
Why is it difficult to walk on slippery roads?
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: Slippery roads have very low coefficient of friction. First, we will see how the frictional force due to the ground helps us to move. Further, we will analyze how the frictional force is related to the coefficient of friction and accordingly determine why exactly it is difficult to walk on slippery surfaces.
Formula used:
${{F}_{FRIC}}=\mu N$
Complete step-by-step solution:
When we walk on the ground we basically push the ground backward at a particular angle. Let us say the force with which we press the ground is F. A brief vector diagram of this scenario is shown in the figure below.
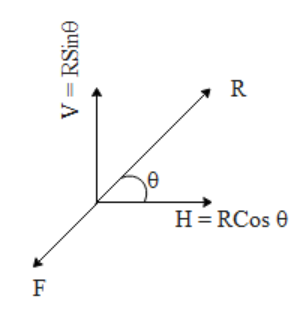
In the above diagram we see that as a consequence of force F, the ground exerts an equal and opposite reaction force R. Let us say the reaction force makes an angle $\theta $ with the ground. Therefore the vertical component of R i.e. V is equal to $V=RSin\theta $ and horizontal component i.e. H is equal to $H=RCos\theta $.
If the surface is very smooth i.e. slippery, the force due to friction due to the ground on the feet will be very small. If $\mu $ is the coefficient of friction of the slippery surface the force of friction is given by ${{F}_{FRIC}}=\mu N$ where N is the normal due to the surface. In the above case, it is equal to $V=RSin\theta $> The amount of force (F)applied on the ground is proportional to the frictional force. If the surface is slippery the feet will slip back as the coefficient of friction will be very small. As a consequence, the reaction force will be very small. Therefore we can conclude that the horizontal component of the reaction force which helps us to move forward will also be very small.
It is because of this we find it very difficult to walk on slippery surfaces.
Note: The vertical component of the reaction force keeps us stable while walking. Whereas the horizontal component keeps us moving forward. It is to be noted that one always has to take small steps while walking on slippery surfaces as the legs will almost remain vertical and will be able to move steadily.
Formula used:
${{F}_{FRIC}}=\mu N$
Complete step-by-step solution:
When we walk on the ground we basically push the ground backward at a particular angle. Let us say the force with which we press the ground is F. A brief vector diagram of this scenario is shown in the figure below.

In the above diagram we see that as a consequence of force F, the ground exerts an equal and opposite reaction force R. Let us say the reaction force makes an angle $\theta $ with the ground. Therefore the vertical component of R i.e. V is equal to $V=RSin\theta $ and horizontal component i.e. H is equal to $H=RCos\theta $.
If the surface is very smooth i.e. slippery, the force due to friction due to the ground on the feet will be very small. If $\mu $ is the coefficient of friction of the slippery surface the force of friction is given by ${{F}_{FRIC}}=\mu N$ where N is the normal due to the surface. In the above case, it is equal to $V=RSin\theta $> The amount of force (F)applied on the ground is proportional to the frictional force. If the surface is slippery the feet will slip back as the coefficient of friction will be very small. As a consequence, the reaction force will be very small. Therefore we can conclude that the horizontal component of the reaction force which helps us to move forward will also be very small.
It is because of this we find it very difficult to walk on slippery surfaces.
Note: The vertical component of the reaction force keeps us stable while walking. Whereas the horizontal component keeps us moving forward. It is to be noted that one always has to take small steps while walking on slippery surfaces as the legs will almost remain vertical and will be able to move steadily.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




