
How do you describe the cell morphology of Escherichia coli?
Answer
481.8k+ views
Hint: Escherichia coli, also known as E. coli, is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped coliform bacteria found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded species. Although most E. coli strains are not infectious to humans, some serotypes can cause acute food poisoning in their hosts and are occasionally to blame for food contamination situations that result in recalls.
Complete answer
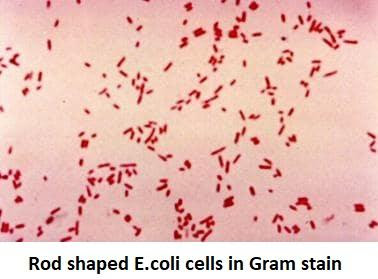
Microscopic morphological features of E. coli are as follows –
1. E. coli is a rod-shaped gram-negative (-ve) bacteria.
2. It is \[1 - 3{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}0.4 - 0.7{\text{ }}m\] in dimension and has a volume of \[0.6 - 0.7{\text{ }}m\].
3. It can be used alone or in pairs.
4. Peritrichous flagella make it motile.
5. Non-motile strains exist.
6. Fimbriated strains are possible. \[Type{\text{ }}1\] fimbriae (hemagglutinating and mannose-sensitive) are seen in both motile and non-motile strains.
6. A polysaccharide capsule has been seen in several E. coli strains recovered from extraintestinal infections.
7. They don't spread through spores.
8. Their cell wall is very thin, with only one or two layers of peptidoglycan.
9. They're facultative anaerobes, which means they can survive in the absence of oxygen.
10. Temperatures ranging from \[15\] to \[45^\circ C\] are conducive to growth.
Note:
E. coli is an intestinal pathogen or commensal of the human or animal gut that is excreted in the faeces and only survives for a few days in the environment. The presence of E. coli in drinking water indicates faecal contamination. It's a facultative anaerobe and an aerobe. The ideal temperature for growth is\[37^\circ C\]. Large, thick, greyish white, wet, smooth, opaque or translucent discs form colonies on Nutrient agar. In saltwater, the smooth (s) form seen in fresh isolation can be easily emulsified, whereas the rough (R) form frequently auto agglutinates.
Complete answer
Microscopic morphological features of E. coli are as follows –
1. E. coli is a rod-shaped gram-negative (-ve) bacteria.
2. It is \[1 - 3{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}0.4 - 0.7{\text{ }}m\] in dimension and has a volume of \[0.6 - 0.7{\text{ }}m\].
3. It can be used alone or in pairs.
4. Peritrichous flagella make it motile.
5. Non-motile strains exist.
6. Fimbriated strains are possible. \[Type{\text{ }}1\] fimbriae (hemagglutinating and mannose-sensitive) are seen in both motile and non-motile strains.
6. A polysaccharide capsule has been seen in several E. coli strains recovered from extraintestinal infections.
7. They don't spread through spores.
8. Their cell wall is very thin, with only one or two layers of peptidoglycan.
9. They're facultative anaerobes, which means they can survive in the absence of oxygen.
10. Temperatures ranging from \[15\] to \[45^\circ C\] are conducive to growth.

Note:
E. coli is an intestinal pathogen or commensal of the human or animal gut that is excreted in the faeces and only survives for a few days in the environment. The presence of E. coli in drinking water indicates faecal contamination. It's a facultative anaerobe and an aerobe. The ideal temperature for growth is\[37^\circ C\]. Large, thick, greyish white, wet, smooth, opaque or translucent discs form colonies on Nutrient agar. In saltwater, the smooth (s) form seen in fresh isolation can be easily emulsified, whereas the rough (R) form frequently auto agglutinates.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




