
Describe enzymes and their function. What type of molecule they are, how they affect chemical reactions, and what conditions can affect enzyme activity?
Answer
516k+ views
Hint: Enzymes are the biological compounds that are required for speeding up a chemical reaction. They are the biocatalysts that speed up the forward reaction without being consumed during the reaction. They are very specific for reactants and also proper physical conditions are required to bring about the chemical change.
Complete answer:
Enzymes are proteins that have been folded into complex shapes that are found all over the body. Enzymes are responsible for the chemical reactions that keep us alive – our metabolism. Enzymes catalyse (speed up) chemical reactions; in some situations, enzymes can make a chemical reaction millions of times faster than it would be otherwise. The enzyme reacts with the substrate to form enzyme-substrate complexes and yields products.
Enzyme reaction: The enzymes have active sites which are specific to the substrate. The active site is bound by a substrate. The enzyme recognises the specific active site and binds. An enzyme from a reliable source is converted into products. The enzyme is able to bind to a new substrate and repeat the process until the products have left the active site. The enzymes speed up the forward reaction by lowering the activation energy.
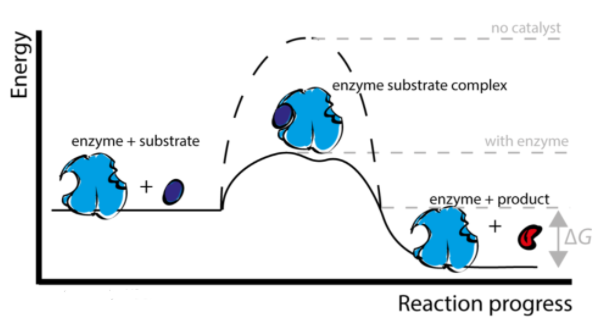
The factors affecting the enzymatic reaction are:
- Temperature: Raising the temperature of a reaction speeds it up while decreasing the temperature slows it down. Extremely high temperatures, on the other hand, may cause an enzyme to lose its shape (denature) and cease to function.
- pH: Each enzyme has a specific pH set that it prefers. If the pH is changed outside of this range, enzyme activity will be slowed. Enzymes will denature if the pH is too high.
- Increased enzyme concentration speeds up the reaction as long as there is a substrate to bind to.
- Substrate concentration: Increasing the substrate concentration speeds up the reaction to a limit.
Note: Catalysts are enzymes. Proteins are the most common, but some RNA molecules also act as enzymes. Enzymes reduce the activation energy of a reaction, which is the amount of energy necessary for it to take place. They do this by attaching themselves to a substrate and keeping it in a position that enables the reaction to proceed more quickly.
Complete answer:
Enzymes are proteins that have been folded into complex shapes that are found all over the body. Enzymes are responsible for the chemical reactions that keep us alive – our metabolism. Enzymes catalyse (speed up) chemical reactions; in some situations, enzymes can make a chemical reaction millions of times faster than it would be otherwise. The enzyme reacts with the substrate to form enzyme-substrate complexes and yields products.
Enzyme reaction: The enzymes have active sites which are specific to the substrate. The active site is bound by a substrate. The enzyme recognises the specific active site and binds. An enzyme from a reliable source is converted into products. The enzyme is able to bind to a new substrate and repeat the process until the products have left the active site. The enzymes speed up the forward reaction by lowering the activation energy.

The factors affecting the enzymatic reaction are:
- Temperature: Raising the temperature of a reaction speeds it up while decreasing the temperature slows it down. Extremely high temperatures, on the other hand, may cause an enzyme to lose its shape (denature) and cease to function.
- pH: Each enzyme has a specific pH set that it prefers. If the pH is changed outside of this range, enzyme activity will be slowed. Enzymes will denature if the pH is too high.
- Increased enzyme concentration speeds up the reaction as long as there is a substrate to bind to.
- Substrate concentration: Increasing the substrate concentration speeds up the reaction to a limit.
Note: Catalysts are enzymes. Proteins are the most common, but some RNA molecules also act as enzymes. Enzymes reduce the activation energy of a reaction, which is the amount of energy necessary for it to take place. They do this by attaching themselves to a substrate and keeping it in a position that enables the reaction to proceed more quickly.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




