
Determine the point in the graph of the linear equation $2x + 3y = 15$, whose abscissa is $3\dfrac{1}{2}$ times its ordinate.
Answer
513k+ views
Hint: In the given question, we need to solve two simultaneous equations in two variables. There are various methods to solve two given equations in two variables like substitution method, cross multiplication method, elimination method, matrix method and many more. The equations given in the question can be solved using any one of the above mentioned methods easily. But we will solve the equations using the substitution method as it is easy to comprehend and less time consuming. First, we will frame the equations and then solve using the substitution method.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question, we are given a linear equation $2x + 3y = 15$. Also, we have to find the point on the graph of this line whose abscissa is $3\dfrac{1}{2}$ times the ordinate. So, we have to find the point whose x coordinate is $3\dfrac{1}{2}$ its y coordinate. So, we get, $x = 3\dfrac{1}{2}y$. Now, we convert the mixed fraction in the equation to an improper fraction. So, we get,
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{7}{2}y$
Now, we have to solve the two equations $2x + 3y = 15$ and $x = \dfrac{7}{2}y$.
We will use a substitution method to solve the equations. In the substitution method, we substitute the value of one variable from an equation into another equation so as to get an equation in only one variable. Now, putting the value of x obtained from equation $x = \dfrac{7}{2}y$ into equation $2x + 3y = 15$.
So, we get, \[2\left( {\dfrac{7}{2}y} \right) + 3y = 15\]
Opening the brackets and simplifying the equation, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 7y + 3y = 15\]
Adding up like terms, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 10y = 15\]
Dividing both sides of the equation by \[10\], we get,
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{15}}{{10}}\]
Cancelling common factors in numerator and denominator, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{3}{2}\]
So, the value of $y$ is \[\dfrac{3}{2}\].
Putting the value of y in any of the two equations, we get,
$x = \dfrac{7}{2}y$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{7}{2} \times \dfrac{3}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{21}}{4}$
So, the value of x is $\dfrac{{21}}{4}$.
Therefore, the coordinates point on the graph of the linear equation $2x + 3y = 15$, whose abscissa is $3\dfrac{1}{2}$ times its ordinate are $\left( {\dfrac{{21}}{4},\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)$.
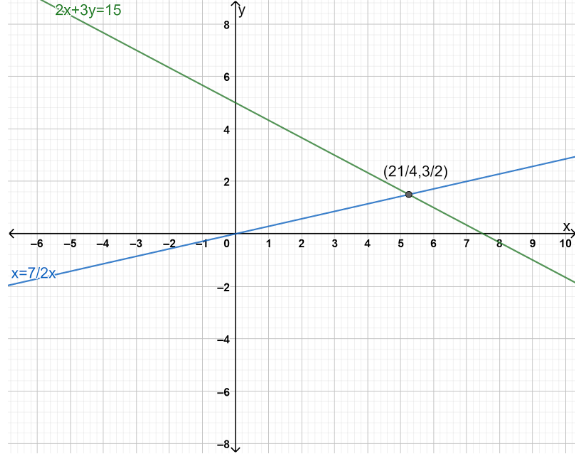
Note:An equation consisting of 2 variables having degree one is known as Linear Equation in two variables. Standard form of Linear Equation in two variables is $ax + by + c = 0$ where $a, b$ and $c$ are the real numbers and $a, b$ which are coefficients of $x$ and $y$ respectively are not equal to zero. We must know ways to solve two simultaneous equations in two variables. We can also verify the solution of the linear equations $2x + 3y = 15$and $x = \dfrac{7}{2}y$ by plotting the graphs of the equations and finding the point of intersection of both the lines.
Complete step by step answer:
In the question, we are given a linear equation $2x + 3y = 15$. Also, we have to find the point on the graph of this line whose abscissa is $3\dfrac{1}{2}$ times the ordinate. So, we have to find the point whose x coordinate is $3\dfrac{1}{2}$ its y coordinate. So, we get, $x = 3\dfrac{1}{2}y$. Now, we convert the mixed fraction in the equation to an improper fraction. So, we get,
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{7}{2}y$
Now, we have to solve the two equations $2x + 3y = 15$ and $x = \dfrac{7}{2}y$.
We will use a substitution method to solve the equations. In the substitution method, we substitute the value of one variable from an equation into another equation so as to get an equation in only one variable. Now, putting the value of x obtained from equation $x = \dfrac{7}{2}y$ into equation $2x + 3y = 15$.
So, we get, \[2\left( {\dfrac{7}{2}y} \right) + 3y = 15\]
Opening the brackets and simplifying the equation, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 7y + 3y = 15\]
Adding up like terms, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 10y = 15\]
Dividing both sides of the equation by \[10\], we get,
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{15}}{{10}}\]
Cancelling common factors in numerator and denominator, we get,
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{3}{2}\]
So, the value of $y$ is \[\dfrac{3}{2}\].
Putting the value of y in any of the two equations, we get,
$x = \dfrac{7}{2}y$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{7}{2} \times \dfrac{3}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{21}}{4}$
So, the value of x is $\dfrac{{21}}{4}$.
Therefore, the coordinates point on the graph of the linear equation $2x + 3y = 15$, whose abscissa is $3\dfrac{1}{2}$ times its ordinate are $\left( {\dfrac{{21}}{4},\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)$.
Note:An equation consisting of 2 variables having degree one is known as Linear Equation in two variables. Standard form of Linear Equation in two variables is $ax + by + c = 0$ where $a, b$ and $c$ are the real numbers and $a, b$ which are coefficients of $x$ and $y$ respectively are not equal to zero. We must know ways to solve two simultaneous equations in two variables. We can also verify the solution of the linear equations $2x + 3y = 15$and $x = \dfrac{7}{2}y$ by plotting the graphs of the equations and finding the point of intersection of both the lines.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




