
Describe the parametric equations of a circle.
Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint: Equation of circle with origin as centre is \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\]. Equation of circle with centre \[\left( h,k \right)\] is \[{{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\]. The general equation of any type of circle is represented by the equation \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0\]. Where \[h=-g\], \[k=-f\] and \[c\] is any constant. A parameter is a variable that appears in a system of equations that can take any value but has the same value everywhere it appears. Parameter values are not plotted on an axis.
Complete step by step answer:
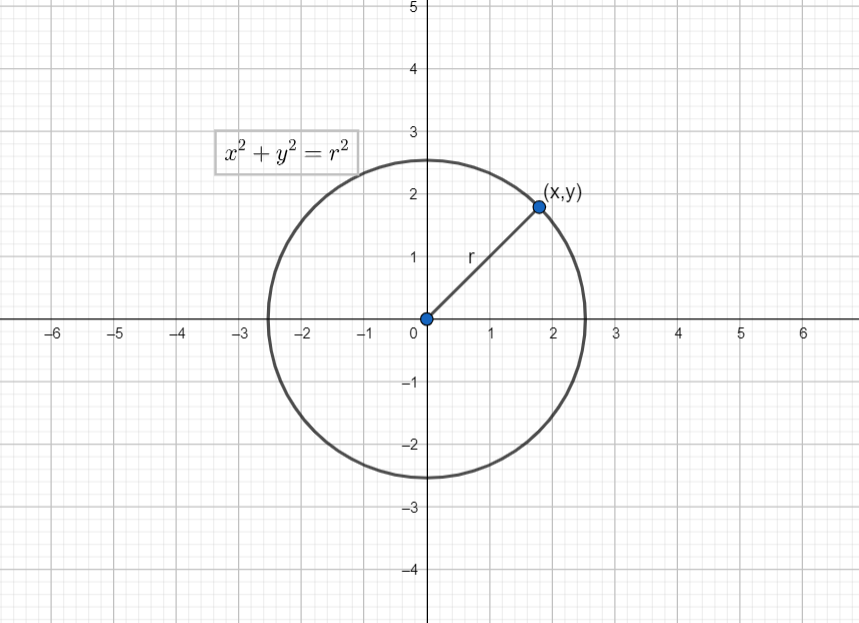
Circle is the locus of a point that moves in the plane such that its distance from a fixed point is always constant. The fixed point is called the centre and the fixed distance is called the radius of the circle.
A parametric equation of a circle is the coordinates of a point on the circle in terms of a single variable. This single variable is called a parameter.
\[x=r\cos \theta \]and \[y=r\sin \theta \] are the parametric equation of the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\].
The parametric equation of the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0\] is \[x=-g+r\cos \theta \], \[y=-f+r\sin \theta \].
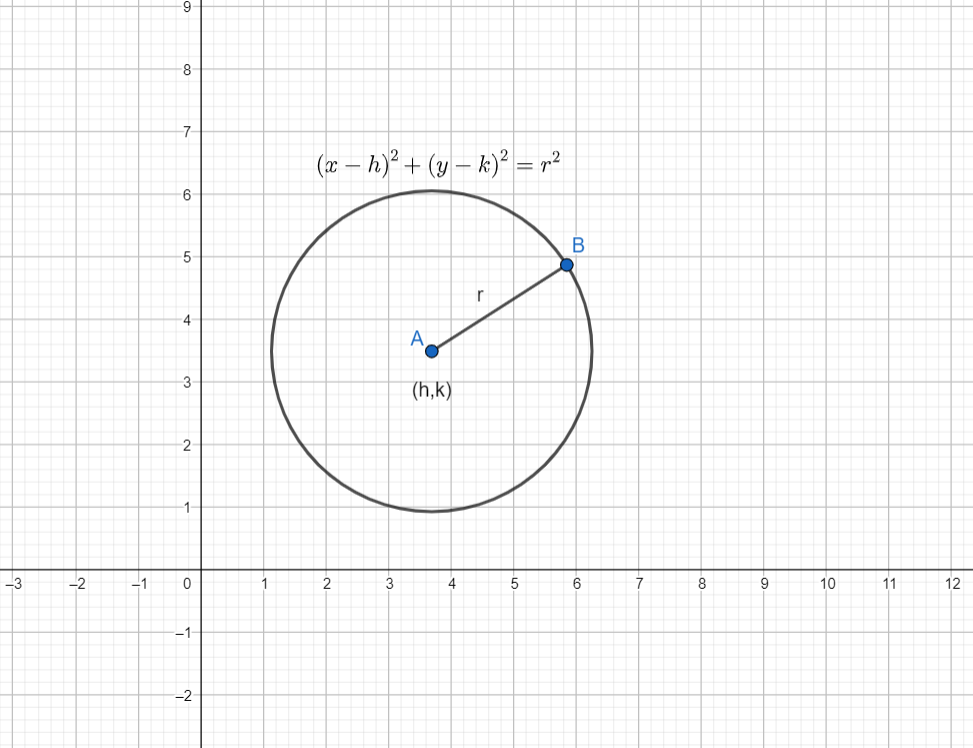
\[\theta \] is the parameter. This is a variable that appears in a system of equations that can take any value but has the same value everywhere it appears. Parameter values are not plotted on an axis.
Here \[\theta \] is the parameter, which represents the angle made by the line joining the point \[\left( x,y \right)\] with the, with the x-axis.
From the parametric equation we can find out the coordinates of any point on the circle if we know the radius, centre coordinates, and the radius of the circle.
Note: students should be careful while answering this type of question. This question is completely based upon concepts. So, students should be aware of some basic concepts of mathematics. Many students may have misconception that \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\] is the circle equation of any type of circle but actually it is circle equation only with centre at origin. \[{{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\]is the circle equation of all circles.
Complete step by step answer:
Circle is the locus of a point that moves in the plane such that its distance from a fixed point is always constant. The fixed point is called the centre and the fixed distance is called the radius of the circle.
A parametric equation of a circle is the coordinates of a point on the circle in terms of a single variable. This single variable is called a parameter.
\[x=r\cos \theta \]and \[y=r\sin \theta \] are the parametric equation of the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\].

The parametric equation of the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0\] is \[x=-g+r\cos \theta \], \[y=-f+r\sin \theta \].

\[\theta \] is the parameter. This is a variable that appears in a system of equations that can take any value but has the same value everywhere it appears. Parameter values are not plotted on an axis.
Here \[\theta \] is the parameter, which represents the angle made by the line joining the point \[\left( x,y \right)\] with the, with the x-axis.
From the parametric equation we can find out the coordinates of any point on the circle if we know the radius, centre coordinates, and the radius of the circle.
Note: students should be careful while answering this type of question. This question is completely based upon concepts. So, students should be aware of some basic concepts of mathematics. Many students may have misconception that \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\] is the circle equation of any type of circle but actually it is circle equation only with centre at origin. \[{{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\]is the circle equation of all circles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




