
Describe with the help of a perfect circuit diagram of how we will calculate the unknown resistance by using meter bridge experiment.
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: A meter bridge can be also referred as the slide wire bridge which will be an instrument which is working on the basis of the theory of a Wheatstone bridge. A meter bridge is helpful in calculating the unknown resistance of a conductor similar to that of a Wheatstone bridge.
Complete answer:
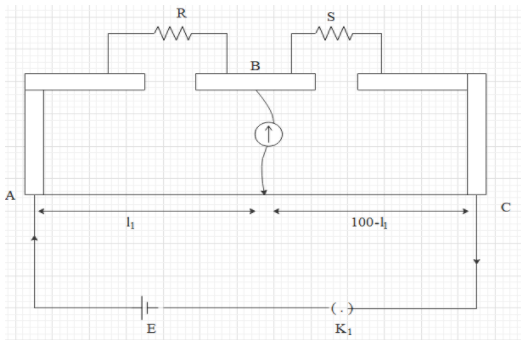
A meter bridge can be also referred as the slide wire bridge which will be an instrument which is working on the basis of the theory of a Wheatstone bridge. A meter bridge is helpful in calculating the unknown resistance of a conductor similar to that of a Wheatstone bridge. The key ${{k}_{1}}$ is closed in order to pass the current by the selection of an appropriate resistance $R$ in the resistance box. The jockey will be tapped along the wire in order to find out the position of the null point. This means that the galvanometer will not be showing any deflection. The bridge is then found to be balanced. Using the principle of wheat stone's bridge.
$\dfrac{R}{S}=\dfrac{{{l}_{1}}}{100-{{l}_{1}}}$
Therefore,
$S=\dfrac{\left( 100-{{l}_{1}} \right)R}{{{l}_{1}}}$
As $R$ is known values of the resistance, therefore the unknown resistance $S$ can be determined. Therefore the answer for the question has been found.
Note:
In the meter bridge we can see that one of the resistances is changed by a wire which is having a length of the uniform cross section of around one metre. The other pair will include one known and an unknown pair of resistances. The one region of the galvanometer has been found to be connected in between both resistances. And the other part of the wire will be determining the null point which is the point where the galvanometer is not visualizing any deflection. This is the point at which the bridge is found to be balanced.
Complete answer:

A meter bridge can be also referred as the slide wire bridge which will be an instrument which is working on the basis of the theory of a Wheatstone bridge. A meter bridge is helpful in calculating the unknown resistance of a conductor similar to that of a Wheatstone bridge. The key ${{k}_{1}}$ is closed in order to pass the current by the selection of an appropriate resistance $R$ in the resistance box. The jockey will be tapped along the wire in order to find out the position of the null point. This means that the galvanometer will not be showing any deflection. The bridge is then found to be balanced. Using the principle of wheat stone's bridge.
$\dfrac{R}{S}=\dfrac{{{l}_{1}}}{100-{{l}_{1}}}$
Therefore,
$S=\dfrac{\left( 100-{{l}_{1}} \right)R}{{{l}_{1}}}$
As $R$ is known values of the resistance, therefore the unknown resistance $S$ can be determined. Therefore the answer for the question has been found.
Note:
In the meter bridge we can see that one of the resistances is changed by a wire which is having a length of the uniform cross section of around one metre. The other pair will include one known and an unknown pair of resistances. The one region of the galvanometer has been found to be connected in between both resistances. And the other part of the wire will be determining the null point which is the point where the galvanometer is not visualizing any deflection. This is the point at which the bridge is found to be balanced.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




