
What is the difference between uniform and constant velocity? Is acceleration zero in case of both constant and uniform velocity?
Answer
537.9k+ views
Hint: The velocity can be categorized as uniform and constant taking into consideration the direction and the magnitude of the velocity. The acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. So, we will answer considering the change of velocity concerning the time.
Formula used:
\[a=\dfrac{dv}{dt}\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
The velocity is the rate of change of displacement or position. The velocity is said to be uniform if the body covers equal distance in equal interval of time. The velocity is said to be constant if the body moves along a straight line without changing its direction. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.
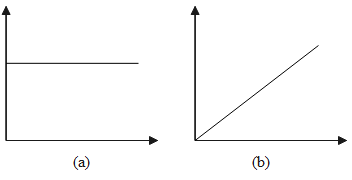
Graph (a) represents the constant velocity and graph (b) represents the uniform velocity.
In the case of constant velocity, over a period of time, the magnitude of the velocity remains the same, that is, constant, or, it can be said that, there is no change in velocity concerning the time. As the acceleration is rate of change of velocity, thus, acceleration will be zero in the case of constant velocity.
\[\begin{align}
& a=\dfrac{dv}{dt} \\
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{0}{dt} \\
& \therefore a=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Again in the case of uniform velocity, over a period of time, the magnitude of the velocity remains the same, that is, constant, or, it can be said that there is no change in velocity concerning the time. As the acceleration is the rate of change of velocity, thus, acceleration will be zero in the case of constant velocity.
\[\therefore \]The velocity is said to be uniform if the body covers an equal distance in an equal interval of time. The velocity is said to be constant if the body moves along a straight line without changing its direction. The acceleration is zero in both cases.
Note: The uniform velocity is also a constant velocity. The change in velocity of a body concerning the time defines the acceleration. So, the magnitude of the velocity is considered while answering.
Formula used:
\[a=\dfrac{dv}{dt}\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
The velocity is the rate of change of displacement or position. The velocity is said to be uniform if the body covers equal distance in equal interval of time. The velocity is said to be constant if the body moves along a straight line without changing its direction. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.

Graph (a) represents the constant velocity and graph (b) represents the uniform velocity.
In the case of constant velocity, over a period of time, the magnitude of the velocity remains the same, that is, constant, or, it can be said that, there is no change in velocity concerning the time. As the acceleration is rate of change of velocity, thus, acceleration will be zero in the case of constant velocity.
\[\begin{align}
& a=\dfrac{dv}{dt} \\
& \Rightarrow a=\dfrac{0}{dt} \\
& \therefore a=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Again in the case of uniform velocity, over a period of time, the magnitude of the velocity remains the same, that is, constant, or, it can be said that there is no change in velocity concerning the time. As the acceleration is the rate of change of velocity, thus, acceleration will be zero in the case of constant velocity.
\[\therefore \]The velocity is said to be uniform if the body covers an equal distance in an equal interval of time. The velocity is said to be constant if the body moves along a straight line without changing its direction. The acceleration is zero in both cases.
Note: The uniform velocity is also a constant velocity. The change in velocity of a body concerning the time defines the acceleration. So, the magnitude of the velocity is considered while answering.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




