
Dimethyl ether and ethyl alcohol are:
A.metamers
B.homologues
C.functional isomers
D.position isomers
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: We know that isomerism is the phenomenon in which two or more compounds have the same chemical formula but different structures. The compounds showing isomerism are known as isomers. There are different types of isomers, such as, position isomers, tautomers, chain isomers etc.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s first discuss metamers, homologues, functional isomers and position isomers in detail.
Metamers are the isomers which differ with respect to the nature of alkyl groups around a particular functional group. Thus, they belong to the same family. For example, the molecular formula ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{4}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{10}}}}{\rm{O}}$ possesses three metamers.
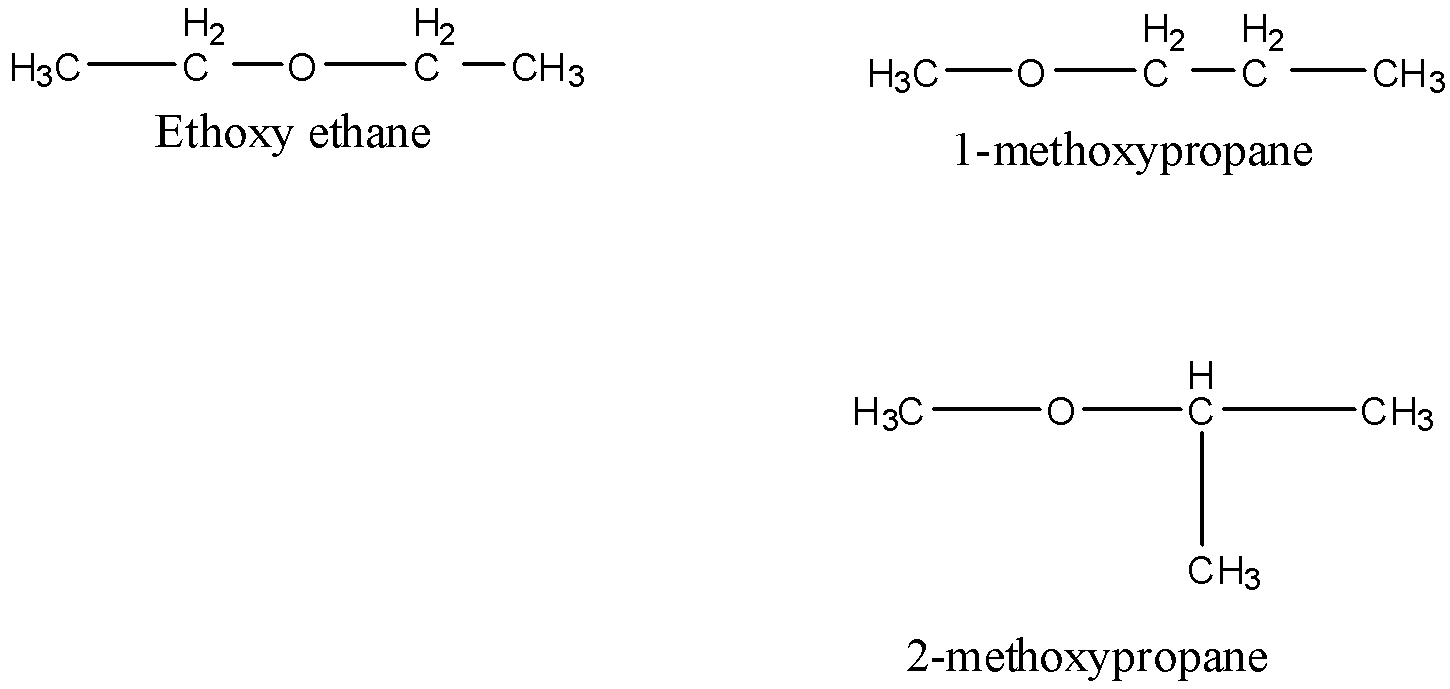
All the isomers belong to the family of ether.
Now, we discuss homologues. Homologues are series of compounds represented by the same molecular formula and a difference of${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}$ group is observed between two successive homologues. Such as, ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}$ and ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}$.
Functional isomers are the isomers that differ with respect to the nature of functional groups. So, both the isomers belong to different families. For example, ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{O}}$ has two functional isomers.

Position isomers are the isomers which differ with respect to the position of multiple bonds (double or triple), substituents or functional groups. For example, ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{3}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{7}}}{\rm{OH}}$ has two position isomers.
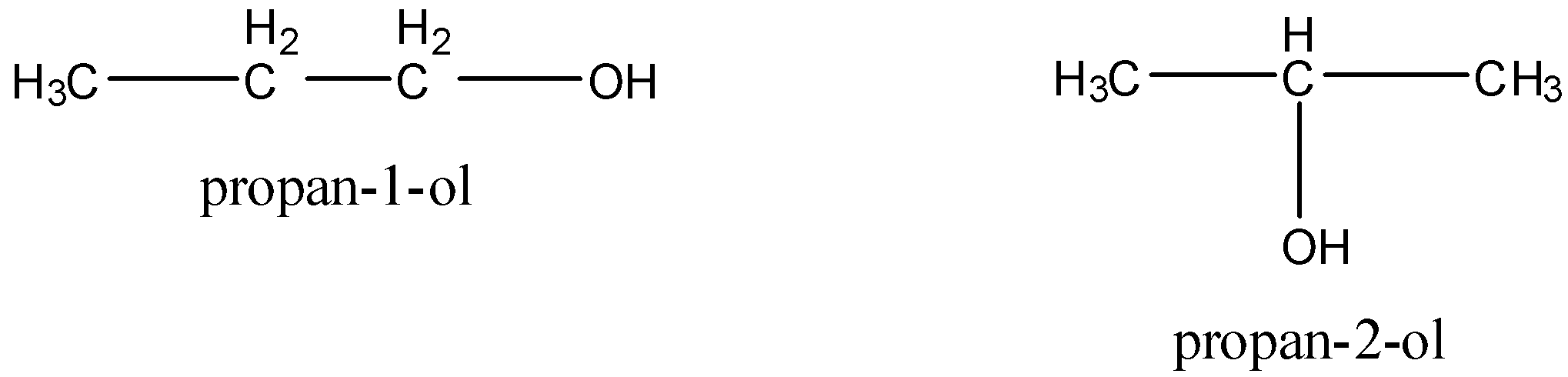
Now, we draw the structure of dimethyl ether and ethyl alcohol.

So, both the compounds differ by their functional groups. So, they are functional isomers.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option C.
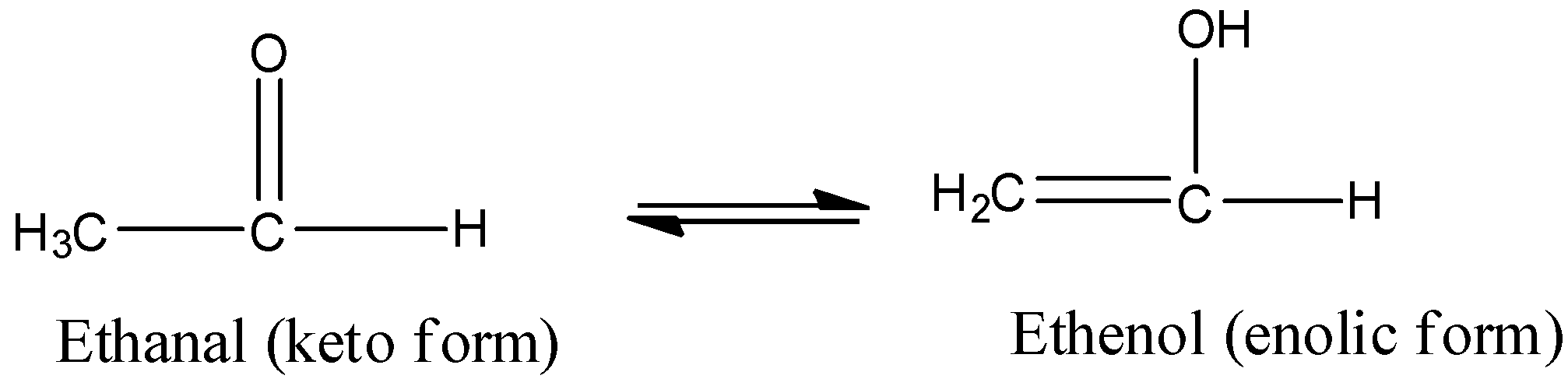
Note: Tautomers are actually functional isomers which exist simultaneously and also in dynamic equilibrium. The isomerism in this case is termed as tautomerism. It is of different types but the most common among them is the keto-enol tautomerism. This isomerism arises due to 1,3 migration of the hydrogen atom from carbon to oxygen atom and vice versa. For example,
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s first discuss metamers, homologues, functional isomers and position isomers in detail.
Metamers are the isomers which differ with respect to the nature of alkyl groups around a particular functional group. Thus, they belong to the same family. For example, the molecular formula ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{4}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{10}}}}{\rm{O}}$ possesses three metamers.

All the isomers belong to the family of ether.
Now, we discuss homologues. Homologues are series of compounds represented by the same molecular formula and a difference of${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}$ group is observed between two successive homologues. Such as, ${\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}$ and ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}$.
Functional isomers are the isomers that differ with respect to the nature of functional groups. So, both the isomers belong to different families. For example, ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{O}}$ has two functional isomers.

Position isomers are the isomers which differ with respect to the position of multiple bonds (double or triple), substituents or functional groups. For example, ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{3}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{7}}}{\rm{OH}}$ has two position isomers.
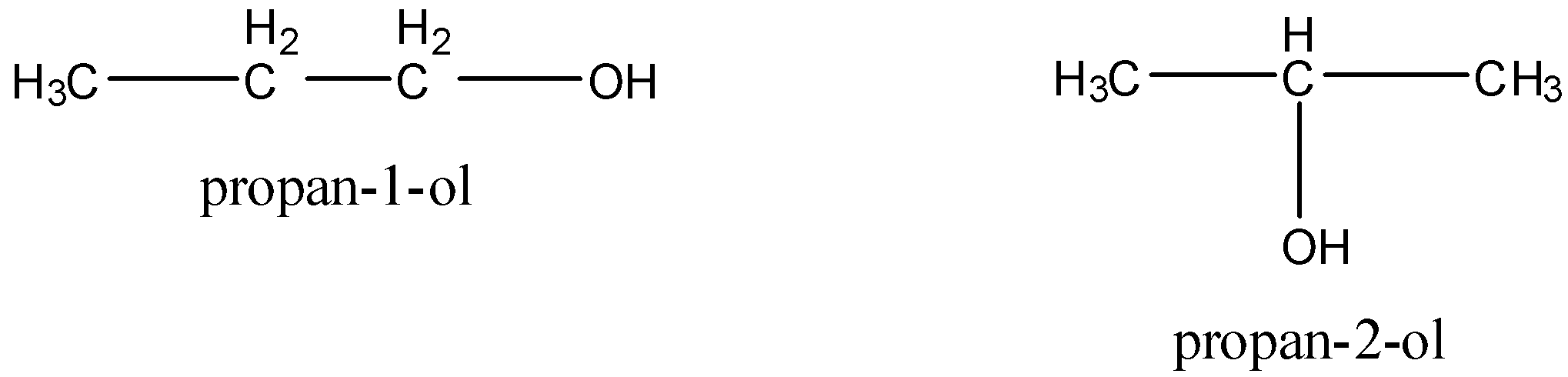
Now, we draw the structure of dimethyl ether and ethyl alcohol.

So, both the compounds differ by their functional groups. So, they are functional isomers.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Tautomers are actually functional isomers which exist simultaneously and also in dynamic equilibrium. The isomerism in this case is termed as tautomerism. It is of different types but the most common among them is the keto-enol tautomerism. This isomerism arises due to 1,3 migration of the hydrogen atom from carbon to oxygen atom and vice versa. For example,

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




