
Describe the locations, structures, and functions of the nervous tissue.
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: Nervous system is composed of neurons (nerve cells) which exercise control by sending electrical signals called nerve impulses.
The nervous control is speedy and flexible but its effect is localized.
Complete answer: 1. Location: The nervous tissue forms the nervous system in animals.
It is ectodermal in origin.
2. Structure: It consists of neurons, nerve fibres forming nerves, packing cells called neuroglia, epithelial cells called ependymal cells, and neurosecretory cells.
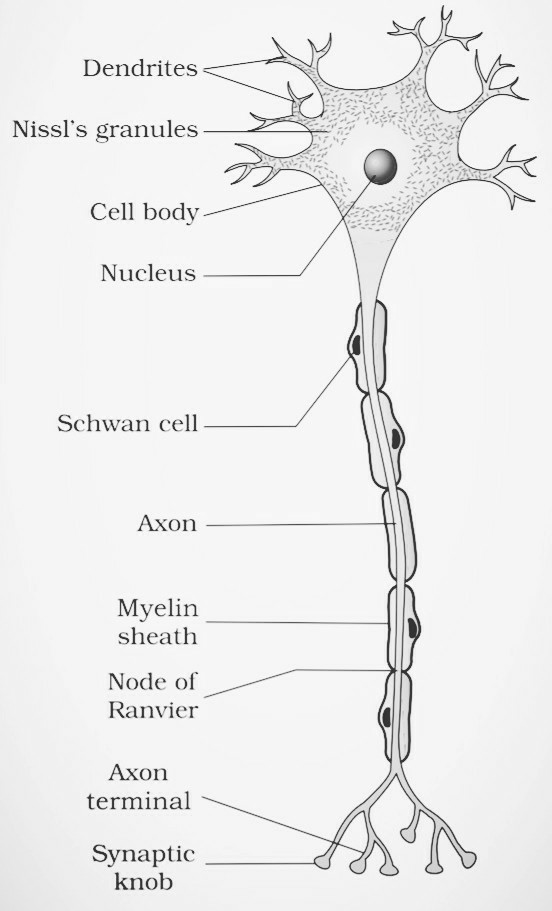
3. Neurons: Neurons or nerve cells are the functional units of the nervous system.
These have a special structure but vary greatly in size and shape.
Each neuron has a cell body that encloses the cytoplasm and has a nucleus.
A number of processes arise from the cell body. There is usually a single axon and a variable number of dendrites. The mass of nuclei inside the central nervous system is called nuclei.
Ganglia are the masses of neurons that lie in the peripheral nervous system.
Tracts are the bundles of nerve fibres within the nervous system
structure of neuron or nerve cell.
4. Nerve fibre: These are the bundles of nerve fibres in the peripheral nervous system.
In the PNS, Schwann cells wrap around the axons of neurons.
They cover the axons with concentric layers of the insulating plasma membrane.
5. Neuroglia: are the packing and supporting cells found in the brain and spinal cord.
6. Ependymal cells: are often ciliated.
These form epithelium that lines the cavities of the central nervous system.
7. Neurosecretory cells: They are specialized cells that elaborate hormones and release them into the bloodstream from their axon endings.
Functions: 1. Control and coordination: Coordinates the working of all parts of the body so that it functions as an integrated unit. Sensory input means the conduction of external information gathered by the sensory receptors about the stimuli acting on them.
2. Integration: Involves analysis and interpretation of the incoming information to produce sensations, such as vision pain, etc.
3. Memory and homeostasis are the other functions of the Nervous system.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The nervous system of a vertebrate is divided into two main parts: Central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). CNS lies along the main axis of the body and PNS consists of all nerves of the body associated with the CNS.
The nervous control is speedy and flexible but its effect is localized.
Complete answer: 1. Location: The nervous tissue forms the nervous system in animals.
It is ectodermal in origin.
2. Structure: It consists of neurons, nerve fibres forming nerves, packing cells called neuroglia, epithelial cells called ependymal cells, and neurosecretory cells.
3. Neurons: Neurons or nerve cells are the functional units of the nervous system.
These have a special structure but vary greatly in size and shape.
Each neuron has a cell body that encloses the cytoplasm and has a nucleus.
A number of processes arise from the cell body. There is usually a single axon and a variable number of dendrites. The mass of nuclei inside the central nervous system is called nuclei.
Ganglia are the masses of neurons that lie in the peripheral nervous system.
Tracts are the bundles of nerve fibres within the nervous system
structure of neuron or nerve cell.
4. Nerve fibre: These are the bundles of nerve fibres in the peripheral nervous system.
In the PNS, Schwann cells wrap around the axons of neurons.
They cover the axons with concentric layers of the insulating plasma membrane.
5. Neuroglia: are the packing and supporting cells found in the brain and spinal cord.
6. Ependymal cells: are often ciliated.
These form epithelium that lines the cavities of the central nervous system.
7. Neurosecretory cells: They are specialized cells that elaborate hormones and release them into the bloodstream from their axon endings.
Functions: 1. Control and coordination: Coordinates the working of all parts of the body so that it functions as an integrated unit. Sensory input means the conduction of external information gathered by the sensory receptors about the stimuli acting on them.
2. Integration: Involves analysis and interpretation of the incoming information to produce sensations, such as vision pain, etc.
3. Memory and homeostasis are the other functions of the Nervous system.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.

Note: The nervous system of a vertebrate is divided into two main parts: Central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). CNS lies along the main axis of the body and PNS consists of all nerves of the body associated with the CNS.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

Draw the diagram of the sectional view of the human class 10 biology CBSE




