
Who discovered Nucleic acid? What was it called then?
Answer
510.6k+ views
Hint: He extracted "nuclein," DNA with associated proteins, from the cell’s nuclei. He was the primary to spot DNA as a definite molecule. This created speculation that the DNA may need something to do with genetics.
Complete answer:
In 1869. Nucleic acids were discovered by Friedrich Miescher.
It was known as nuclein.
Richard Altmann in 1889 discovered that nuclein shows properties of and it had been named as nucleic acid later.
-DNA contains the genetic material of a person as well as the human genome.
-Its chemistry shows that it is a compound of several smaller molecules linked together.
-The 2 DNA strands are known as Polynucleotides as they are made up of simpler monomeric units called nucleotides.
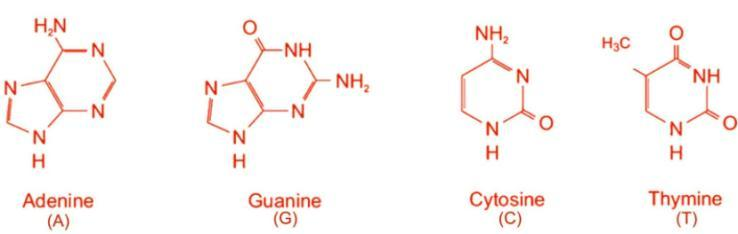
-Each nucleotide is composed of one of the four nitrogen-containing nucleobases which are: cytosine, guanine, adenine, or thymine.
-It is an organic compound that has a special molecular structure. It is seen in all eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
-The molecule of DNA is a double helix structure that is negatively charged.
-Humans have approximately 20,000 – 25,000 protein-coding genes.
-DNA is also responsible for introducing a mutation in the species by random rearrangement of gene sequences or recombination during reproduction.
Note:
-The DNA was first named and recognized by Johannes Friedrich Miescher in 1869, during his work on white blood cells. There are different types of DNA, they are A-DNA, B-DNA, and Z-DNA.
-"Nucleic acid" is the term we use to explain specific large molecules within the cell. And they are formed from polymers of repeating units, and therefore the two most famous nucleic acids that you've heard about are our DNA and RNA. And nucleic acids within the cell act to truly store information.
Complete answer:
In 1869. Nucleic acids were discovered by Friedrich Miescher.
It was known as nuclein.
Richard Altmann in 1889 discovered that nuclein shows properties of and it had been named as nucleic acid later.
-DNA contains the genetic material of a person as well as the human genome.
-Its chemistry shows that it is a compound of several smaller molecules linked together.
-The 2 DNA strands are known as Polynucleotides as they are made up of simpler monomeric units called nucleotides.
-Each nucleotide is composed of one of the four nitrogen-containing nucleobases which are: cytosine, guanine, adenine, or thymine.
-It is an organic compound that has a special molecular structure. It is seen in all eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
-The molecule of DNA is a double helix structure that is negatively charged.
-Humans have approximately 20,000 – 25,000 protein-coding genes.
-DNA is also responsible for introducing a mutation in the species by random rearrangement of gene sequences or recombination during reproduction.
Note:
-The DNA was first named and recognized by Johannes Friedrich Miescher in 1869, during his work on white blood cells. There are different types of DNA, they are A-DNA, B-DNA, and Z-DNA.
-"Nucleic acid" is the term we use to explain specific large molecules within the cell. And they are formed from polymers of repeating units, and therefore the two most famous nucleic acids that you've heard about are our DNA and RNA. And nucleic acids within the cell act to truly store information.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




