
Dimethyl ether and ethyl alcohol are ______ of each other.
(A) Mesomers
(B) Functional isomers
(C) Both a and b
(D) None
Answer
492.9k+ views
Hint: Isomers in chemistry are molecules or polyatomic ions that have the same molecular formula — that is, the same number of atoms of each element — but different atomic configurations in space. Isomerism refers to the existence or potential of isomers. Isomers don't always have the same chemical or physical characteristics as one another. Structural or constitutional isomerism, in which the bonds between the atoms differ, and stereoisomerism or spatial isomerism, in which the bonds are the same but the relative locations of the atoms differ, are the two primary types of isomerism.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The functional groups and atoms in these isomers' molecules are connected in various ways. Because structural isomers may or may not include the same functional group, they are given various IUPAC designations. Functional group isomerism is another name for it. It refers to compounds that have the same chemical formula but various functional groups linked to them, as the name indicates. The chemical molecule $ {{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{O}} $ is an example of functional isomerism.
Another example is the pair ethanol $ {H_3}C-C{H_2}-OH $ (an alcohol) and dimethyl ether $ {H_3}C-O-C{H_2}H $ (an ether).
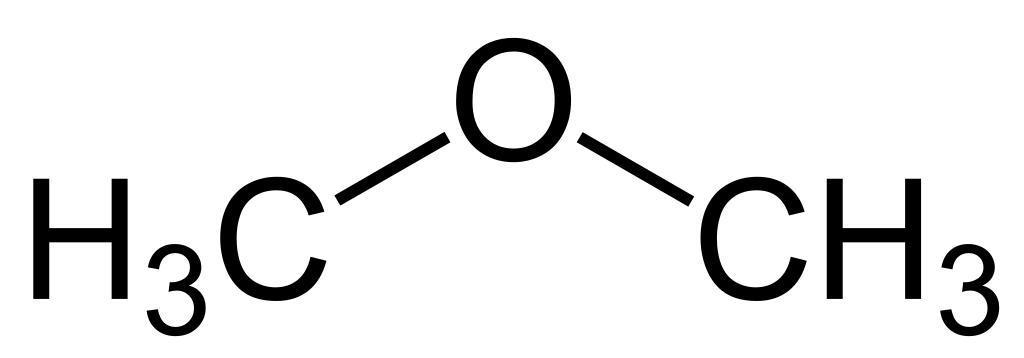
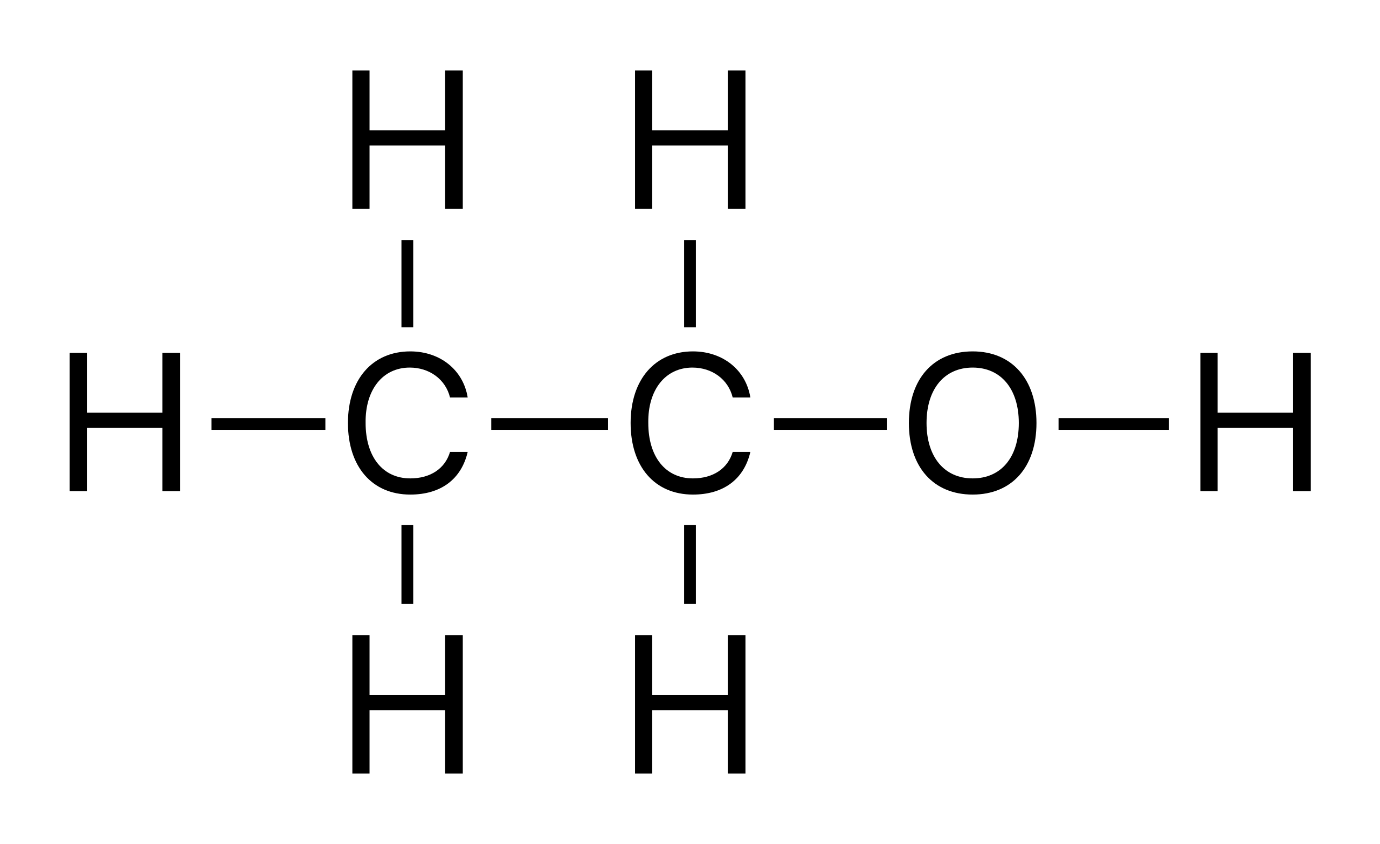
When compounds have the same molecular formula but distinct functional groups, this is known as functional isomerism. Functional isomers belong to various homologous series as a result of this.
Alcohols and ethers are the two functional group isomers that you should be aware of.
ketones and aldehydes
Esters and carboxylic acids.
Note:
A hierarchy of isomeric connections exists. Two compounds may have the same constitutional isomer yet are stereoisomers of each other when examined further. Two molecules with the same stereoisomer but distinct conformational forms or isotopologues might be in various conformational forms or be separate isotopologues. The scope of the investigation is determined by the subject of research or the chemical and physical qualities that are of interest.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The functional groups and atoms in these isomers' molecules are connected in various ways. Because structural isomers may or may not include the same functional group, they are given various IUPAC designations. Functional group isomerism is another name for it. It refers to compounds that have the same chemical formula but various functional groups linked to them, as the name indicates. The chemical molecule $ {{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{O}} $ is an example of functional isomerism.
Another example is the pair ethanol $ {H_3}C-C{H_2}-OH $ (an alcohol) and dimethyl ether $ {H_3}C-O-C{H_2}H $ (an ether).


When compounds have the same molecular formula but distinct functional groups, this is known as functional isomerism. Functional isomers belong to various homologous series as a result of this.
Alcohols and ethers are the two functional group isomers that you should be aware of.
ketones and aldehydes
Esters and carboxylic acids.
Note:
A hierarchy of isomeric connections exists. Two compounds may have the same constitutional isomer yet are stereoisomers of each other when examined further. Two molecules with the same stereoisomer but distinct conformational forms or isotopologues might be in various conformational forms or be separate isotopologues. The scope of the investigation is determined by the subject of research or the chemical and physical qualities that are of interest.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




