
How do you divide $\left( {5{x^4} - 3{x^3} + 2{x^2} - 1} \right) \div \left( {{x^2} + 4} \right)$ using long division?
Answer
544.2k+ views
Hint: First make sure the polynomial is written in descending order. If any terms are missing, use a zero to fill in the missing term. Next, divide the term with the highest power inside the division symbol by the term with the highest power outside the division symbol. Next, multiply (or distribute) the answer obtained in the previous step by the polynomial in front of the division symbol. Next, subtract and bring down the next term. Next, divide the term with the highest power inside the division symbol by the term with the highest power outside the division symbol. Next, multiply (or distribute) the answer obtained in the previous step by the polynomial in front of the division symbol. Next, subtract and notice there are no more terms to bring down. Next, write the final answer using a division algorithm for polynomials.
Division Algorithm for polynomials:
If $p\left( x \right)$ and $g\left( x \right)$ are two polynomials with $g\left( x \right) \ne 0$, then we can find two polynomials $q\left( x \right)$ and $r\left( x \right)$ such that
$p\left( x \right) = g\left( x \right) \times q\left( x \right) + r\left( x \right)$
Where $r\left( x \right) = 0$ or degree of $r\left( x \right) < $ degree of $g\left( x \right)$.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to find $\left( {5{x^4} - 3{x^3} + 2{x^2} - 1} \right) \div \left( {{x^2} + 4} \right)$.
So, first make sure the polynomial is written in descending order. If any terms are missing, use a zero to fill in the missing term (this will help with the spacing). In this case, the problem is ready as is.
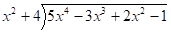
Next, divide the term with the highest power inside the division symbol by the term with the highest power outside the division symbol. In this case, we have $5{x^4}$ divided by ${x^2}$ which is $5{x^2}$.
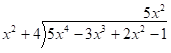
Next, multiply (or distribute) the answer obtained in the previous step by the polynomial in front of the division symbol. In this case, we need to multiply $5{x^2}$ and ${x^2} + 4$.
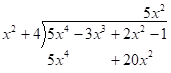
Next, subtract and bring down the next term.
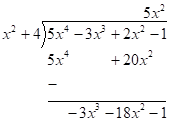
Next, divide the term with the highest power inside the division symbol by the term with the highest power outside the division symbol. In this case, we have $ - 3{x^3}$ divided by ${x^2}$ which is $ - 3x$.
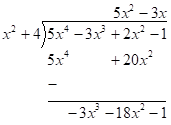
Next, multiply (or distribute) the answer obtained in the previous step by the polynomial in front of the division symbol. In this case, we need to multiply $ - 3x$ and ${x^2} + 4$.
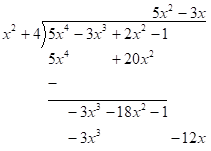
Next, subtract and notice there are no more terms to bring down.
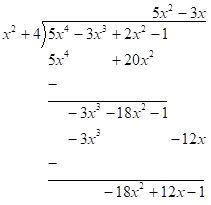
Next, divide the term with the highest power inside the division symbol by the term with the highest power outside the division symbol. In this case, we have $ - 18{x^2}$ divided by ${x^2}$ which is $ - 18$.
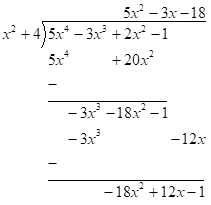
Next, multiply (or distribute) the answer obtained in the previous step by the polynomial in front of the division symbol. In this case, we need to multiply $ - 18$ and ${x^2} + 4$.
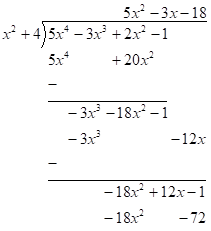
Next, subtract and notice there are no more terms to bring down.
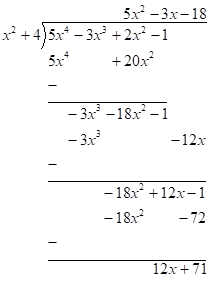
Next, write the final answer. The term remaining after the last subtract step is the remainder and must be written as a fraction in the final answer.
$5{x^2} - 3x - 18 + \dfrac{{12x + 71}}{{{x^2} + 4}}$
Hence, the quotient is $5{x^2} - 3x - 18$ and the remainder is $12x + 71$.
Note: We can verify our answer by the following formula.
Dividend = (Divisor $ \times $ Quotient) + Remainder
Here, the dividend is $5{x^4} - 3{x^3} + 2{x^2} - 1$. Divisor is ${x^2} + 4$. Quotient is $5{x^2} - 3x - 18$. Remainder is $12x + 71$.
Let us take the right-hand side.
RHS = (Divisor $ \times $ Quotient) + Remainder
Let us put all the values.
$ \Rightarrow RHS = \left( {{x^2} + 4} \right) \times \left( {5{x^4} - 3{x^3} + 2{x^2} - 1} \right) + 12x + 71$
Simplify the above term.
$ \Rightarrow RHS = 5{x^4} - 3{x^3} + 2{x^2} - 1$
$\therefore LHS = RHS$
Division Algorithm for polynomials:
If $p\left( x \right)$ and $g\left( x \right)$ are two polynomials with $g\left( x \right) \ne 0$, then we can find two polynomials $q\left( x \right)$ and $r\left( x \right)$ such that
$p\left( x \right) = g\left( x \right) \times q\left( x \right) + r\left( x \right)$
Where $r\left( x \right) = 0$ or degree of $r\left( x \right) < $ degree of $g\left( x \right)$.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to find $\left( {5{x^4} - 3{x^3} + 2{x^2} - 1} \right) \div \left( {{x^2} + 4} \right)$.
So, first make sure the polynomial is written in descending order. If any terms are missing, use a zero to fill in the missing term (this will help with the spacing). In this case, the problem is ready as is.
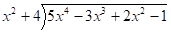
Next, divide the term with the highest power inside the division symbol by the term with the highest power outside the division symbol. In this case, we have $5{x^4}$ divided by ${x^2}$ which is $5{x^2}$.
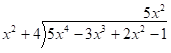
Next, multiply (or distribute) the answer obtained in the previous step by the polynomial in front of the division symbol. In this case, we need to multiply $5{x^2}$ and ${x^2} + 4$.
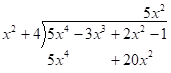
Next, subtract and bring down the next term.
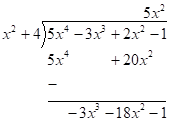
Next, divide the term with the highest power inside the division symbol by the term with the highest power outside the division symbol. In this case, we have $ - 3{x^3}$ divided by ${x^2}$ which is $ - 3x$.
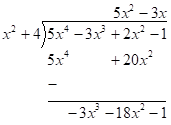
Next, multiply (or distribute) the answer obtained in the previous step by the polynomial in front of the division symbol. In this case, we need to multiply $ - 3x$ and ${x^2} + 4$.
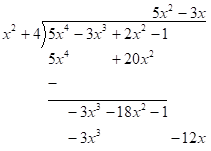
Next, subtract and notice there are no more terms to bring down.
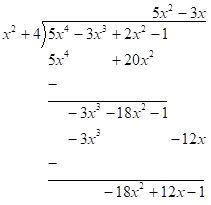
Next, divide the term with the highest power inside the division symbol by the term with the highest power outside the division symbol. In this case, we have $ - 18{x^2}$ divided by ${x^2}$ which is $ - 18$.
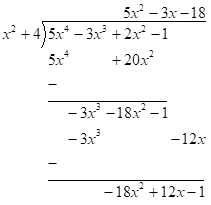
Next, multiply (or distribute) the answer obtained in the previous step by the polynomial in front of the division symbol. In this case, we need to multiply $ - 18$ and ${x^2} + 4$.
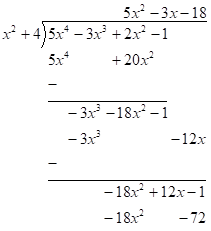
Next, subtract and notice there are no more terms to bring down.
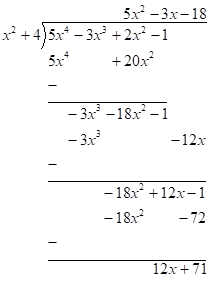
Next, write the final answer. The term remaining after the last subtract step is the remainder and must be written as a fraction in the final answer.
$5{x^2} - 3x - 18 + \dfrac{{12x + 71}}{{{x^2} + 4}}$
Hence, the quotient is $5{x^2} - 3x - 18$ and the remainder is $12x + 71$.
Note: We can verify our answer by the following formula.
Dividend = (Divisor $ \times $ Quotient) + Remainder
Here, the dividend is $5{x^4} - 3{x^3} + 2{x^2} - 1$. Divisor is ${x^2} + 4$. Quotient is $5{x^2} - 3x - 18$. Remainder is $12x + 71$.
Let us take the right-hand side.
RHS = (Divisor $ \times $ Quotient) + Remainder
Let us put all the values.
$ \Rightarrow RHS = \left( {{x^2} + 4} \right) \times \left( {5{x^4} - 3{x^3} + 2{x^2} - 1} \right) + 12x + 71$
Simplify the above term.
$ \Rightarrow RHS = 5{x^4} - 3{x^3} + 2{x^2} - 1$
$\therefore LHS = RHS$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





