
Describe the process of fermentation in plants and animals (the chart is not required).
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: Fermentation is a type of respiration pathway occurring in plants and animals when oxygen is absent or insufficient for aerobic respiration to take place. These are of two types based on the nature of its products.
Complete step by step answer:
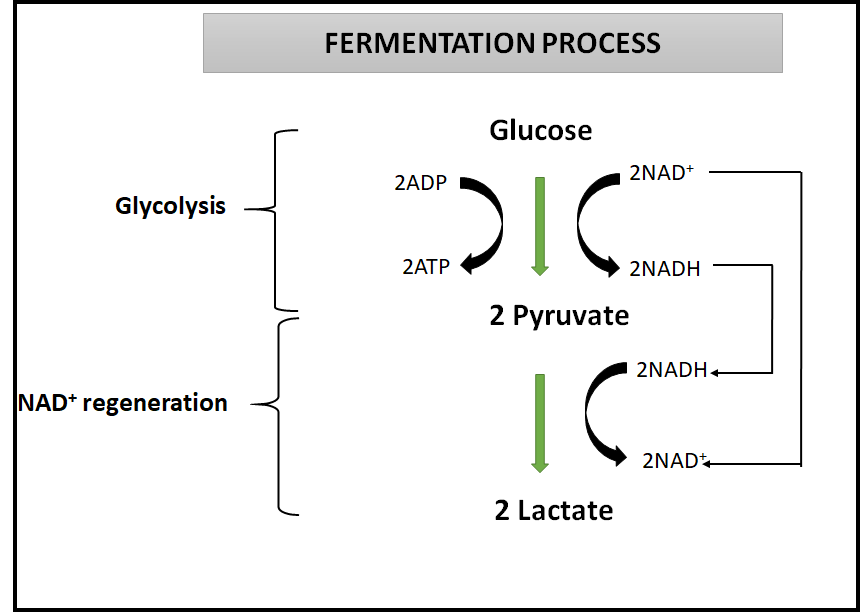
Fermentation is an enzyme-mediated energy liberating process in the absence or insufficient amounts of oxygen. This leads to the incomplete breakdown of the substrates and thus water is not produced as the end product in this process. The substrates which are usually carbohydrates after undergoing glycolysis and producing pyruvate takes a different turn. The lack of sufficient oxygen leads to the release of different products which may be lactic acid or ethyl alcohol.
In alcoholic fermentation, the pyruvic acid formed at the end of the glycolysis is converted to alcohol by using two enzymes, pyruvic acid decarboxylase, and alcohol dehydrogenase. The end products are two moles of ethyl alcohol, carbon dioxide, and ATP. E.g. plants, yeasts.
In lactic acid fermentation, lactate dehydrogenase catalyzes the transformation of pyruvate into lactate or lactic acid. The NADH released during glycolysis is consumed and ${ NAD }^{ + }$ is released. Its regeneration in the reduction of pyruvate to lactate sustains the continued operation of glycolysis under anaerobic conditions. E.g Muscle cells of humans, Lactobacillus.
Note:
- In alcoholic fermentation, Yeast poison to death when the concentration of alcohol reaches about 13%.
- Lactic acid accumulates in the muscle cells during extensive exercise and the oxygen demand becomes insufficient. Its accumulation leads to minor muscle cramps and pain in the body.
- The process of fermentation is used in various industries to produce dairy products, antibiotics, and chemicals like lactic acid and acetic acid.
Complete step by step answer:
Fermentation is an enzyme-mediated energy liberating process in the absence or insufficient amounts of oxygen. This leads to the incomplete breakdown of the substrates and thus water is not produced as the end product in this process. The substrates which are usually carbohydrates after undergoing glycolysis and producing pyruvate takes a different turn. The lack of sufficient oxygen leads to the release of different products which may be lactic acid or ethyl alcohol.

In alcoholic fermentation, the pyruvic acid formed at the end of the glycolysis is converted to alcohol by using two enzymes, pyruvic acid decarboxylase, and alcohol dehydrogenase. The end products are two moles of ethyl alcohol, carbon dioxide, and ATP. E.g. plants, yeasts.
In lactic acid fermentation, lactate dehydrogenase catalyzes the transformation of pyruvate into lactate or lactic acid. The NADH released during glycolysis is consumed and ${ NAD }^{ + }$ is released. Its regeneration in the reduction of pyruvate to lactate sustains the continued operation of glycolysis under anaerobic conditions. E.g Muscle cells of humans, Lactobacillus.
Note:
- In alcoholic fermentation, Yeast poison to death when the concentration of alcohol reaches about 13%.
- Lactic acid accumulates in the muscle cells during extensive exercise and the oxygen demand becomes insufficient. Its accumulation leads to minor muscle cramps and pain in the body.
- The process of fermentation is used in various industries to produce dairy products, antibiotics, and chemicals like lactic acid and acetic acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




