
Describe with diagram the laboratory method of preparation of ethylene. Write its chemical reaction with the following. Also write the relevant chemical equations:
(i) Baeyer's reagent
(ii) Ozone
(iii) Sulphur monochloride
(iv) Chlorine
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint:Ethylene is a hydrocarbon having the chemical formula of or . It is a colourless and flammable gas and possesses a faint "sweet or musky" odour in its pure form. It is considered to be the simplest alkene.
Complete answer:
The dehydration of ethanol in the presence of either concentrated sulphuric acid or concentrated phosphoric acid at laboratory-scale leads to the production of ethylene as shown in the reaction below:
$C{H_3} - C{H_2} - OH\xrightarrow[{ - {H_2}O}]{{conc.{H_2}S{O_4}}}C{H_2} = C{H_2}$
This laboratory method of preparation of ethylene can be better understood from the schematic diagram demonstrated below:
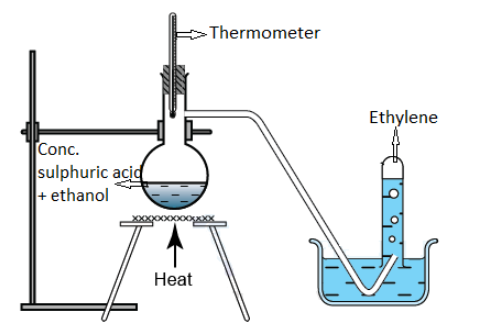
The relevant chemical reactions of ethylene are written below with different reactants:
(i) Baeyer's reagent: It is an alkaline solution of the cold potassium permanganate (powerful oxidant). When Ethylene reacts with Baeyer's reagent, ethylene glycol is produced. The colour of the solution changes from pink to colourless.
$C{H_2} = C{H_2}\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{{alkalineKMn{O_4}}}2HCOOH \to 2C{O_2} + 2{H_2}$
(ii) Ozone: When Ethylene reacts with ozone, initially ozonide of ethylene is formed which then reacts with \[Zn/{H_2}O\] to finally form methanal as shown below:
$C{H_2} = C{H_2}\xrightarrow[{2)Zn/{H_2}O}]{{1){O_3}}}2HCHO$
(iii) Sulphur monochloride: Ethylene reacts with Sulphur monochloride to yield mustard gas or sulphur mustard (\[{C_4}{H_8}C{l_2}S\]) as shown below:
$2{H_2}C = C{H_2} + {S_2}C{l_2} \to S{( - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - Cl)_2} + S$
(iv) Chlorine: When ethylene reacts with chlorine, Dichloroethane is produced as shown below:
${H_2}C = C{H_2} + C{l_2} \to {C_2}{H_4}C{l_2}$
Note:
There are multiple applications of ethylene. Ethylene is generally used as an anaesthetic in hospitals. It is also used as an oxy-fuel gas in welding, metal cutting, and high velocity thermal spraying. Other uses of ethylene include it is utilised as a refrigerant and also employed in the extraction of rubber.
Complete answer:
The dehydration of ethanol in the presence of either concentrated sulphuric acid or concentrated phosphoric acid at laboratory-scale leads to the production of ethylene as shown in the reaction below:
$C{H_3} - C{H_2} - OH\xrightarrow[{ - {H_2}O}]{{conc.{H_2}S{O_4}}}C{H_2} = C{H_2}$
This laboratory method of preparation of ethylene can be better understood from the schematic diagram demonstrated below:

The relevant chemical reactions of ethylene are written below with different reactants:
(i) Baeyer's reagent: It is an alkaline solution of the cold potassium permanganate (powerful oxidant). When Ethylene reacts with Baeyer's reagent, ethylene glycol is produced. The colour of the solution changes from pink to colourless.
$C{H_2} = C{H_2}\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{{alkalineKMn{O_4}}}2HCOOH \to 2C{O_2} + 2{H_2}$
(ii) Ozone: When Ethylene reacts with ozone, initially ozonide of ethylene is formed which then reacts with \[Zn/{H_2}O\] to finally form methanal as shown below:
$C{H_2} = C{H_2}\xrightarrow[{2)Zn/{H_2}O}]{{1){O_3}}}2HCHO$
(iii) Sulphur monochloride: Ethylene reacts with Sulphur monochloride to yield mustard gas or sulphur mustard (\[{C_4}{H_8}C{l_2}S\]) as shown below:
$2{H_2}C = C{H_2} + {S_2}C{l_2} \to S{( - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - Cl)_2} + S$
(iv) Chlorine: When ethylene reacts with chlorine, Dichloroethane is produced as shown below:
${H_2}C = C{H_2} + C{l_2} \to {C_2}{H_4}C{l_2}$
Note:
There are multiple applications of ethylene. Ethylene is generally used as an anaesthetic in hospitals. It is also used as an oxy-fuel gas in welding, metal cutting, and high velocity thermal spraying. Other uses of ethylene include it is utilised as a refrigerant and also employed in the extraction of rubber.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




