
Describe the structure of the cerebrum in the human brain and mention its functions.
Answer
604.5k+ views
Hint: Cerebrum is a part of the forebrain or prosencephalon, it is also known as the telencephalon.
Complete answer:
The structural features of the cerebrum are as follows:
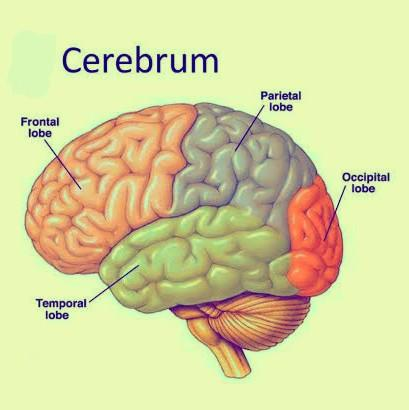
> It is divided into five regions or lobes, frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe, and the insula.
> The insula is a hidden lobe and it is present deep inside the Sylvian fissure.
> A fissure named rhinal fissure separates the cerebral hemisphere from the olfactory lobes.
> The cerebral hemisphere is divided into the right cerebral hemisphere and the left cerebral hemisphere by another fissure known as the median fissure,
> Three deep and wide fissures are formed by few well-developed sulci that divide each of the cerebral hemispheres into four lobes, anterior frontal lobe, middle parietal lobe, posterior occipital lobe, and the lateral temporal lobe.
> Between the frontal and the parietal lobe lies the central fissure or sulcus.
> The parietal lobe and occipital lobe are divided by the parieto-occipital fissure.
> The later or Sylvian fissure separates the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobes.
> A fluid-filled cavity known as lateral ventricle or paracoel is present in each cerebral hemisphere.
The cerebrum controls the following:
- Intelligence Center
- Emotion
- Memory
- Will power
- Imagination and consciousness
- Knowledge
- Reasoning
- Voluntary movement
- Micturition and defecation
- Crying and Laughing
Note: The left and right cerebral hemispheres are interconnected with the help of a thick band of nerve fibers, composed mainly of white fibers, known as the corpus callosum. It is important to know that the cerebral cortex is the highest center of many neural activities and if removal of the cerebrum is done then the animal turns into a simple reflex animal.
Complete answer:
The structural features of the cerebrum are as follows:
> It is divided into five regions or lobes, frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe, and the insula.
> The insula is a hidden lobe and it is present deep inside the Sylvian fissure.
> A fissure named rhinal fissure separates the cerebral hemisphere from the olfactory lobes.
> The cerebral hemisphere is divided into the right cerebral hemisphere and the left cerebral hemisphere by another fissure known as the median fissure,
> Three deep and wide fissures are formed by few well-developed sulci that divide each of the cerebral hemispheres into four lobes, anterior frontal lobe, middle parietal lobe, posterior occipital lobe, and the lateral temporal lobe.
> Between the frontal and the parietal lobe lies the central fissure or sulcus.
> The parietal lobe and occipital lobe are divided by the parieto-occipital fissure.
> The later or Sylvian fissure separates the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobes.
> A fluid-filled cavity known as lateral ventricle or paracoel is present in each cerebral hemisphere.
The cerebrum controls the following:
- Intelligence Center
- Emotion
- Memory
- Will power
- Imagination and consciousness
- Knowledge
- Reasoning
- Voluntary movement
- Micturition and defecation
- Crying and Laughing
Note: The left and right cerebral hemispheres are interconnected with the help of a thick band of nerve fibers, composed mainly of white fibers, known as the corpus callosum. It is important to know that the cerebral cortex is the highest center of many neural activities and if removal of the cerebrum is done then the animal turns into a simple reflex animal.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




