
Describe the energy pyramid?
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: The energy pyramid can be used at each trophic level in an ecosystem to reflect the flow of energy because of the way that energy is used up and lost in the system.
Complete answer:
An energy pyramid (sometimes called a trophic pyramid or an ecological pyramid) is a graphical representation which shows the flow of energy in an ecosystem at each trophic level.
The width of each bar reflects the energy units for each trophic level available; the height is always the same. The energy flow travels from the bottom-up through the layers of the energy pyramid and is eventually decreased as energy is used up at each level by the species.
- The energy pyramid base structure shows the available energy within the primary producers. Primary producers also referred to as autotrophs, are species that generate their food by taking their nutrition from non-living energy sources. In most cases, these are photosynthesizing plants that use solar energy to produce their fuel in the form of simple sugars, but there are exceptions such as deep-sea species that use chemical energy from hydrothermal vents.
- The second tropical stage is made up of primary consumers. These are the herbivores that only feed on the primary producers.
- Secondary consumers and tertiary consumers form the third and fourth stages of the pyramid. These are carnivores and omnivores which can feed on all of the lower levels, but they often eat species immediately below them from the trophic stage.
- The energy pyramid top organisms include apex predators. Mostly these are carnivorous animals with no natural predators.
The same amount of energy (90%) is lost as heat at each of the subsequent trophic stages, while 10% is converted into usable biomatter. The apex predators can obtain just 0.01% of the primary energy by the time the energy hits the top trophic level.
Decomposers and detritivores break down the tissues and other organic matter that was not eaten by animals higher up the food chain in the entire energy pyramid. These species, in doing so, recycle the nutrients back into the soil, playing a crucial role in the cycles of carbon and nitrogen.
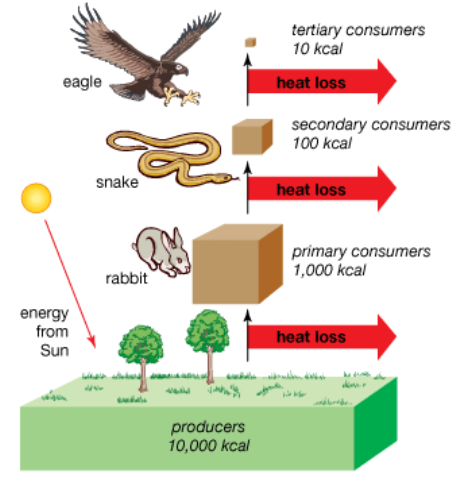
Note: Energy is used up for all aspects of life, such as breathing, movement, metabolic processes and reproduction. Thus, of the plants 100% total capacity, only about 10% is converted into plant tissues, while 90 per cent is used up and lost as heat.
Complete answer:
An energy pyramid (sometimes called a trophic pyramid or an ecological pyramid) is a graphical representation which shows the flow of energy in an ecosystem at each trophic level.
The width of each bar reflects the energy units for each trophic level available; the height is always the same. The energy flow travels from the bottom-up through the layers of the energy pyramid and is eventually decreased as energy is used up at each level by the species.
- The energy pyramid base structure shows the available energy within the primary producers. Primary producers also referred to as autotrophs, are species that generate their food by taking their nutrition from non-living energy sources. In most cases, these are photosynthesizing plants that use solar energy to produce their fuel in the form of simple sugars, but there are exceptions such as deep-sea species that use chemical energy from hydrothermal vents.
- The second tropical stage is made up of primary consumers. These are the herbivores that only feed on the primary producers.
- Secondary consumers and tertiary consumers form the third and fourth stages of the pyramid. These are carnivores and omnivores which can feed on all of the lower levels, but they often eat species immediately below them from the trophic stage.
- The energy pyramid top organisms include apex predators. Mostly these are carnivorous animals with no natural predators.
The same amount of energy (90%) is lost as heat at each of the subsequent trophic stages, while 10% is converted into usable biomatter. The apex predators can obtain just 0.01% of the primary energy by the time the energy hits the top trophic level.
Decomposers and detritivores break down the tissues and other organic matter that was not eaten by animals higher up the food chain in the entire energy pyramid. These species, in doing so, recycle the nutrients back into the soil, playing a crucial role in the cycles of carbon and nitrogen.

Note: Energy is used up for all aspects of life, such as breathing, movement, metabolic processes and reproduction. Thus, of the plants 100% total capacity, only about 10% is converted into plant tissues, while 90 per cent is used up and lost as heat.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




