
How do you determine the intervals where \[f\left( x \right) = 3{x^2} - \dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}\] is concave up or down?
Answer
481.2k+ views
Hint: In above question, we are given a function as \[f\left( x \right) = 3{x^2} - \dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}\] . We have to determine the intervals where the function is concave up or concave down. The first derivative of a function determines the slope of the tangent and the second derivative of a function determines its concavity.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given function is \[f\left( x \right) = 3{x^2} - \dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}\] .
We have to find the interval where it is concave up and concave down.
The function \[f\left( x \right) = 3{x^2} - \dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}\] is a polynomial function, which is continuous and derivable on \[\mathbb{R}\] .
Now we can differentiate the function with respect to \[x\] to find the first and second derivatives of the function.
Hence, we have
\[ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right) = 3{x^2} - \dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}\]
Differentiating once, we get
\[ \Rightarrow f'\left( x \right) = 3.2x - \dfrac{{3{x^2}}}{3}\]
Or,
\[ \Rightarrow f'\left( x \right) = 6x - {x^2}\]
Differentiating again, we get
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( x \right) = 6 - 2x\]
Now, if the second derivative of a function is positive then the function is said to be concave up, and if the second derivative of a function is negative, then it is said to be concave down. The point where concavity changes from down to up is called the point of inflection. At the point of inflection the value of second derivative is zero.
Therefore, for the point of inflection,
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( x \right) = 0\]
That gives,
\[ \Rightarrow 6 - 2x = 0\]
Or,
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{6}{2}\]
Hence,
\[ \Rightarrow x = 3\]
We have only one point of inflection, that means we have to check the concavity on two intervals on both sides on the inflection point.
i.e. we have to check the concavity in the two intervals \[\left( { - \infty ,3} \right)\] and \[\left( {3,\infty } \right)\] .
Sign chart of concavity of the function in the two intervals:
Therefore, from the sign chart we can say that the function \[f\left( x \right) = 3{x^2} - \dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}\] is concave up in the interval \[\left( { - \infty ,3} \right)\] and concave down in the in the interval \[\left( {3,\infty } \right)\] .
Note: When \[x = 3\] then
\[ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right) = 3 \cdot {3^2} - \dfrac{{{3^3}}}{3}\]
i.e.
\[ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right) = 27 - 9\]
Hence,
\[ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right) = 18\]
Therefore, the point of inflection is \[\left( {3,18} \right)\] .
Now, we can also clearly see the concavity of the function \[f\left( x \right) = 3{x^2} - \dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}\] in the graph given below.
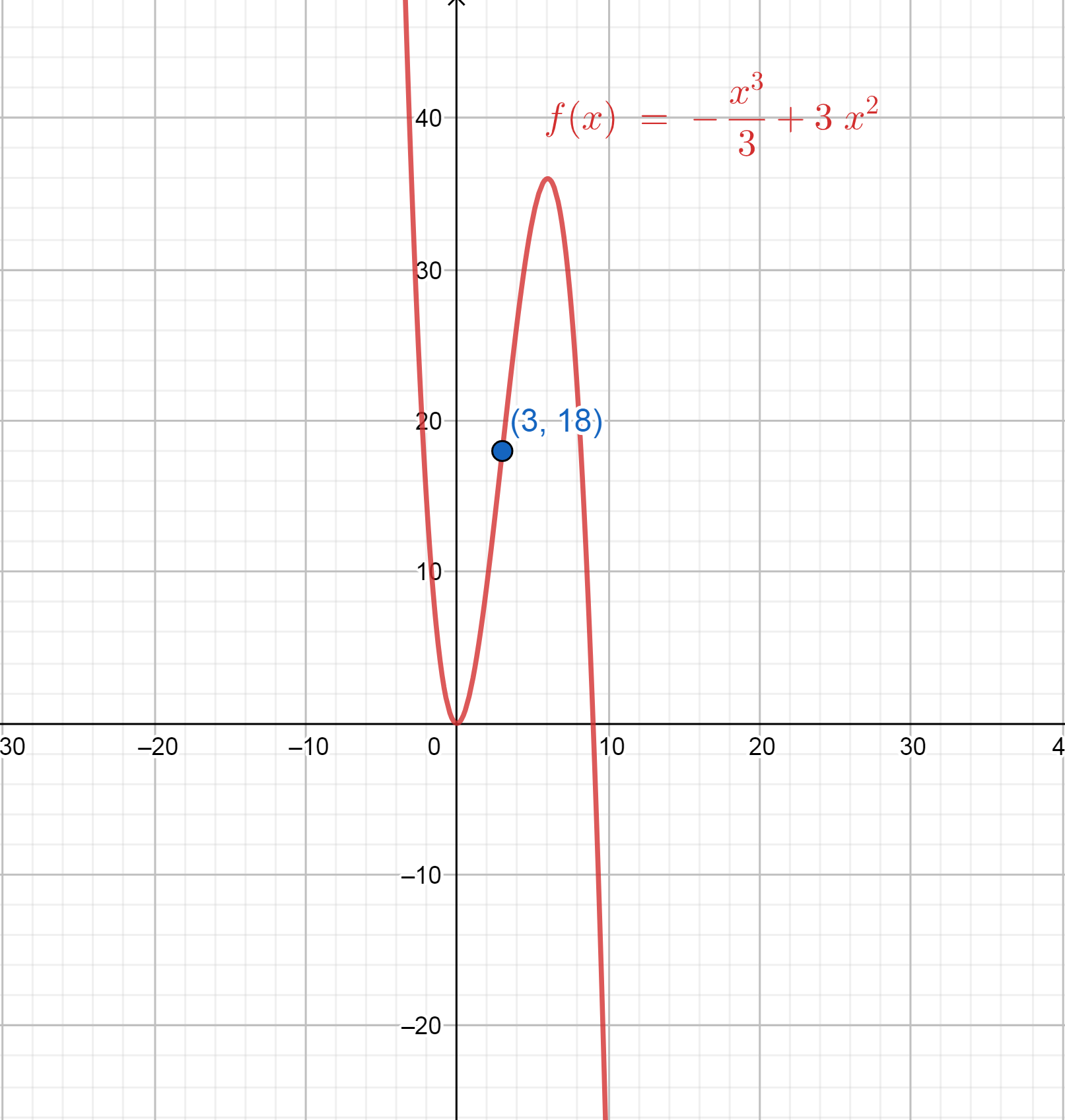
The graph of the function is concave up till the point of inflection and then it starts changing its path and becomes concave down after leaving the inflection point \[\left( {3,18} \right)\] .
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given function is \[f\left( x \right) = 3{x^2} - \dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}\] .
We have to find the interval where it is concave up and concave down.
The function \[f\left( x \right) = 3{x^2} - \dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}\] is a polynomial function, which is continuous and derivable on \[\mathbb{R}\] .
Now we can differentiate the function with respect to \[x\] to find the first and second derivatives of the function.
Hence, we have
\[ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right) = 3{x^2} - \dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}\]
Differentiating once, we get
\[ \Rightarrow f'\left( x \right) = 3.2x - \dfrac{{3{x^2}}}{3}\]
Or,
\[ \Rightarrow f'\left( x \right) = 6x - {x^2}\]
Differentiating again, we get
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( x \right) = 6 - 2x\]
Now, if the second derivative of a function is positive then the function is said to be concave up, and if the second derivative of a function is negative, then it is said to be concave down. The point where concavity changes from down to up is called the point of inflection. At the point of inflection the value of second derivative is zero.
Therefore, for the point of inflection,
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( x \right) = 0\]
That gives,
\[ \Rightarrow 6 - 2x = 0\]
Or,
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{6}{2}\]
Hence,
\[ \Rightarrow x = 3\]
We have only one point of inflection, that means we have to check the concavity on two intervals on both sides on the inflection point.
i.e. we have to check the concavity in the two intervals \[\left( { - \infty ,3} \right)\] and \[\left( {3,\infty } \right)\] .
Sign chart of concavity of the function in the two intervals:
| Interval | \[\left( { - \infty ,3} \right)\] | \[\left( {3,\infty } \right)\] |
| Sign of \[f''\left( x \right)\] | Positive | Negative |
| Concavity | Concave Up \[ \cup \] | Concave Down \[ \cap \] |
Therefore, from the sign chart we can say that the function \[f\left( x \right) = 3{x^2} - \dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}\] is concave up in the interval \[\left( { - \infty ,3} \right)\] and concave down in the in the interval \[\left( {3,\infty } \right)\] .
Note: When \[x = 3\] then
\[ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right) = 3 \cdot {3^2} - \dfrac{{{3^3}}}{3}\]
i.e.
\[ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right) = 27 - 9\]
Hence,
\[ \Rightarrow f\left( x \right) = 18\]
Therefore, the point of inflection is \[\left( {3,18} \right)\] .
Now, we can also clearly see the concavity of the function \[f\left( x \right) = 3{x^2} - \dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3}\] in the graph given below.

The graph of the function is concave up till the point of inflection and then it starts changing its path and becomes concave down after leaving the inflection point \[\left( {3,18} \right)\] .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 11 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




