
Describe how urine is formed in the nephron through filtration, reabsorption and secretion.
Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint: The operating unit of the kidney is the Nephron. Excretion and osmoregulation are two major functions performed by the kidneys. In mammals, the kidneys help to produce hypertonic urine, which serves to retain water.
Complete answer:
Urine formation takes place in the following manner-
1. Glomerular Filtration: In the glomerular capillaries, this mechanism happens. The filtration process ends in the creation of an ultrafiltrate. The blood gushes high into these capillaries and is pumped through the skinny capillary walls. To create the ultrafiltrate, all but the blood cells and proteins are forced into the capsular space of the Bowman's capsule. 125ml/min or 180 litres/day is the glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
2. Tubular Reabsorption: All contaminants, except blood cells and proteins, are forced into the capillaries at elevated levels during glomerular filtration. A variety of compounds from the filtrate are reabsorbed at the extent of the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT). Popular sodium, phosphorus, glucose, amino acids, bicarbonate, and 75 percent of water contain these. Absorption of some substances is passive; while others are co-transported, some substances are deliberately transported. The absorption relies on the permeability of the nephron's various parts. Selective absorption is expressed in the distal tangled tubule. The peritubular capillaries haunt the chemicals and water which are reabsorbed to be added to the blood.
3. Tubular secretion: The peritubular capillaries that assist in the transfer into the bloodstream of the reabsorbed compounds often help to effectively secrete substances such as H+ ions, $K^+$ ions. $Na^+$ ions are actively reabsorbed to take care of the Na-K equilibrium if excess $K^+$ is secreted into the filtrate. In the glomerulus, certain drugs are not purified and so are effectively secreted during the tubular secretion process into the filtrate.
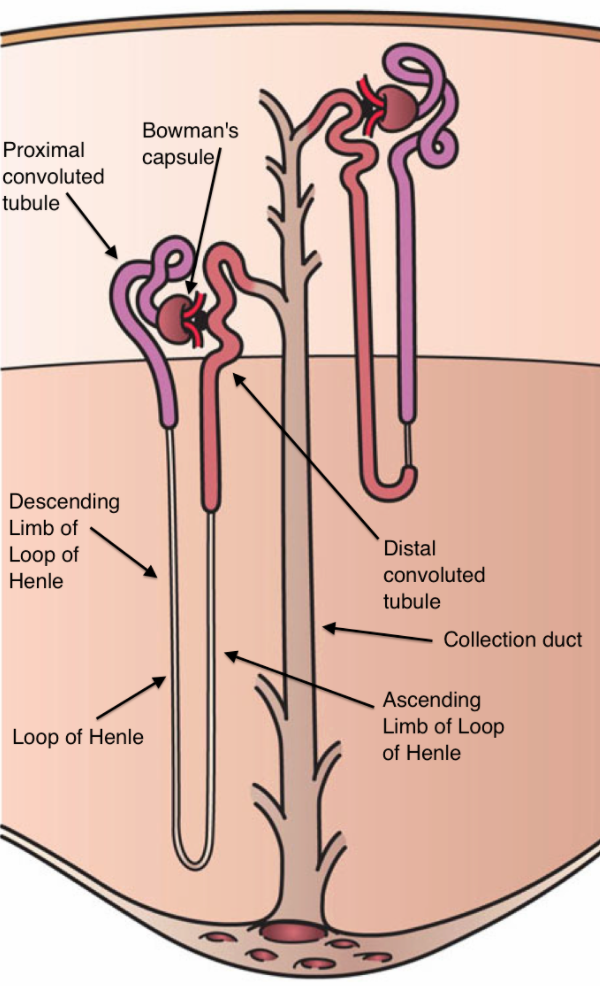
Note: The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron and components of the nephron include Bowman's capsule, proximal tubule, Loop of Henle, distal tubule and the collecting duct. Each kidney (human) contains approximately 1 million nephrons and each of it is capable of forming urine.
Complete answer:
Urine formation takes place in the following manner-
1. Glomerular Filtration: In the glomerular capillaries, this mechanism happens. The filtration process ends in the creation of an ultrafiltrate. The blood gushes high into these capillaries and is pumped through the skinny capillary walls. To create the ultrafiltrate, all but the blood cells and proteins are forced into the capsular space of the Bowman's capsule. 125ml/min or 180 litres/day is the glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
2. Tubular Reabsorption: All contaminants, except blood cells and proteins, are forced into the capillaries at elevated levels during glomerular filtration. A variety of compounds from the filtrate are reabsorbed at the extent of the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT). Popular sodium, phosphorus, glucose, amino acids, bicarbonate, and 75 percent of water contain these. Absorption of some substances is passive; while others are co-transported, some substances are deliberately transported. The absorption relies on the permeability of the nephron's various parts. Selective absorption is expressed in the distal tangled tubule. The peritubular capillaries haunt the chemicals and water which are reabsorbed to be added to the blood.
3. Tubular secretion: The peritubular capillaries that assist in the transfer into the bloodstream of the reabsorbed compounds often help to effectively secrete substances such as H+ ions, $K^+$ ions. $Na^+$ ions are actively reabsorbed to take care of the Na-K equilibrium if excess $K^+$ is secreted into the filtrate. In the glomerulus, certain drugs are not purified and so are effectively secreted during the tubular secretion process into the filtrate.

Note: The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron and components of the nephron include Bowman's capsule, proximal tubule, Loop of Henle, distal tubule and the collecting duct. Each kidney (human) contains approximately 1 million nephrons and each of it is capable of forming urine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




