
Describe the working principle of a solar cell. Mention three basic processes involved in the generation of EMF.
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: Solar cells are photovoltaic devices that convert light energy coming from sun into electrical energy. The generation of voltage across the PN junction of a semiconductor due to the absorption of light radiation is known as Photovoltaic effect and the devices based on this effect are known as photovoltaic devices. Use this information to answer the given question.
Complete answer:
Solar cell is also known as a Photovoltaic cell or PV cell. From the name itself we can understand that it works on the principle of photovoltaic effect. Photovoltaic effect can be defined as a process which generates voltage or electric current in a photovoltaic cell or a solar cell when it is exposed to sunlight. It can also be defined as the photogeneration of charge carriers in a light absorbing material as a result of absorption of light radiation. The diagram of a single solar cell is shown below.
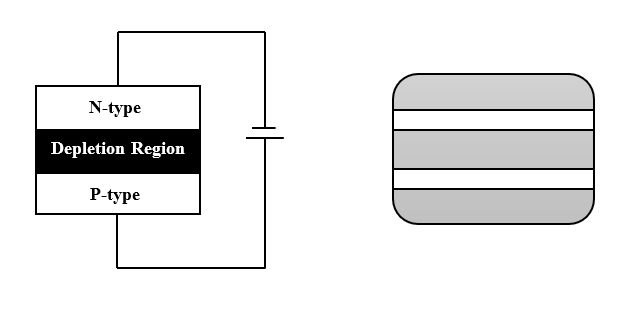
Generation, separation and collection are the three basic processes involved in the generation of EMF.
1. When a solar cell is illuminated with light photons of energy ($h\nu$) greater than the energy gap of the semiconductor electron-hole pairs are generated due to absorption of photons.
2. Electrons and holes are separated due to the electric field of the depletion region. Electrons swept to n-side and holes to p-side.
3. When electrons reach n-side, they get collected by the front contact and when holes reach p-side, they get collected by the back contact. This makes p-side more positive and n-side more negative giving rise to photovoltage
Note:
There are many types of semiconductors used for making solar cells but silicon is widely used. Silicon semiconductors have properties such as low weight volume ratio, strength and they have an extended life cycle. It is less expensive as compared to other semiconductors and abundantly available in nature. There are a lot of advantages of solar cells such as it reduces environmental problems, it reduces health issues etc.
Complete answer:
Solar cell is also known as a Photovoltaic cell or PV cell. From the name itself we can understand that it works on the principle of photovoltaic effect. Photovoltaic effect can be defined as a process which generates voltage or electric current in a photovoltaic cell or a solar cell when it is exposed to sunlight. It can also be defined as the photogeneration of charge carriers in a light absorbing material as a result of absorption of light radiation. The diagram of a single solar cell is shown below.

Generation, separation and collection are the three basic processes involved in the generation of EMF.
1. When a solar cell is illuminated with light photons of energy ($h\nu$) greater than the energy gap of the semiconductor electron-hole pairs are generated due to absorption of photons.
2. Electrons and holes are separated due to the electric field of the depletion region. Electrons swept to n-side and holes to p-side.
3. When electrons reach n-side, they get collected by the front contact and when holes reach p-side, they get collected by the back contact. This makes p-side more positive and n-side more negative giving rise to photovoltage
Note:
There are many types of semiconductors used for making solar cells but silicon is widely used. Silicon semiconductors have properties such as low weight volume ratio, strength and they have an extended life cycle. It is less expensive as compared to other semiconductors and abundantly available in nature. There are a lot of advantages of solar cells such as it reduces environmental problems, it reduces health issues etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




