
Describe the brief structure and function of placenta?
Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint:Thus, you may recall that the placenta is the composite structure of undeveloped and maternal tissues that provisions supplements to the creating incipient organism. The placenta is an exceptional organ, discovered distinctly in vertebrates, that permits the mother to give a lot of supplements to her posterity for an all-encompassing timeframe before they are even conceived.
Complete answer:
Structure of placenta: Along these lines, you may recollect that the placenta is the composite structure of undeveloped and maternal tissues that provisions supplements to the creating incipient organism. The placenta is an extraordinary organ, discovered distinctly in warm blooded creatures, that permits the mother to give an extremely enormous measure of supplements to her posterity for an all-inclusive timeframe before they are even conceived. Placental warm blooded creatures, for example, people, have a chorioallantoic placenta that structures from the chorion and allantois. In people, the placenta midpoints 22 cm (9 inch) long and 2–2.5 cm (0.8–1 inch) in thickness, with the middle being the thickest, and the edges being the slenderest.
Function of placenta: The placenta capacities as a fetomaternal organ with two part the fetal placenta (Chorion frondosum), which creates from a similar blastocyst that frames the hatchling, and the maternal placenta (Decidua basalis), which creates from the maternal uterine tissue. It utilizes various substances and can deliver metabolic items into maternal or fetal disseminations. The placenta is ousted from the endless supply of the baby.
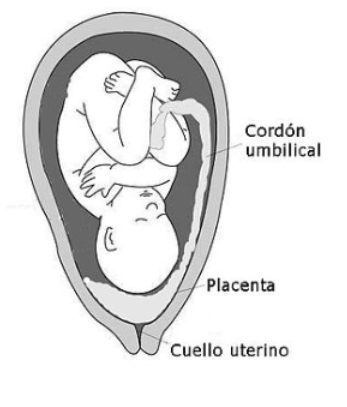
Notes:The placenta is the composite structure of undeveloped and maternal tissues that gracefully supplements to the creating incipient organism. The placenta serves three fundamental capacities: Attach the hatchling to the uterine divider. Permit the hatchling to move squander items to the mother's blood.
Complete answer:
Structure of placenta: Along these lines, you may recollect that the placenta is the composite structure of undeveloped and maternal tissues that provisions supplements to the creating incipient organism. The placenta is an extraordinary organ, discovered distinctly in warm blooded creatures, that permits the mother to give an extremely enormous measure of supplements to her posterity for an all-inclusive timeframe before they are even conceived. Placental warm blooded creatures, for example, people, have a chorioallantoic placenta that structures from the chorion and allantois. In people, the placenta midpoints 22 cm (9 inch) long and 2–2.5 cm (0.8–1 inch) in thickness, with the middle being the thickest, and the edges being the slenderest.
Function of placenta: The placenta capacities as a fetomaternal organ with two part the fetal placenta (Chorion frondosum), which creates from a similar blastocyst that frames the hatchling, and the maternal placenta (Decidua basalis), which creates from the maternal uterine tissue. It utilizes various substances and can deliver metabolic items into maternal or fetal disseminations. The placenta is ousted from the endless supply of the baby.

Notes:The placenta is the composite structure of undeveloped and maternal tissues that gracefully supplements to the creating incipient organism. The placenta serves three fundamental capacities: Attach the hatchling to the uterine divider. Permit the hatchling to move squander items to the mother's blood.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




