
Determine the frequency range for visible regions.
Answer
550.5k+ views
Hint: In this case, we will first see the definition of the electromagnetic spectrum and then see the range of different regions in this spectrum. The only range which is visible to the human eye is the visible spectrum. We will see both frequency and wavelength range for visible regions.
Complete answer:
There are many types of electromagnetic radiations, which differ from one another in wavelength (or frequency). These constitute what is called the electromagnetic spectrum.
Different regions of the spectrum are identified by different names. Different kinds of units are used to represent electromagnetic radiation. These radiations are characterised by the properties, namely, frequency ($\nu $) and wavelength ($\lambda $).
In vacuum all types of electromagnetic radiations, regardless of wavelength, travel at the same speed, i.e. $3 \times {10^8}m{s^{ - 1}}$. This is called speed of light and is given the symbol ‘c‘. The frequency ($\nu $), wavelength ($\lambda $) and velocity of light (c) are related by the equation-
$c = \nu \lambda $.
Below, shows various types of electro-magnetic radiations which differ from one another in wavelengths and frequencies.
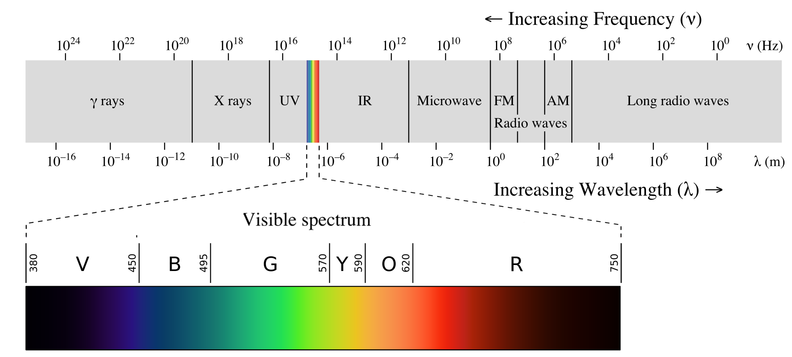
The small portion around ${10^{15}}$Hz is what is ordinarily called visible light. It is only this part which our eyes can see (or detect). Special instruments are required to detect non-visible radiation.
Note:
Radio frequency region around ${10^6}$ Hz, used for broadcasting; microwave region around ${10^{10}}$ Hz used for radar; infrared region around ${10^{13}}$ Hz used for heating; ultraviolet region around 1016Hz a component of sun’s radiation. In terms of wavelength of range of visible spectrum is around 400nm to 750nm.
Complete answer:
There are many types of electromagnetic radiations, which differ from one another in wavelength (or frequency). These constitute what is called the electromagnetic spectrum.
Different regions of the spectrum are identified by different names. Different kinds of units are used to represent electromagnetic radiation. These radiations are characterised by the properties, namely, frequency ($\nu $) and wavelength ($\lambda $).
In vacuum all types of electromagnetic radiations, regardless of wavelength, travel at the same speed, i.e. $3 \times {10^8}m{s^{ - 1}}$. This is called speed of light and is given the symbol ‘c‘. The frequency ($\nu $), wavelength ($\lambda $) and velocity of light (c) are related by the equation-
$c = \nu \lambda $.
Below, shows various types of electro-magnetic radiations which differ from one another in wavelengths and frequencies.

The small portion around ${10^{15}}$Hz is what is ordinarily called visible light. It is only this part which our eyes can see (or detect). Special instruments are required to detect non-visible radiation.
Note:
Radio frequency region around ${10^6}$ Hz, used for broadcasting; microwave region around ${10^{10}}$ Hz used for radar; infrared region around ${10^{13}}$ Hz used for heating; ultraviolet region around 1016Hz a component of sun’s radiation. In terms of wavelength of range of visible spectrum is around 400nm to 750nm.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




