
Do centrioles have DNA?
Answer
536.1k+ views
Hint: Centriole is a cylindrical organelle that is composed mainly of a protein which is known as tubulin. Their main function arises during the process of cell division where the production of cilia occurs during the interphase while the aster and the spindle fibers occur during the cell division.
Complete answer:
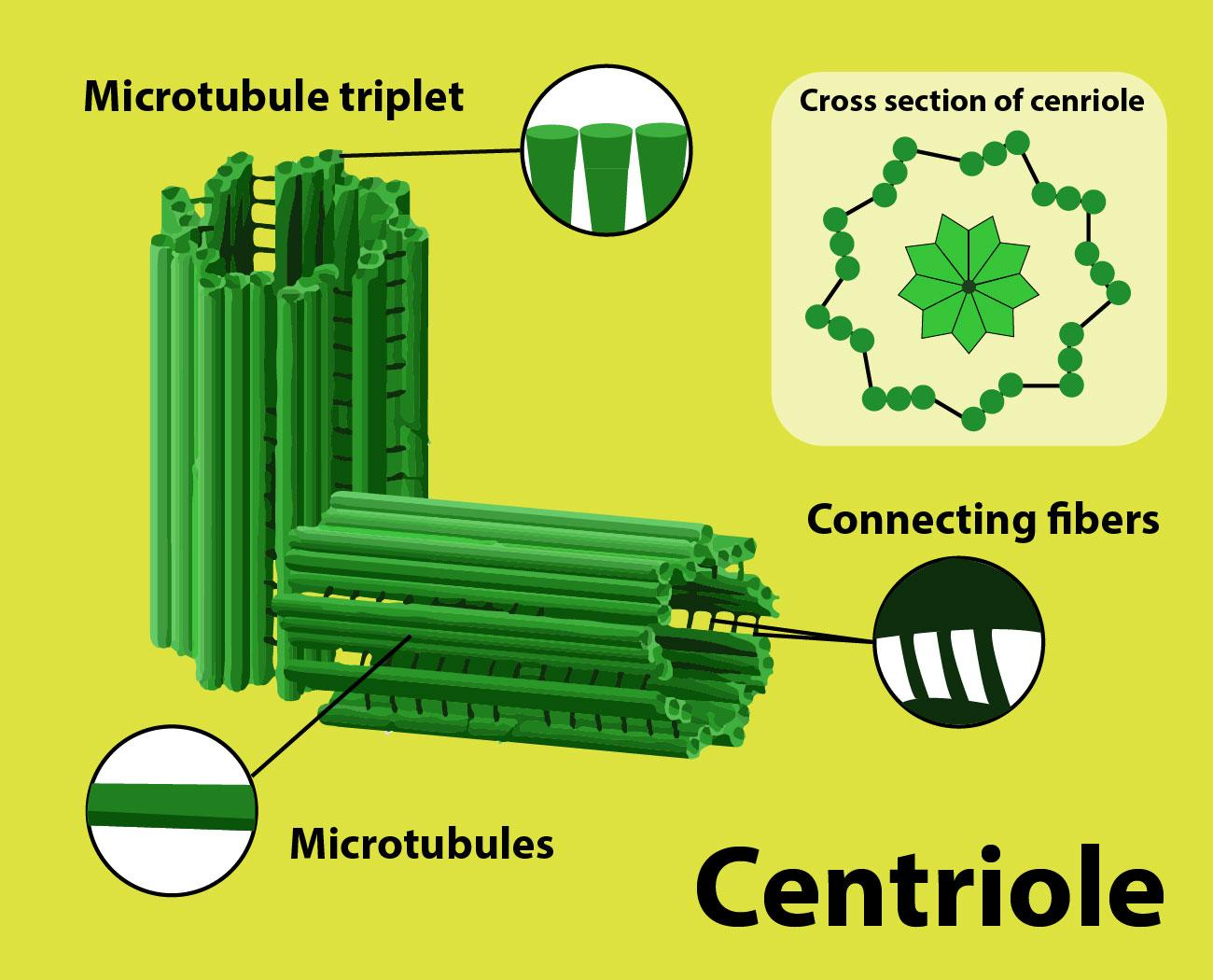
It is an organelle that is cylindrical and composed of proteins known as tubulin and lacks DNA. They are the characteristics of a eukaryotic cell where a pair of centrioles are found that are surrounded by the pericentriolar material (PCM) which is a highly ordered mass of dense material resulting in the formation of a centrosome. Centrioles are commonly found in certain eukaryotic cells that include the male gametes of charophytes, vascular plants, bryophytes, and ginkgo. Their structure is made up of short microtubule arms triplets that are 9 in number with the additional proteins namely centrin, calnexin, and testing that results in the formation of cilia during interphase and spindle during cell division.
The centrioles mainly function with the organization of the mitotic spindle and results in the completion of cytokinesis. Earlier the Centrioles were thought to be required in the animal cells for the formation of a mitotic spindle. During the process of cellular division, the centrioles can self-replicate. It was found that In non-dividing cells, centrioles also are involved in the formation of flagella and cilia. However, centrosomes were only responsible for the formation of the spindle apparatus as a cellular division.
Note:
In the 1880s Boveri and Van Beneden were the first ones to discover the centriole. It is a non-membranous organelle. The non-membranous organelles are the types of organelles that are not surrounded by a membrane.
Complete answer:
It is an organelle that is cylindrical and composed of proteins known as tubulin and lacks DNA. They are the characteristics of a eukaryotic cell where a pair of centrioles are found that are surrounded by the pericentriolar material (PCM) which is a highly ordered mass of dense material resulting in the formation of a centrosome. Centrioles are commonly found in certain eukaryotic cells that include the male gametes of charophytes, vascular plants, bryophytes, and ginkgo. Their structure is made up of short microtubule arms triplets that are 9 in number with the additional proteins namely centrin, calnexin, and testing that results in the formation of cilia during interphase and spindle during cell division.
The centrioles mainly function with the organization of the mitotic spindle and results in the completion of cytokinesis. Earlier the Centrioles were thought to be required in the animal cells for the formation of a mitotic spindle. During the process of cellular division, the centrioles can self-replicate. It was found that In non-dividing cells, centrioles also are involved in the formation of flagella and cilia. However, centrosomes were only responsible for the formation of the spindle apparatus as a cellular division.

Note:
In the 1880s Boveri and Van Beneden were the first ones to discover the centriole. It is a non-membranous organelle. The non-membranous organelles are the types of organelles that are not surrounded by a membrane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




