
Divide the quadratic polynomial \[2{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }1\] by $x+2$ and find quotient and remainder.
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint: We will divide \[2{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }1\] by $x+2$ using the long division method.
Let us first know about the algebraic division method.
1. Divide the first term of the dividend (the polynomial to be divided) by the first term of the divisor. This gives the first term of the quotient.
2. Multiply the divisor by the first term of the quotient.
3. Subtract the product from the dividend then bring down the next term. The difference and the next term will be the new dividend.
Note: Remember the rule in subtraction: "change the sign of the subtrahend then proceed to addition".
4. Repeat steps 2 – 4 to find the second term of the quotient.
5. Continue the process until a remainder is obtained. This can be zero or is of a lower index than the divisor.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let us take an example first.
We shall divide \[3{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }16x\text{ }+\text{ }5\] by x + 5.
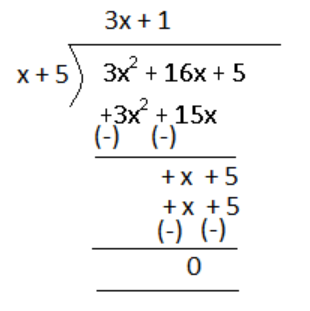
So, the quotient in this division is 3x + 1 while the remainder is 0.
Let us now verify this division.
We know that to verify any division sum, we follow the following rule:-
\[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
Dividend\text{ }=\text{ }Divisor\times Quotient\text{ }+\text{ }Remainder \\
3{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }16x\text{ }+\text{ }5\text{ }=\text{ }\left( x\text{ }+\text{ }5 \right)\times \left( 3x\text{ }+\text{ }1 \right)\text{ }+\text{ }0 \\
\end{array}\]
\[\Rightarrow 3{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }16x\text{ }+\text{ }5\text{ }=\text{ x}\left( 3x\text{ }+\text{ }1 \right)\text{ }+5(3x+1)\]
\[\Rightarrow 3{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }16x\text{ }+\text{ }5\text{ }=\text{ 3}{{\text{x}}^{2}}\text{+x }+15x+5\]
\[\Rightarrow 3{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }16x\text{ }+\text{ }5=3{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }16x\text{ }+\text{ }5\]
Hence, verified.
Let us now solve this question.
So, firstly we will write \[2{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }1\] and $x+2$ in the long division form.
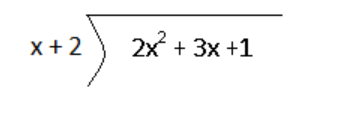 Now, we will divide \[2{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }1\] by $x+2$
Now, we will divide \[2{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }1\] by $x+2$
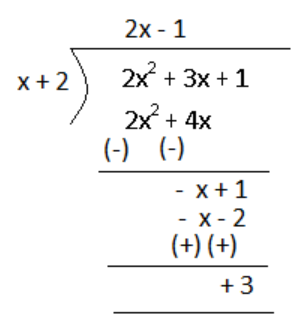
So, after dividing \[2{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }1\] by $x+2$ using the method explained in the hint provided above, the quotient so obtained is 2x – 1 and the remainder left is +3.
Let us now verify this division by the method mentioned in the hint provided above:-
\[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
Dividend\text{ }=\text{ }Divisor\times Quotient\text{ }+\text{ }Remainder \\
2{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }1\text{ }=\text{ }\left( x\text{ }+\text{ }2 \right)\times \left( 2x\text{ }\text{ }1 \right)\text{ }+\text{ }3 \\
\Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }1\text{ }=\text{ }x\text{ }\left( 2x\text{ }\text{ }1 \right)\text{ }+\text{ }2\text{ }\left( 2x\text{ }\text{ }1 \right)\text{ }+\text{ }3 \\
\Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }1\text{ }=\text{ }2{{x}^{2}}\text{ }x\text{ }+\text{ }4x\text{ }\text{ }2\text{ }+\text{ }3 \\
\Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }1\text{ }=\text{ }2{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }1 \\
\end{array}\]
Hence, verified.
Note: We can verify our division by following the below given method \[\text{DIVIDEND}=\text{DIVISOR}\times\text{QUOTIENT}+\text{REMAINDER}\]
By this method, we can check whether our answer and our calculations are correct or not.
This method states that the dividend of a division sum is equal to the sum of the remainder and the product of the divisor and quotient. If the sum is not equal to the dividend, then the division sum would be wrong. Try to avoid calculation mistakes while solving the question.
Let us first know about the algebraic division method.
1. Divide the first term of the dividend (the polynomial to be divided) by the first term of the divisor. This gives the first term of the quotient.
2. Multiply the divisor by the first term of the quotient.
3. Subtract the product from the dividend then bring down the next term. The difference and the next term will be the new dividend.
Note: Remember the rule in subtraction: "change the sign of the subtrahend then proceed to addition".
4. Repeat steps 2 – 4 to find the second term of the quotient.
5. Continue the process until a remainder is obtained. This can be zero or is of a lower index than the divisor.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let us take an example first.
We shall divide \[3{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }16x\text{ }+\text{ }5\] by x + 5.
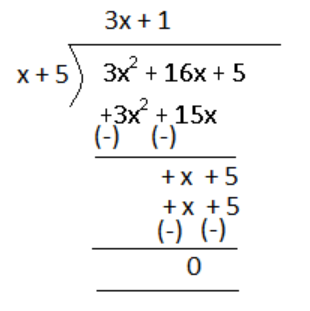
So, the quotient in this division is 3x + 1 while the remainder is 0.
Let us now verify this division.
We know that to verify any division sum, we follow the following rule:-
\[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
Dividend\text{ }=\text{ }Divisor\times Quotient\text{ }+\text{ }Remainder \\
3{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }16x\text{ }+\text{ }5\text{ }=\text{ }\left( x\text{ }+\text{ }5 \right)\times \left( 3x\text{ }+\text{ }1 \right)\text{ }+\text{ }0 \\
\end{array}\]
\[\Rightarrow 3{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }16x\text{ }+\text{ }5\text{ }=\text{ x}\left( 3x\text{ }+\text{ }1 \right)\text{ }+5(3x+1)\]
\[\Rightarrow 3{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }16x\text{ }+\text{ }5\text{ }=\text{ 3}{{\text{x}}^{2}}\text{+x }+15x+5\]
\[\Rightarrow 3{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }16x\text{ }+\text{ }5=3{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }16x\text{ }+\text{ }5\]
Hence, verified.
Let us now solve this question.
So, firstly we will write \[2{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }1\] and $x+2$ in the long division form.
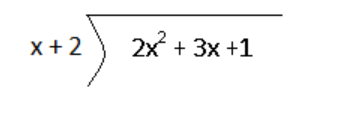
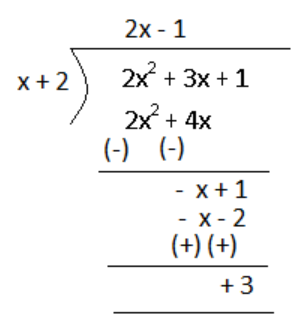
So, after dividing \[2{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }1\] by $x+2$ using the method explained in the hint provided above, the quotient so obtained is 2x – 1 and the remainder left is +3.
Let us now verify this division by the method mentioned in the hint provided above:-
\[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
Dividend\text{ }=\text{ }Divisor\times Quotient\text{ }+\text{ }Remainder \\
2{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }1\text{ }=\text{ }\left( x\text{ }+\text{ }2 \right)\times \left( 2x\text{ }\text{ }1 \right)\text{ }+\text{ }3 \\
\Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }1\text{ }=\text{ }x\text{ }\left( 2x\text{ }\text{ }1 \right)\text{ }+\text{ }2\text{ }\left( 2x\text{ }\text{ }1 \right)\text{ }+\text{ }3 \\
\Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }1\text{ }=\text{ }2{{x}^{2}}\text{ }x\text{ }+\text{ }4x\text{ }\text{ }2\text{ }+\text{ }3 \\
\Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }1\text{ }=\text{ }2{{x}^{2}}+\text{ }3x\text{ }+\text{ }1 \\
\end{array}\]
Hence, verified.
Note: We can verify our division by following the below given method \[\text{DIVIDEND}=\text{DIVISOR}\times\text{QUOTIENT}+\text{REMAINDER}\]
By this method, we can check whether our answer and our calculations are correct or not.
This method states that the dividend of a division sum is equal to the sum of the remainder and the product of the divisor and quotient. If the sum is not equal to the dividend, then the division sum would be wrong. Try to avoid calculation mistakes while solving the question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 12 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Convert 40circ C to Fahrenheit A 104circ F B 107circ class 8 maths CBSE

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE




