
Diazotization of \[{\text{n - Bu - N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\] with \[{\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/HCl}}\] gives ______ isomeric butene.
A.2
B.3
C.4
D.5
Answer
558k+ views
Hint:The chemical process used in converting a primary aromatic amine into the corresponding diazonium salt of the amine is commonly referred to as diazotization. This process is also known as ‘diazotization’.
Complete step-by-step answer:Here reagent given to us is \[{\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/HCl}}\]. The reaction between \[{\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] and \[{\text{HCl}}\] is as follows:
\[{\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + HCl}} \to {\text{ NaCl + HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]
The structure of \[{\text{n - Bu - N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\] amine is as follows:
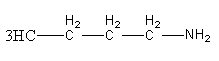
Diazotization of \[{\text{n - Bu - N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\] with \[{\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/HCl}}\] gives diazonium ion as the intermediate product.
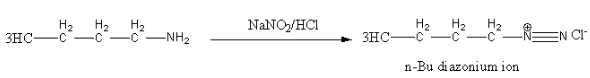
Alkyl diazonium salts are unstable so converted into carbocation. In this reaction \[{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\] is a good leaving group.
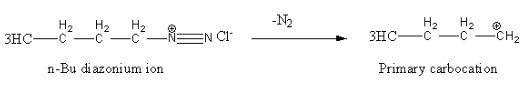
This primary carbocation converted into 1-butene after the loss of hydrogen as follows.
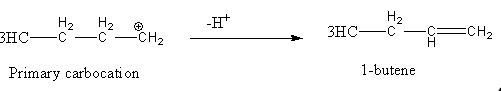
So, we can say that Diazotization of \[{\text{n - Bu - N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\] with \[{\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/HCl}}\] gives 1-butene as one of the products.
Primary carbocation also shows rearrangement of the hydrogen atom and converts into secondary carbocation as follows:

This secondary carbocation converted into 2-butene after the loss of hydrogen as follows
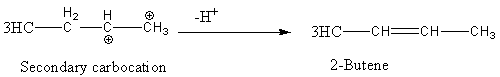
2-butene has two types of isomers cis and trans.
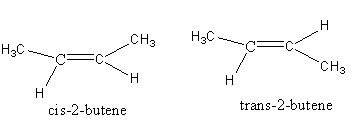
Diazotization of \[{\text{n - Bu - N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\] with \[{\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/HCl}}\] gives 1-butene, cis-2-butene and trans-2-butene isomers.
So, we can say that diazotization of \[{\text{n - Bu - N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\] with \[{\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/HCl}}\] gives 3 isomeric butene.
Hence, the correct option is (B) 3
Note: Isomer having similar groups on the same side is known as a cis isomer. Isomers having similar groups on opposite sides are known as the trans isomer. Cis and trans isomers are known as a geometrical isomers. Alkenes having two different substituents at each end of \[{\text{C = C}}\] show geometrical isomers. 1-butene does not show any isomer.
Complete step-by-step answer:Here reagent given to us is \[{\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/HCl}}\]. The reaction between \[{\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\] and \[{\text{HCl}}\] is as follows:
\[{\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + HCl}} \to {\text{ NaCl + HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\]
The structure of \[{\text{n - Bu - N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\] amine is as follows:

Diazotization of \[{\text{n - Bu - N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\] with \[{\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/HCl}}\] gives diazonium ion as the intermediate product.
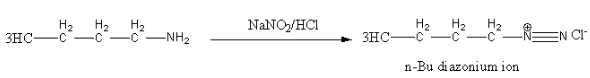
Alkyl diazonium salts are unstable so converted into carbocation. In this reaction \[{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}\] is a good leaving group.
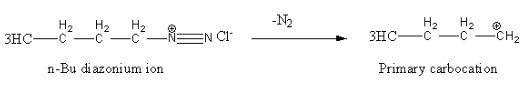
This primary carbocation converted into 1-butene after the loss of hydrogen as follows.

So, we can say that Diazotization of \[{\text{n - Bu - N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\] with \[{\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/HCl}}\] gives 1-butene as one of the products.
Primary carbocation also shows rearrangement of the hydrogen atom and converts into secondary carbocation as follows:

This secondary carbocation converted into 2-butene after the loss of hydrogen as follows

2-butene has two types of isomers cis and trans.

Diazotization of \[{\text{n - Bu - N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\] with \[{\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/HCl}}\] gives 1-butene, cis-2-butene and trans-2-butene isomers.
So, we can say that diazotization of \[{\text{n - Bu - N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\] with \[{\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/HCl}}\] gives 3 isomeric butene.
Hence, the correct option is (B) 3
Note: Isomer having similar groups on the same side is known as a cis isomer. Isomers having similar groups on opposite sides are known as the trans isomer. Cis and trans isomers are known as a geometrical isomers. Alkenes having two different substituents at each end of \[{\text{C = C}}\] show geometrical isomers. 1-butene does not show any isomer.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE

Explain sex determination in humans with line diag class 12 biology CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE




