
Dilute $HCl$ is treated with acetaldehyde diethyl acetal:
Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint:
To answer this question, you must recall the characteristics of an acetal group. An acetal is a compound which contains a carbon atom attached to two ether groups at the same time.
Complete step by step solution:
Acetaldehyde diethyl acetal is the common name for 1, 1- diethoxy ethane. It is known as Acetaldehyde diethyl acetal because it is prepared using acetaldehyde and two moles of ethyl alcohol.
It consists of a carbon atom bonded to two ethyl ethers on each side and a methyl group. Since the carbon atom is bonded to two oxygen atoms directly, it is highly electrophilic in nature and is thus reactive and susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
When treated with dilute hydrochloric acid, the acetaldehyde diethyl acetal undergoes acid catalyzed hydrolysis. The hydrogen ions present in the acidic solution, protonate an ether group. The oxygen atom is now positively charged and hence the bond is cleaved and the oxygen atom leaves with the bond pair. The carbon now carries a positive charge and is thus attacked by a water molecule. The other ether group also departs in a similar fashion leaving behind acetaldehyde.
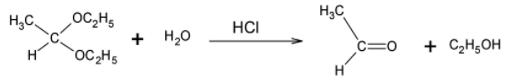
Overall, when Acetaldehyde diethyl acetal is reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid, we obtain acetaldehyde and two moles of ethyl alcohol.
Note:
Acetal group and hemiacetal group are very similar in both their names as well as their structures. Acetal group contains a carbon atom bonded to two ether groups at the same time and is thus very similar to the hemiacetal group in which the carbon atom is attached to an ether group and a hydroxyl group.
To answer this question, you must recall the characteristics of an acetal group. An acetal is a compound which contains a carbon atom attached to two ether groups at the same time.
Complete step by step solution:
Acetaldehyde diethyl acetal is the common name for 1, 1- diethoxy ethane. It is known as Acetaldehyde diethyl acetal because it is prepared using acetaldehyde and two moles of ethyl alcohol.
It consists of a carbon atom bonded to two ethyl ethers on each side and a methyl group. Since the carbon atom is bonded to two oxygen atoms directly, it is highly electrophilic in nature and is thus reactive and susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
When treated with dilute hydrochloric acid, the acetaldehyde diethyl acetal undergoes acid catalyzed hydrolysis. The hydrogen ions present in the acidic solution, protonate an ether group. The oxygen atom is now positively charged and hence the bond is cleaved and the oxygen atom leaves with the bond pair. The carbon now carries a positive charge and is thus attacked by a water molecule. The other ether group also departs in a similar fashion leaving behind acetaldehyde.

Overall, when Acetaldehyde diethyl acetal is reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid, we obtain acetaldehyde and two moles of ethyl alcohol.
Note:
Acetal group and hemiacetal group are very similar in both their names as well as their structures. Acetal group contains a carbon atom bonded to two ether groups at the same time and is thus very similar to the hemiacetal group in which the carbon atom is attached to an ether group and a hydroxyl group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




