
How does a concentration cell work?
Answer
499.8k+ views
Hint: Concentration cells are basically an electrochemical cell which is made up of two half-cells. The electrodes used in concentration cells are the same, but they differ only in terms of concentration of electrolyte. The working of a concentration cell depends on the equilibrium position of concentration of the cell by means of transfer of electrons.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
A concentration cell is composed of two half-cells which have the same electrodes but they differ in the concentration of electrolyte. The working of a concentration cell depends on maintaining the equilibrium between the concentration of two cells. The concentration cell will dilute the more concentration cell and similarly will make concentrated the more dilute solution. Thus it creates an equilibrium between the two half-cells by transfer of electrons. The electrons will be transferred from half-cell having lower concentration to half-cell having higher concentration. The e.m.f of cell can be found as:
$ {E^ \circ }_{cell}{\text{ = }}{E^ \circ }_{cathode} - {E^ \circ }_{anode} $
When the cell reaches at equilibrium position, it will create a voltage which can be found by using Nernst equation as:
$ {E_{cell}}{\text{ = }}{E^ \circ }_{cell} - \dfrac{{0.0592}}{n}\log Q $
Where,
$ {E^ \circ }_{cell} $ is the standard reduction potential of a cell.
$ n $ is the number of electrons transferred.
$ Q $ is the reaction quotient.
The whole reaction takes place at room temperature of $ {\text{25}}{{\text{ }}^ \circ }C $ .
Note:
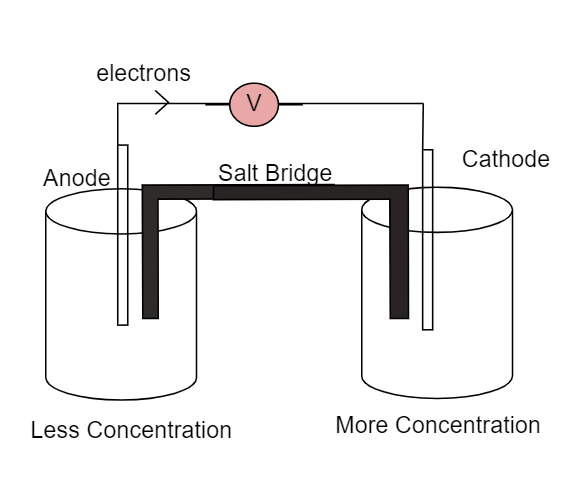
Here the salt bridge connects the two half-cells and maintains the electrical neutrality between them. We cannot use a wire to connect both the cells as it would react with ions which flow from one end to other end. The electrons will flow from left side to right side as due to lower concentration at left side and higher concentration at right side.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
A concentration cell is composed of two half-cells which have the same electrodes but they differ in the concentration of electrolyte. The working of a concentration cell depends on maintaining the equilibrium between the concentration of two cells. The concentration cell will dilute the more concentration cell and similarly will make concentrated the more dilute solution. Thus it creates an equilibrium between the two half-cells by transfer of electrons. The electrons will be transferred from half-cell having lower concentration to half-cell having higher concentration. The e.m.f of cell can be found as:
$ {E^ \circ }_{cell}{\text{ = }}{E^ \circ }_{cathode} - {E^ \circ }_{anode} $
When the cell reaches at equilibrium position, it will create a voltage which can be found by using Nernst equation as:
$ {E_{cell}}{\text{ = }}{E^ \circ }_{cell} - \dfrac{{0.0592}}{n}\log Q $
Where,
$ {E^ \circ }_{cell} $ is the standard reduction potential of a cell.
$ n $ is the number of electrons transferred.
$ Q $ is the reaction quotient.
The whole reaction takes place at room temperature of $ {\text{25}}{{\text{ }}^ \circ }C $ .

Note:
Here the salt bridge connects the two half-cells and maintains the electrical neutrality between them. We cannot use a wire to connect both the cells as it would react with ions which flow from one end to other end. The electrons will flow from left side to right side as due to lower concentration at left side and higher concentration at right side.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE

a Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode class 12 chemistry CBSE




