
How do you determine the correct molecular shapes of ${\text{Ge}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$, ${\text{Se}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ and ${\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ ?
Answer
555.3k+ views
Hint: To determine the shape of a molecule we should know how to write the Lewis structure and about VSEPR theory. We can draw the Lewis structure of the molecules to determine the electron pair of the central atom. Then by using valence shell electron pair repulsion theory the geometry can be determined.
Complete step-by-step answer:We will write the Lewis structure as follows:
First we will write the basic structure. Then we will decide the central atom around which we will write all atoms of the molecule. The least electronegative atom is the central atom.
Then we will count total valence electrons.
Two electrons are used in the formation of a bond.
So, we will count the total electron used in bond formation.
Then we will subtract the electrons used in bond formation from the total valence electrons.
Then we will arrange the remaining electrons around each atom to complete the octet.
The valence shell electron pair repulsion theory is as follows:
Electron pair is the number of electron pairs present around the central atom in a molecule.
According to VSEPR the electron pairs present around the central atom repel each other. So, all the pairs get arranged to minimize the repulsion. Based on the number of electron pair the geometry can be determined as follows:
Lewis structure of ${\text{Ge}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ ion is as follows:
Total valence electrons in ${\text{Ge}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ are as follows:
$ = \,\left( {4 \times 1} \right) + \left( {7 \times 4} \right)$
$ = \,32$
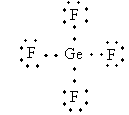
The total electron pair around central atom germanium is four so, the geometry will be tetrahedral which is shown as follows:
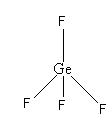
All four electron pairs are the same. So, the shape of ${\text{Ge}}{{\text{F}}_4}$ is tetrahedral.
Lewis structure of ${\text{Se}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ ion is as follows:
Total valence electrons in ${\text{Se}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ are as follows:
$ = \,\left( {6 \times 1} \right) + \left( {7 \times 4} \right)$
$ = \,34$
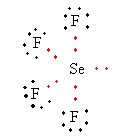
The total electron pair around central atom selenium is five so, the geometry will be trigonal bipyramidal which is shown as follows:
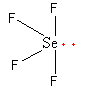
All five electron pairs are not the same. Out of the five, four are bond pair and one is lone pair So, the shape of ${\text{Se}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ is sea-sew.
Lewis structure of ${\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ ion is as follows:
Total valence electrons in ${\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ are as follows:
$ = \,\left( {8 \times 1} \right) + \left( {7 \times 4} \right)$
$ = \,36$
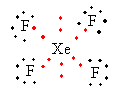
The total electron pair around central atom xenon is six so, the geometry will be octahedral which is shown as follows:
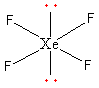
All six electron pairs are not the same. Out of the six, four are bond pairs and two are lone pairs. So, the shape of ${\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ is square planar.
Therefore, the correct molecular shapes of ${\text{Ge}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$, ${\text{Se}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ and ${\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ are tetrahedral, sea-sew and square planer respectively.
Note: To determine the total valence electrons of a molecule, we add all the valence electrons of the atoms present in the molecule. We subtract one for every positive charge and add one for every negative charge. Geometry around the central atom is decided only on the basis of sigma bond pair and lone pair only. Pi bonds are not counted to determine the geometry. Geometry is decided by counting the number of lone pair and sigma bonds where the shape is determined on the basis of sigma bond pairs only.
Complete step-by-step answer:We will write the Lewis structure as follows:
First we will write the basic structure. Then we will decide the central atom around which we will write all atoms of the molecule. The least electronegative atom is the central atom.
Then we will count total valence electrons.
Two electrons are used in the formation of a bond.
So, we will count the total electron used in bond formation.
Then we will subtract the electrons used in bond formation from the total valence electrons.
Then we will arrange the remaining electrons around each atom to complete the octet.
The valence shell electron pair repulsion theory is as follows:
Electron pair is the number of electron pairs present around the central atom in a molecule.
According to VSEPR the electron pairs present around the central atom repel each other. So, all the pairs get arranged to minimize the repulsion. Based on the number of electron pair the geometry can be determined as follows:
| Number of electron pair | Geometry |
| $2$ | Linear |
| $3$ | Trigonal planar |
| $4$ | Tetrahedral |
| $5$ | Trigonal bipyramid |
| $6$ | Octahedral |
Lewis structure of ${\text{Ge}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ ion is as follows:
Total valence electrons in ${\text{Ge}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ are as follows:
$ = \,\left( {4 \times 1} \right) + \left( {7 \times 4} \right)$
$ = \,32$

The total electron pair around central atom germanium is four so, the geometry will be tetrahedral which is shown as follows:

All four electron pairs are the same. So, the shape of ${\text{Ge}}{{\text{F}}_4}$ is tetrahedral.
Lewis structure of ${\text{Se}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ ion is as follows:
Total valence electrons in ${\text{Se}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ are as follows:
$ = \,\left( {6 \times 1} \right) + \left( {7 \times 4} \right)$
$ = \,34$

The total electron pair around central atom selenium is five so, the geometry will be trigonal bipyramidal which is shown as follows:

All five electron pairs are not the same. Out of the five, four are bond pair and one is lone pair So, the shape of ${\text{Se}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ is sea-sew.
Lewis structure of ${\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ ion is as follows:
Total valence electrons in ${\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ are as follows:
$ = \,\left( {8 \times 1} \right) + \left( {7 \times 4} \right)$
$ = \,36$

The total electron pair around central atom xenon is six so, the geometry will be octahedral which is shown as follows:

All six electron pairs are not the same. Out of the six, four are bond pairs and two are lone pairs. So, the shape of ${\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ is square planar.
Therefore, the correct molecular shapes of ${\text{Ge}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$, ${\text{Se}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ and ${\text{Xe}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}$ are tetrahedral, sea-sew and square planer respectively.
Note: To determine the total valence electrons of a molecule, we add all the valence electrons of the atoms present in the molecule. We subtract one for every positive charge and add one for every negative charge. Geometry around the central atom is decided only on the basis of sigma bond pair and lone pair only. Pi bonds are not counted to determine the geometry. Geometry is decided by counting the number of lone pair and sigma bonds where the shape is determined on the basis of sigma bond pairs only.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




