
What is DNA replication? What is the significance?
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: DNA is known to be a storehouse of genetic information. Replication is the process in which two complementary strands of DNA unwind and each strand serves as a template for synthesizing new complementary strands.
Complete step by step answer:
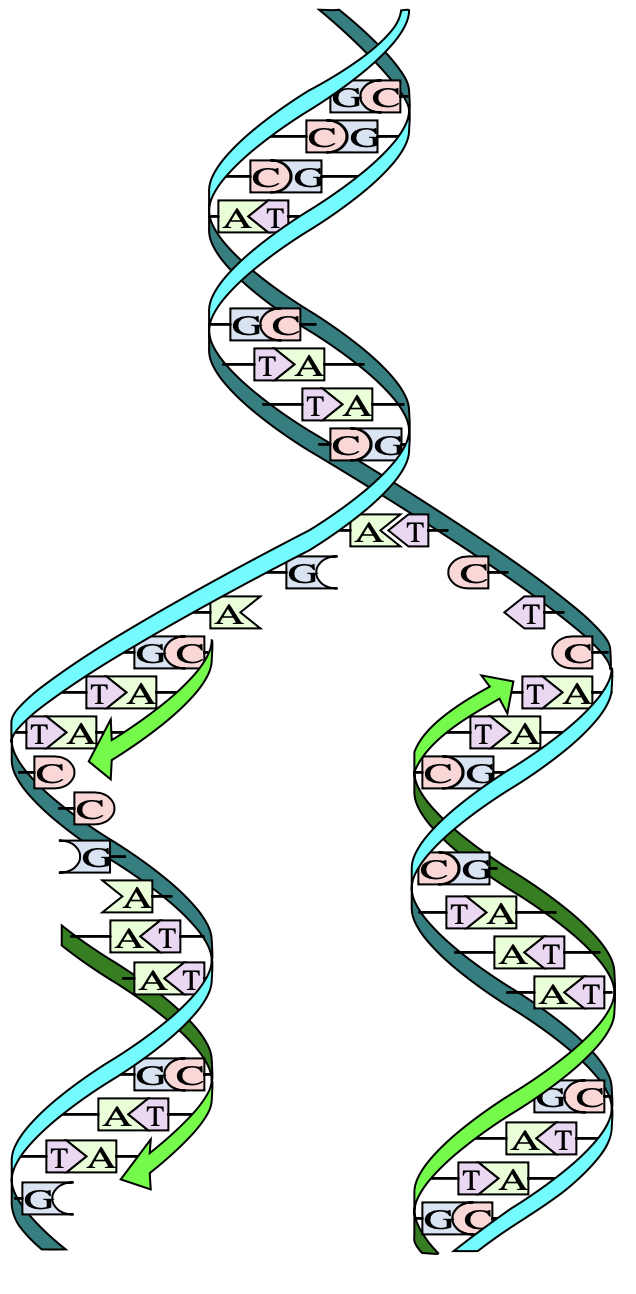
DNA replication is the process by which an organism duplicates its DNA into another copy that is passed on to daughter cells. It usually occurs before cell division and ensures that both the daughter cells get the exact same copy of the parent DNA. The specific regions in the genome of an organism where replication begins are called ‘origin’. The process involves the action of many different enzymes the first of which is helicase. It helps in the unwinding of the double-stranded DNA molecule. There exist certain proteins called Single-strand binding proteins (SSB) that stabilize the unwound DNA strands. Another enzyme named as Topoisomerase helps in reducing the stress that occurs in the molecule as a result of unwinding. This entire assembly, with unwound DNA which
looks like an inverted Y shape, is called the Replication fork.
Many theories for the replication model were introduced, out of which ‘semi-conservative’ is the widely accepted model. It was suggested by Meselson and Stahl. According to this process, parent DNA double helix results in two-hybrid DNA. Each of the daughter DNA molecules retains one strand from the parent and synthesizes a new one. The enzyme catalyzing the synthesis of DNA is DNA polymerase. Its fundamental reaction is phosphoryl group transfer between incoming nucleotides and the growing chain of DNA. Given below is a DNA replication process:
Note:
DNA polymerase can catalyze polymerization in 3’ to 5’ direction and hence continuous polymerization occurs on this strand i.e. it is the leading strand. Whereas, on the other strands, short segments of DNA are synthesized called Okazaki fragments which are joined later with the help of DNA ligases.
Complete step by step answer:
DNA replication is the process by which an organism duplicates its DNA into another copy that is passed on to daughter cells. It usually occurs before cell division and ensures that both the daughter cells get the exact same copy of the parent DNA. The specific regions in the genome of an organism where replication begins are called ‘origin’. The process involves the action of many different enzymes the first of which is helicase. It helps in the unwinding of the double-stranded DNA molecule. There exist certain proteins called Single-strand binding proteins (SSB) that stabilize the unwound DNA strands. Another enzyme named as Topoisomerase helps in reducing the stress that occurs in the molecule as a result of unwinding. This entire assembly, with unwound DNA which
looks like an inverted Y shape, is called the Replication fork.
Many theories for the replication model were introduced, out of which ‘semi-conservative’ is the widely accepted model. It was suggested by Meselson and Stahl. According to this process, parent DNA double helix results in two-hybrid DNA. Each of the daughter DNA molecules retains one strand from the parent and synthesizes a new one. The enzyme catalyzing the synthesis of DNA is DNA polymerase. Its fundamental reaction is phosphoryl group transfer between incoming nucleotides and the growing chain of DNA. Given below is a DNA replication process:

Note:
DNA polymerase can catalyze polymerization in 3’ to 5’ direction and hence continuous polymerization occurs on this strand i.e. it is the leading strand. Whereas, on the other strands, short segments of DNA are synthesized called Okazaki fragments which are joined later with the help of DNA ligases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




