
What does Acetyl CoA do in cellular respiration?
Answer
478.5k+ views
Hint: Acetyl CoA is produced from Pyruvate (a $3$- carbon compound) by the action of the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase. In this process, one molecule of Carbon dioxide is released. Acetyl CoA is a $2$ carbon-containing compound.
Complete answer:
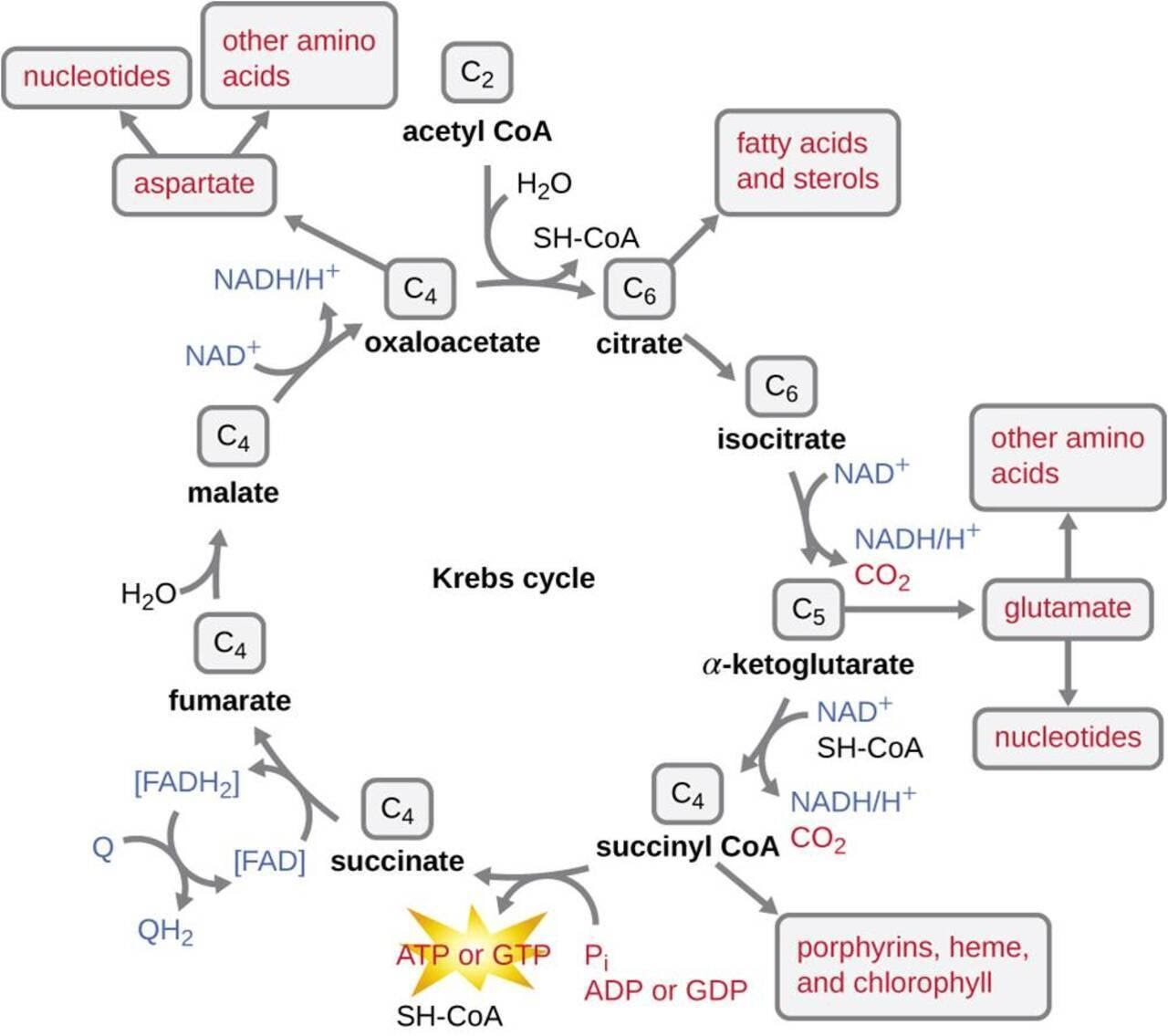
Acetyl coA is the starting material of the Krebs’ cycle or the TCA cycle. Through this cycle, Acetyl CoA is metabolized to form Carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. The cycle begins with the reaction of Acetyl CoA and OxaloAcetic acid (OAA) to form citric acid by utilization of one molecule of water under the action of enzyme citrate synthetase. This is a type of condensation reaction.
1. Next dehydration of citric acid takes place under the action of enzyme aconitase to form cis aconitic acid and water which on hydration in the later stage forms isocitric acid.
2. The isocitric acid under the action of enzyme isocitric acid dehydrogenase and NAD forms oxalosuccinic acid which on decarboxylation by enzyme decarboxylase forms α-ketoglutaric acid.
3. α-ketoglutaric acid on the action of CoA NAD and enzyme α-ketoglutaric acid dehydrogenase forms succinyl CoA which is oxidized to succinic acid in presence of GDP. The enzyme here involved is succinic thiokinase.
4. Succinic acid with enzyme succinic dehydrogenase and FAD forms Fumaric acid which on hydration and under fumarase enzyme action forms malic acid.
5. The malic acid in the action of enzyme malic dehydrogenase and NAD form oxaloacetic acid. $12$ molecules of ATPs are produced.
Note. :
The Coenzyme A present with the acetyl molecule at the start of the reaction is released by the Acetyl molecule before the condensation with the Oxaloacetic acid. The CoA-SH molecule binds with the pyruvate and forms a new Acetyl CoA molecule under the action of the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase. Oxaloacetic acid is a $4$ carbon-containing compound.
Complete answer:
Acetyl coA is the starting material of the Krebs’ cycle or the TCA cycle. Through this cycle, Acetyl CoA is metabolized to form Carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. The cycle begins with the reaction of Acetyl CoA and OxaloAcetic acid (OAA) to form citric acid by utilization of one molecule of water under the action of enzyme citrate synthetase. This is a type of condensation reaction.
1. Next dehydration of citric acid takes place under the action of enzyme aconitase to form cis aconitic acid and water which on hydration in the later stage forms isocitric acid.
2. The isocitric acid under the action of enzyme isocitric acid dehydrogenase and NAD forms oxalosuccinic acid which on decarboxylation by enzyme decarboxylase forms α-ketoglutaric acid.
3. α-ketoglutaric acid on the action of CoA NAD and enzyme α-ketoglutaric acid dehydrogenase forms succinyl CoA which is oxidized to succinic acid in presence of GDP. The enzyme here involved is succinic thiokinase.
4. Succinic acid with enzyme succinic dehydrogenase and FAD forms Fumaric acid which on hydration and under fumarase enzyme action forms malic acid.
5. The malic acid in the action of enzyme malic dehydrogenase and NAD form oxaloacetic acid. $12$ molecules of ATPs are produced.

Note. :
The Coenzyme A present with the acetyl molecule at the start of the reaction is released by the Acetyl molecule before the condensation with the Oxaloacetic acid. The CoA-SH molecule binds with the pyruvate and forms a new Acetyl CoA molecule under the action of the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase. Oxaloacetic acid is a $4$ carbon-containing compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




