
Describe with the help of diagram, how compressions and rarefactions are produced in air near a source of sound.
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint:Consider the example of tuning fork as the source of sound. The inward and outward movement of the prongs creates a region of high pressure and low pressure near the prongs. Draw the diagram of compressions and rarefactions as the region of high pressure and the region of low pressure respectively.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, we consider the example of tuning forks. When we hit the prong of the tuning fork on the rubber pad, the two prongs of the tuning fork swings back and forth about their mean position. This vibration of the tuning fork produces a sound of a certain frequency. We know that the sound wave is a longitudinal wave and thus, it requires a medium for the propagation. The vibrations of source of sound create disturbances in the surrounding air by displacing the air molecules from their mean position.
Now, when the prongs of the tuning fork move outward, they push and compress the air near the prongs which results in a region of high pressure. This region is called compression. When the prongs move inward from their mean position, it forms a region of low pressure known as a rarefaction. These series of compressions and rarefactions move away from the source which makes the sound wave to propagate through the air.The following figure will ease our understanding.
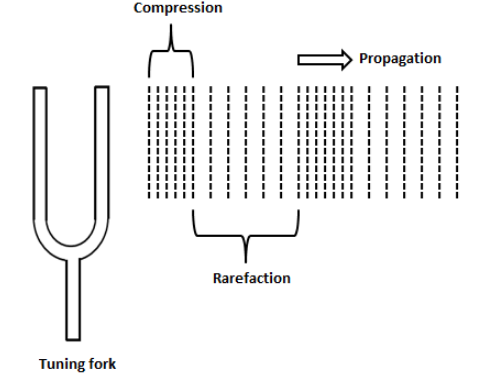
We can see the series of compressions and rarefactions of air molecules near the prongs of the tuning fork.
Note: For the propagation of sound waves, there must be a material medium present around the source of sound. If the tuning fork is sounded in vacuum, there will not be a region of high pressure and low pressure since there are no air molecules or any other molecules. In case of light, it is a transverse wave which does not require a medium for its propagation.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, we consider the example of tuning forks. When we hit the prong of the tuning fork on the rubber pad, the two prongs of the tuning fork swings back and forth about their mean position. This vibration of the tuning fork produces a sound of a certain frequency. We know that the sound wave is a longitudinal wave and thus, it requires a medium for the propagation. The vibrations of source of sound create disturbances in the surrounding air by displacing the air molecules from their mean position.
Now, when the prongs of the tuning fork move outward, they push and compress the air near the prongs which results in a region of high pressure. This region is called compression. When the prongs move inward from their mean position, it forms a region of low pressure known as a rarefaction. These series of compressions and rarefactions move away from the source which makes the sound wave to propagate through the air.The following figure will ease our understanding.

We can see the series of compressions and rarefactions of air molecules near the prongs of the tuning fork.
Note: For the propagation of sound waves, there must be a material medium present around the source of sound. If the tuning fork is sounded in vacuum, there will not be a region of high pressure and low pressure since there are no air molecules or any other molecules. In case of light, it is a transverse wave which does not require a medium for its propagation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




