of the body (Always acting downwards) – Force of buoyancy (Always acting upwards)
Or $F_{net} = W - F_B$
Putting the values of $W=mg = \rho Vg \ and \ F_B = \sigma Vg$, we get;
$F_{net} = \rho Vg - \sigma Vg = (\rho - \sigma)Vg$
Now, we can see that if $\rho > \sigma$, net force is positive (Here downward force is taken positive, e.g. weight) and hence the block will sink.
If $\rho < \sigma$, net force is negative and the block will float.
Now, the density of iron nail = $7.8 gcm^{-3} \ (approx..)$
The density of water = $1 gcm^{-3} \ (approx..)$
The density of mercury = $13.6 gcm^{-3} \ (approx..)$
Hence we can see that the density of iron nails is greater than water, hence sink in it and is lesser than mercury and hence float. Hence option A. is correct.
Note: There is no need to remember all the densities of different materials. But students should remember the density of mercury and water as these two are the most widely used fluids. In the case of the above question, the density of iron is not actually required to answer the question but one can definitely guess the correct reason in these types of questions.
Formula Used:
$F_{Buoyancy} = \sigma Vg, \quad \rho = \dfrac{m}{V} , \ where \ \sigma$ is the density of the liquid and $\rho$is the density of the object of volume ‘V‘ and mass ‘m’.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Whenever a body is immersed in a liquid, the two forces acting on the body is its weight and the force of buoyancy. Hence the net force acting on the body is:

Net Force = Weight of the body (Always acting downwards) – Force of buoyancy (Always acting upwards)
Or $F_{net} = W - F_B$
Putting the values of $W=mg = \rho Vg \ and \ F_B = \sigma Vg$, we get;
$F_{net} = \rho Vg - \sigma Vg = (\rho - \sigma)Vg$
Now, we can see that if $\rho > \sigma$, net force is positive (Here downward force is taken positive, e.g. weight) and hence the block will sink.
If $\rho < \sigma$, net force is negative and the block will float.
Now, the density of iron nail = $7.8 gcm^{-3} \ (approx..)$
The density of water = $1 gcm^{-3} \ (approx..)$
The density of mercury = $13.6 gcm^{-3} \ (approx..)$
Hence we can see that the density of iron nails is greater than water, hence sink in it and is lesser than mercury and hence float. Hence option A. is correct.
Note: There is no need to remember all the densities of different materials. But students should remember the density of mercury and water as these two are the most widely used fluids. In the case of the above question, the density of iron is not actually required to answer the question but one can definitely guess the correct reason in these types of questions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




