
Why is the Diels Alder reaction classified as a \[{\mathbf{4}} + {\mathbf{2}}\] cycloaddition?
Answer
469.2k+ views
Hint: The coordinated joining together of two distinct pi-electron systems to generate a new ring of atoms is known as a cycloaddition reaction. Because the diene has four pi-electrons that shift position in the reaction and the dienophile has two, the Diels-Alder cycloaddition is classed as a $[4 + 2]$ process.
Complete step by step Answer:
The Diels-Alder reaction is an example of an organic chemical reaction that follows a pericyclic pathway rather than a polar or free radical pathway. The $[4 + 2]$ -cycload addition of a conjugated diene with a dienophile (an alkene or alkyne), an electrocyclic process involving the diene's $4$ and dienophile's $2$ electrons. The production of new -bonds, which are energetically more stable than the -bonds, is the reaction's driving force.
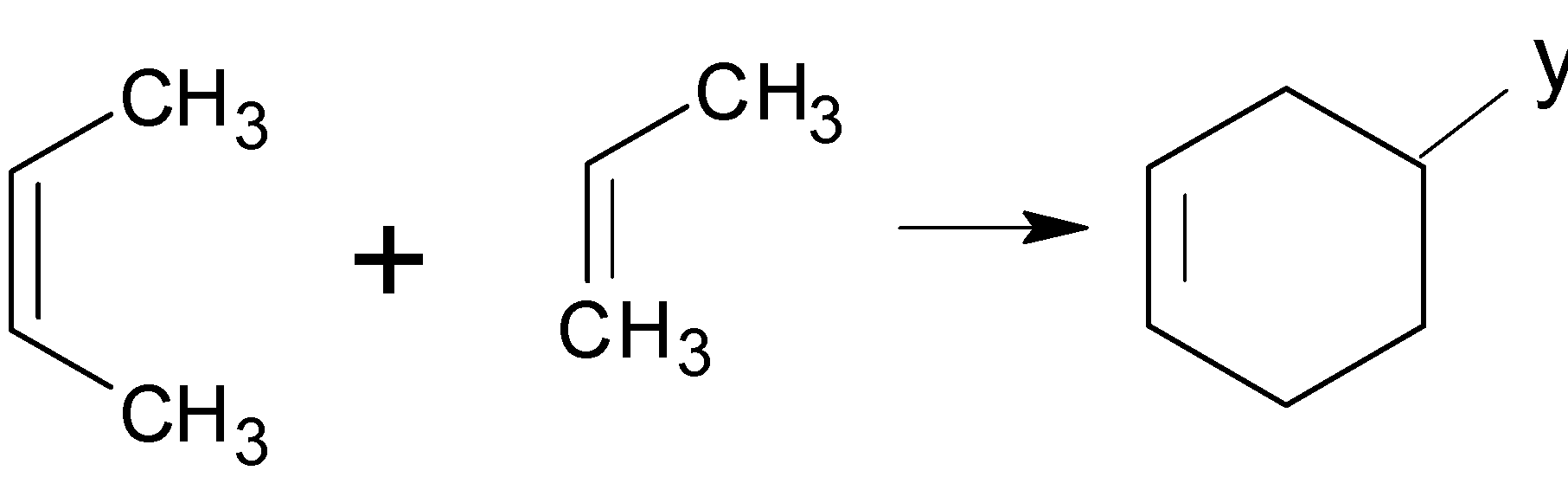
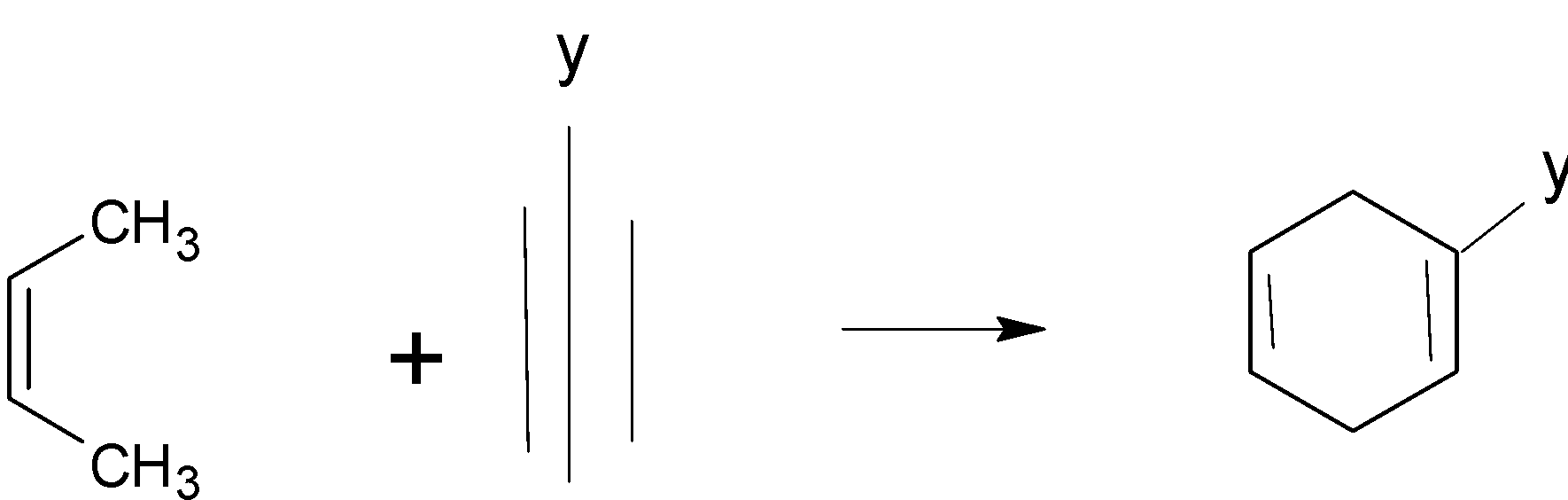
For a reaction to occur, the conjugated diene must be s-cis. Otherwise, the diene’s carbons $1$ and $4$ are too far apart to react in a coordinated manner. (Trans-$1,3$-butadiene, thus would not react) .When the reactants are symmetrical or don't have any electron-withdrawing/donating groups, they're pretty much all like that (with heat).
Mechanism:
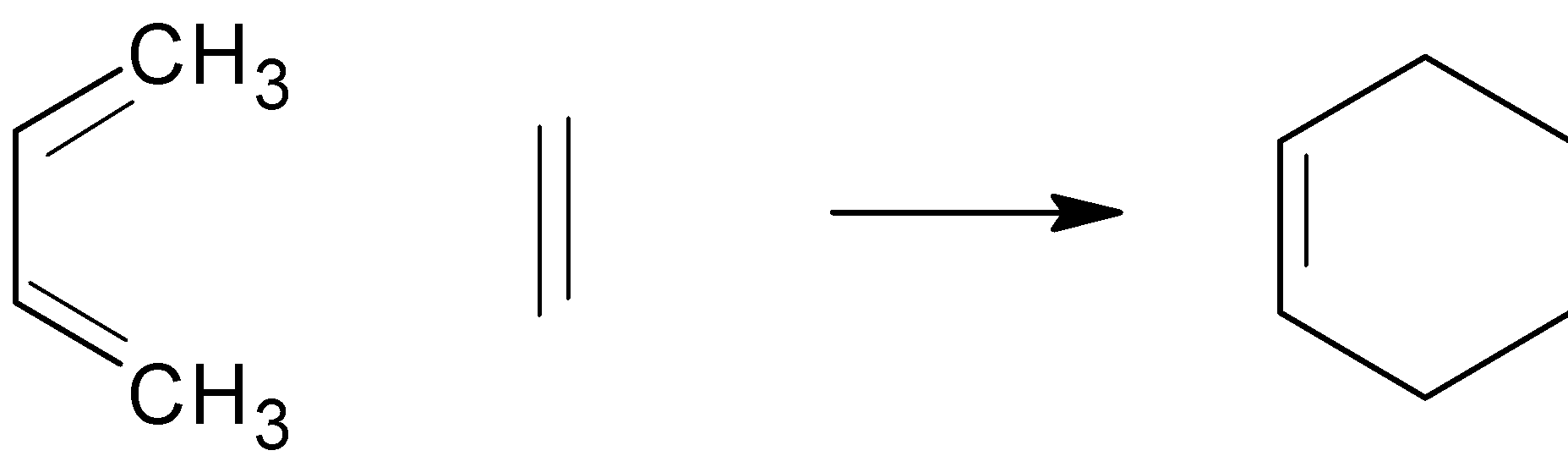
Conjugated Diene $ + $ Substituted $ \to $ Substituted Cyclohexane ($4 + 2$ cycloaddition)
Two pi bonds were changed into two sigma bonds in the above image. This is due to the coordinated bonding of two separate pi-electron systems. In addition, the Diels-Alder reaction requires the shift of four diene pi electrons and two dienophile pi electrons.
Note:
In the industrial synthesis of cyclopentadiene, the reverse Diels-Alder process is used. Many norbornane, which are common monomers, are produced from cyclopentadiene. In the manufacture of vitamin $B6$, the Diels-Alder process is also used. Vitamin \[B6\] is made via this process. On a large scale, the reverse reaction (also known as a retro-Diels-Alder reaction) is utilised to create cyclopentadiene.
Complete step by step Answer:
The Diels-Alder reaction is an example of an organic chemical reaction that follows a pericyclic pathway rather than a polar or free radical pathway. The $[4 + 2]$ -cycload addition of a conjugated diene with a dienophile (an alkene or alkyne), an electrocyclic process involving the diene's $4$ and dienophile's $2$ electrons. The production of new -bonds, which are energetically more stable than the -bonds, is the reaction's driving force.


For a reaction to occur, the conjugated diene must be s-cis. Otherwise, the diene’s carbons $1$ and $4$ are too far apart to react in a coordinated manner. (Trans-$1,3$-butadiene, thus would not react) .When the reactants are symmetrical or don't have any electron-withdrawing/donating groups, they're pretty much all like that (with heat).
Mechanism:
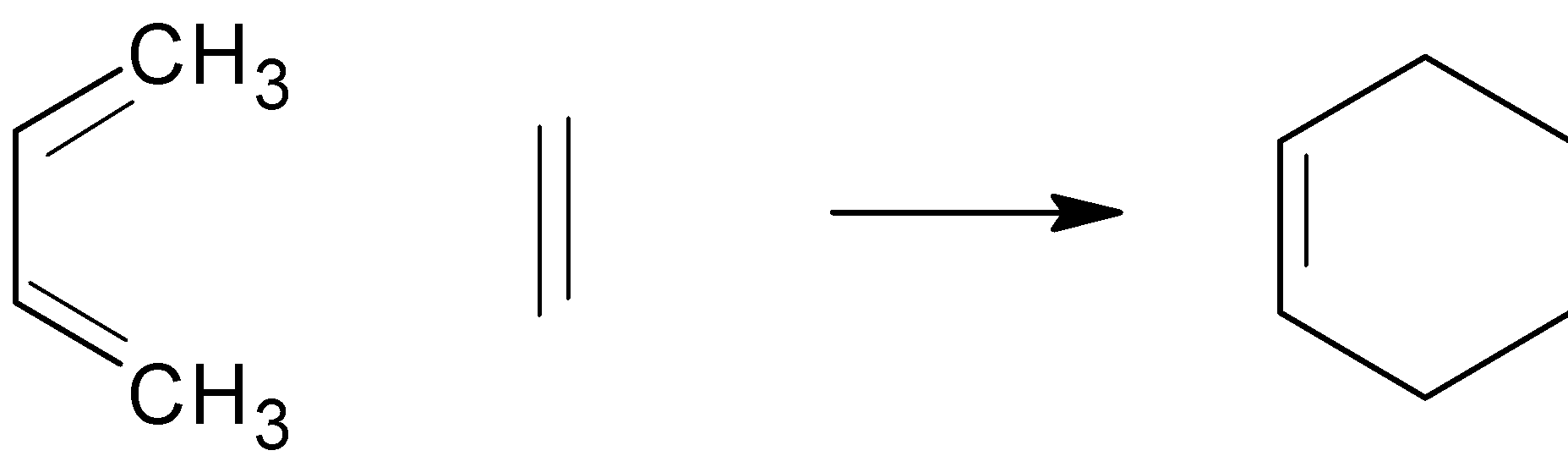
Conjugated Diene $ + $ Substituted $ \to $ Substituted Cyclohexane ($4 + 2$ cycloaddition)
Two pi bonds were changed into two sigma bonds in the above image. This is due to the coordinated bonding of two separate pi-electron systems. In addition, the Diels-Alder reaction requires the shift of four diene pi electrons and two dienophile pi electrons.
Note:
In the industrial synthesis of cyclopentadiene, the reverse Diels-Alder process is used. Many norbornane, which are common monomers, are produced from cyclopentadiene. In the manufacture of vitamin $B6$, the Diels-Alder process is also used. Vitamin \[B6\] is made via this process. On a large scale, the reverse reaction (also known as a retro-Diels-Alder reaction) is utilised to create cyclopentadiene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




