
What is the difference between a jump and a removable discontinuity?
Answer
505.8k+ views
Hint: A function \[f(x)\]is said to be discontinuous at a point ‘a’ of its domain D if it is not continuous there. The point ‘a’ is then called a point of discontinuity of the function. Discontinuities can be classified as jump, infinite, removable, endpoint, or mixed.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The discontinuity may arise due to any of the following situation:
The right-hand limit or the left-hand limit or both of a function may not exist.
The right-hand limit and the left-hand limit of function may exist but are unequal.
The right-hand limit, as well as the left-hand limit of a function, may exist, but either of the two or both may not be equal to \[f(a)\].
Discontinuities can be classified as jump, infinite, removable, endpoint, or mixed.
Removable discontinuities can be "fixed" by re-defining the function.
Removable discontinuities are characterized by the fact that the limit exists.
The other types of discontinuities are characterized by the fact that the limit does not exist. Specifically:
Jump Discontinuities: both one-sided limits exist, but have different values.
Infinite Discontinuities: both one-sided limits are infinite.
Endpoint Discontinuities: only one of the one-sided limits exists.
Mixed : at least one of the one-sided limits does not exist.
Jump discontinuity: In a jump discontinuity, \[\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {a^ - }} f(x) \ne \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {a^ + }} f(x)\]. That means, the function on both sides of a value approaches different values, that is, the function appears to "jump" from one place to another.
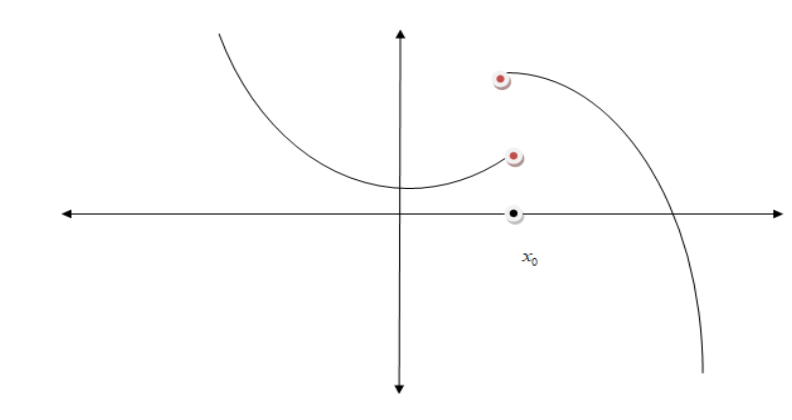
This is a jump discontinuity.
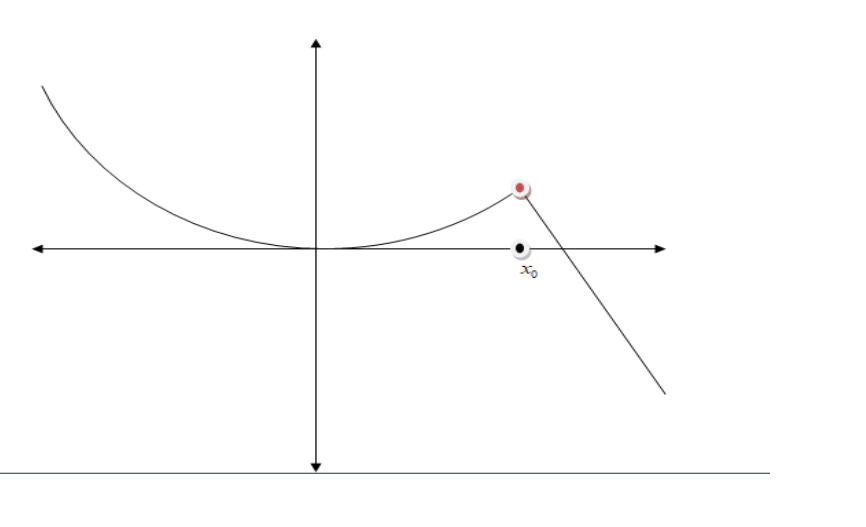
Removable discontinuity: Here, the function appears to come to a point, but the actual function value is elsewhere or does not exist. This can be written as \[\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {a^ - }} f(x) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {a^ + }} f(x) \ne f(a)\]
This is a removable discontinuity (sometimes called a hole).
Note: In mathematics, a continuous function is a function that does not have any abrupt changes in value, known as discontinuities. More precisely, a function is continuous if arbitrarily small changes in its output can be assured by restricting to sufficiently small changes in its input. A function \[f(x)\]is said to be discontinuous at a point ‘a’ of its domain D if it is not continuous there. The point ‘a’ is then called a point of discontinuity of the function. Discontinuities can be classified as jump, infinite, removable, endpoint, or mixed.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The discontinuity may arise due to any of the following situation:
The right-hand limit or the left-hand limit or both of a function may not exist.
The right-hand limit and the left-hand limit of function may exist but are unequal.
The right-hand limit, as well as the left-hand limit of a function, may exist, but either of the two or both may not be equal to \[f(a)\].
Discontinuities can be classified as jump, infinite, removable, endpoint, or mixed.
Removable discontinuities can be "fixed" by re-defining the function.
Removable discontinuities are characterized by the fact that the limit exists.
The other types of discontinuities are characterized by the fact that the limit does not exist. Specifically:
Jump Discontinuities: both one-sided limits exist, but have different values.
Infinite Discontinuities: both one-sided limits are infinite.
Endpoint Discontinuities: only one of the one-sided limits exists.
Mixed : at least one of the one-sided limits does not exist.
Jump discontinuity: In a jump discontinuity, \[\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {a^ - }} f(x) \ne \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {a^ + }} f(x)\]. That means, the function on both sides of a value approaches different values, that is, the function appears to "jump" from one place to another.

This is a jump discontinuity.
Removable discontinuity: Here, the function appears to come to a point, but the actual function value is elsewhere or does not exist. This can be written as \[\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {a^ - }} f(x) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {a^ + }} f(x) \ne f(a)\]
This is a removable discontinuity (sometimes called a hole).

Note: In mathematics, a continuous function is a function that does not have any abrupt changes in value, known as discontinuities. More precisely, a function is continuous if arbitrarily small changes in its output can be assured by restricting to sufficiently small changes in its input. A function \[f(x)\]is said to be discontinuous at a point ‘a’ of its domain D if it is not continuous there. The point ‘a’ is then called a point of discontinuity of the function. Discontinuities can be classified as jump, infinite, removable, endpoint, or mixed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




