
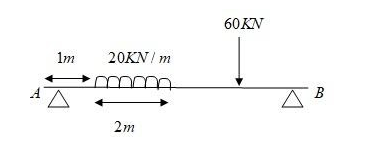
Determine the reaction at support $ A $ and $ B $ of loaded beam shown in figure below.

Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint: As we know that we can use a concept of equilibrium in this question, as given the beam is balancing the load applied in a downward direction with supports on both ends, the supports of the same magnitude but in opposite directions.
Given First downward load, $ {L_1} = 60KN $
Second downward load $ {L_2} = 20KN/m $
Distance where second downward load occur, $ D = 2m $
Now, Second downward load will be, $ 20KN/m \times 2m = 40KN $ .
Complete step by step solution:
A loaded beam has two loads in downward direction, and it is still stationary means a force of the same magnitude but in the opposite direction helps this beam to be stationary.
Firstly we will calculate total downward load given on the beam.
$ {L_{Total}} = {L_1} + {L_2} $
Put values of $ {L_1} $ and $ {L_2} $ in above equation
$ {L_{Total}} = 60 + 40 = 100KN $
Here, we got the total load on the beam in a downward direction that is $ 60KN $ , means $ 60KN $ force is also applied in an upward direction.
So, let the first support in upward direction $ = {U_1} $
And second support in upward direction $ = {U_2} $
Total support in upward direction $ = {U_{Total}} $
$ $ $ {U_{Total}} = {U_1} + {U_2}......1 $
As per question we can give two supports on $ A $ and $ B $ to keep this beam stationary, and the magnitude of that force we have already calculated.
Hence, $ {U_{Total}} = {L_{Total}} $
Both upward support should be equal.
So, $ {U_1} = {U_2} $
Now, equation 1 can be written as
$ {U_{Total}} = {U_1} + {U_1} $
$ {U_{Total}} = 2{U_1} = 100KN $
$ \Rightarrow {U_1} = {U_2} = \dfrac{{100KN}}{2} = 50KN $
Here, two supports of $ 50KN $ strength will act upward on $ A $ and $ B $ to balance the beam.
Note:
We should know the concept of equilibrium to solve the above question. In equilibrium, a beam is supported by force at both ends, all the download loads are balanced by equal and opposite upward forces and the beam gets stationary.
Given First downward load, $ {L_1} = 60KN $
Second downward load $ {L_2} = 20KN/m $
Distance where second downward load occur, $ D = 2m $
Now, Second downward load will be, $ 20KN/m \times 2m = 40KN $ .
Complete step by step solution:
A loaded beam has two loads in downward direction, and it is still stationary means a force of the same magnitude but in the opposite direction helps this beam to be stationary.
Firstly we will calculate total downward load given on the beam.
$ {L_{Total}} = {L_1} + {L_2} $
Put values of $ {L_1} $ and $ {L_2} $ in above equation
$ {L_{Total}} = 60 + 40 = 100KN $
Here, we got the total load on the beam in a downward direction that is $ 60KN $ , means $ 60KN $ force is also applied in an upward direction.
So, let the first support in upward direction $ = {U_1} $
And second support in upward direction $ = {U_2} $
Total support in upward direction $ = {U_{Total}} $
$ $ $ {U_{Total}} = {U_1} + {U_2}......1 $
As per question we can give two supports on $ A $ and $ B $ to keep this beam stationary, and the magnitude of that force we have already calculated.
Hence, $ {U_{Total}} = {L_{Total}} $
Both upward support should be equal.
So, $ {U_1} = {U_2} $
Now, equation 1 can be written as
$ {U_{Total}} = {U_1} + {U_1} $
$ {U_{Total}} = 2{U_1} = 100KN $
$ \Rightarrow {U_1} = {U_2} = \dfrac{{100KN}}{2} = 50KN $
Here, two supports of $ 50KN $ strength will act upward on $ A $ and $ B $ to balance the beam.
Note:
We should know the concept of equilibrium to solve the above question. In equilibrium, a beam is supported by force at both ends, all the download loads are balanced by equal and opposite upward forces and the beam gets stationary.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




