
How would you describe the structure and synthesis of ATP and its universal role as energy currency in all living organisms?
Answer
530.1k+ views
Hint: It is dissolvable so it very well may be shipped effectively around the body, to any place it is required. The inorganic phosphate can be utilized to decrease the initiation energy of phosphorylating, so it permits responses to happen with less energy.
Complete answer:
All living things including plants, creatures, birds, creepy crawlies, people need energy for the appropriate working of cells, tissues, and other organ frameworks. As we know that green plants get their energy from the daylight, and creatures get their energy by benefiting from these plants. Energy goes about as a wellspring of fuel.
We, people, acquire energy from the food we eat, yet how is the energy created and put away in our body. Loss of phosphate prompts energy discharge. On hydrolysis of ATP to ADP, $30.5 KJ mol^-1$ of energy is delivered. ADP + Pi ó ATP (reversible response). Adept is integrated from substrate-level phosphorylation during glycolysis and Krebs cycles.
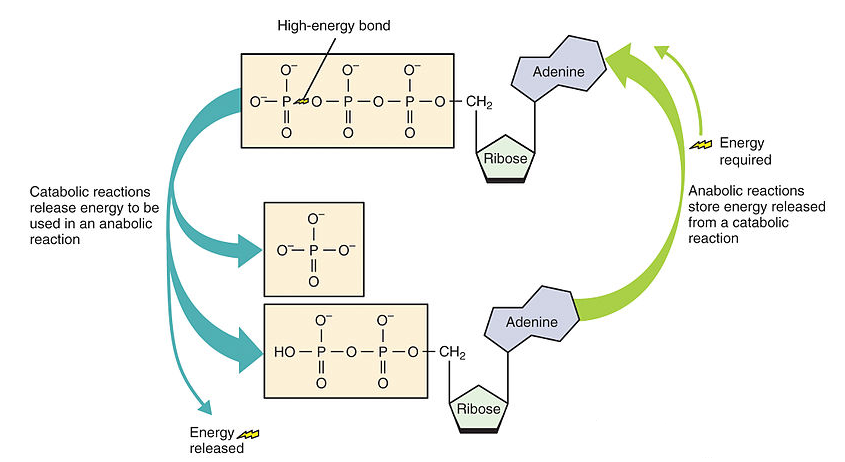
ATP is combined utilizing electron transporters in oxidative phosphorylation and photophosphorylation. ATP creation happens in mitochondria and chloroplast. In these organelles, ATP synthase is available which goes about as a channel for hydrogen particles, driving a chemiosmotic ally to the creation of ATP. ATP is utilized by cells as a prompt energy benefactor. ATP goes about as a connection between energy-yielding and energy-requiring responses. ATP is associated with Active Transport, Muscle Contraction, Calvin Cycle, and Protein Synthesis.
Note: It comprises adenine, ribose (a sugar), and three phosphate gatherings. It very well may be delivered of its energy by breaking the phosphate bond, in a 1 stage hydrolysis, subsequently, it is a snappy wellspring of energy.
Complete answer:
All living things including plants, creatures, birds, creepy crawlies, people need energy for the appropriate working of cells, tissues, and other organ frameworks. As we know that green plants get their energy from the daylight, and creatures get their energy by benefiting from these plants. Energy goes about as a wellspring of fuel.
We, people, acquire energy from the food we eat, yet how is the energy created and put away in our body. Loss of phosphate prompts energy discharge. On hydrolysis of ATP to ADP, $30.5 KJ mol^-1$ of energy is delivered. ADP + Pi ó ATP (reversible response). Adept is integrated from substrate-level phosphorylation during glycolysis and Krebs cycles.

ATP is combined utilizing electron transporters in oxidative phosphorylation and photophosphorylation. ATP creation happens in mitochondria and chloroplast. In these organelles, ATP synthase is available which goes about as a channel for hydrogen particles, driving a chemiosmotic ally to the creation of ATP. ATP is utilized by cells as a prompt energy benefactor. ATP goes about as a connection between energy-yielding and energy-requiring responses. ATP is associated with Active Transport, Muscle Contraction, Calvin Cycle, and Protein Synthesis.
Note: It comprises adenine, ribose (a sugar), and three phosphate gatherings. It very well may be delivered of its energy by breaking the phosphate bond, in a 1 stage hydrolysis, subsequently, it is a snappy wellspring of energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




