
Derive the formula for electric potential energy of an electric dipole in a uniform electric field.
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: Potential energy can be described as the capacity for performing work which is due to the position or configuration. In the electrical case, a charge can exert a force on any other charge and potential energy is felt from any group of charges. As the potential energy increases, then electric potential increases.
Complete step by step answer:
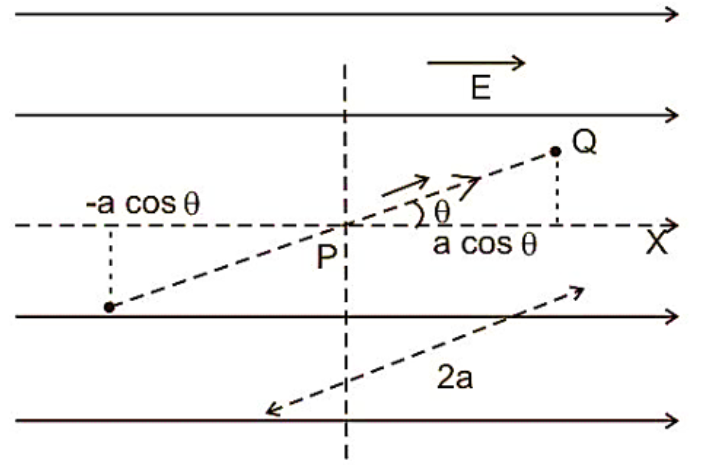
First of all let us discuss the electrical potential energy. Electric potential energy is the energy that is required to move a charge against the electric field. The energy that we used to move a particle away from the plate is stored in the particle itself as electrical potential energy. It is the potential that the particle is taken to move when it's let go. So here the potential energy of a dipole in uniform electric field. $\overrightarrow{\tau }=\overrightarrow{P}\times \overrightarrow{E}$
Work done in rotating dipole by smaller angle
$dw=\tau d\theta $
$=-PE\sin \theta d\theta $
Therefore the potential energy is given by
$dU=-dW=pE\sin \theta d\theta $
If changes from $90{}^\circ $ to $\theta {}^\circ $
Therefore we can write that,
$U\left( \theta \right)-U\left( 90{}^\circ \right)=\int\limits_{90{}^\circ }^{0{}^\circ }{PE\sin \theta d\theta }$
Perform the integration, then we can write that
$=PE\left[ -\cos \theta \right]_{90}^{0}$
That is,
$=-\overrightarrow{P}\cdot \overrightarrow{E}$
Therefore the potential energy of an electric dipole in a uniform electric field is,
$U\left( \theta \right)=-\overrightarrow{P}\cdot \overrightarrow{E}$
Note: The major difference between electric potential and electric potential energy is that electric potential at a point in an electric field is the measure of work done to bring the unit positive charge from the infinity to the particular point. In the similar sense, electric potential energy is the energy that is required to move a charge against the electric field. Unit of electrical potential energy is given in $J$. And it is a scalar quantity also.
Complete step by step answer:

First of all let us discuss the electrical potential energy. Electric potential energy is the energy that is required to move a charge against the electric field. The energy that we used to move a particle away from the plate is stored in the particle itself as electrical potential energy. It is the potential that the particle is taken to move when it's let go. So here the potential energy of a dipole in uniform electric field. $\overrightarrow{\tau }=\overrightarrow{P}\times \overrightarrow{E}$
Work done in rotating dipole by smaller angle
$dw=\tau d\theta $
$=-PE\sin \theta d\theta $
Therefore the potential energy is given by
$dU=-dW=pE\sin \theta d\theta $
If changes from $90{}^\circ $ to $\theta {}^\circ $
Therefore we can write that,
$U\left( \theta \right)-U\left( 90{}^\circ \right)=\int\limits_{90{}^\circ }^{0{}^\circ }{PE\sin \theta d\theta }$
Perform the integration, then we can write that
$=PE\left[ -\cos \theta \right]_{90}^{0}$
That is,
$=-\overrightarrow{P}\cdot \overrightarrow{E}$
Therefore the potential energy of an electric dipole in a uniform electric field is,
$U\left( \theta \right)=-\overrightarrow{P}\cdot \overrightarrow{E}$
Note: The major difference between electric potential and electric potential energy is that electric potential at a point in an electric field is the measure of work done to bring the unit positive charge from the infinity to the particular point. In the similar sense, electric potential energy is the energy that is required to move a charge against the electric field. Unit of electrical potential energy is given in $J$. And it is a scalar quantity also.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




