
Derive the formula for efficiency of the Carnot engine.
Answer
508.5k+ views
Hint: Carnot engine was proposed by Nicolas Leonard sadi Carnot in 1824. Carnot engine which gives an estimate of the maximum possible efficiency of a heat engine during the conversion process of heat into work. A carnot engine is used in heat pumps and working fluid has a fixed mass throughout a cycle.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Carnot cycle consist of following four processes and carnot engine is an ideal reversible closed thermodynamic cycle
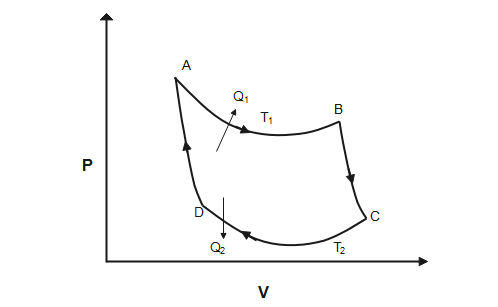
1) Isothermal expansion
Heat ${{Q}_{1}}$ is absorbed from the reservoir at temperature ${{T}_{1}}$ and gas is taken from ${{P}_{1}},{{V}_{1}},{{T}_{1}}$ to ${{P}_{2}},{{V}_{2}},{{T}_{2}}$. The total change in internal energy is zero and work done by the gas on the environment is equal to the heat absorbed by the gas.
Work done by the gas is given by:
${{W}_{12}}={{Q}_{1}}=\mu R{{T}_{1}}\times \ln \dfrac{{{v}_{2}}}{{{v}_{1}}}$
2) Adiabatic expansion
From ${{P}_{2}},{{V}_{2}},{{T}_{1}}$ to ${{P}_{3}},{{V}_{3}},{{T}_{2}}$ gas expands adiabatically
Work done by the gas is given by:
${{W}_{23}}=\dfrac{\mu R}{\gamma -1}({{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}})$
3) Isothermal compression:
From ${{P}_{3}},{{V}_{3}},{{T}_{2}}$ to ${{P}_{4}},{{V}_{4}},{{T}_{2}}$ gas is compressed isothermally
Work done by the gas is given by:
${{W}_{34}}=\mu R{{T}_{2}}\ln \dfrac{{{v}_{3}}}{{{v}_{4}}}$
4) Adiabatic compression
From ${{P}_{4}},{{V}_{4}},{{T}_{2}}$ to ${{P}_{1}},{{V}_{1}},{{T}_{1}}$ gas is compressed adiabatically
Work done by the gas is given by:
${{W}_{41}}=\dfrac{\mu R}{\gamma -1}({{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}})$
Total work done by the gas in one complete cycle is given by:
\[\begin{align}
& W={{W}_{12}}+{{W}_{23}}+{{W}_{34}}+{{W}_{41}} \\
& W=\mu R{{T}_{1}}\ln \dfrac{{{v}_{2}}}{{{v}_{1}}}-\mu R{{T}_{2}}\ln \dfrac{{{v}_{3}}}{{{v}_{4}}} \\
\end{align}\]
Net efficiency (Ne) of engine is equal to ratio of net work done by the gas to the heat absorbed by the gas
$\begin{align}
& Ne=\dfrac{W}{{{Q}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{Q}_{1}}-{{Q}_{2}}}{{{Q}_{1}}} \\
& Ne=1-\dfrac{{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{1}}}\dfrac{\ln \dfrac{{{v}_{3}}}{{{v}_{4}}}}{\ln \dfrac{{{v}_{2}}}{{{v}_{1}}}} \\
\end{align}$
(1) and (2) process is an adiabatic process
${{T}_{1}}{{V}_{2}}^{\gamma -1}={{T}_{2}}{{V}_{3}}^{\gamma -1}$
(4) And (1) process we can write
$\dfrac{{{v}_{1}}}{{{v}_{2}}}={{(\dfrac{{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{1}}})}^{\dfrac{1}{\gamma -1}}}$
Net efficiency of Carnot engine =$1-\dfrac{{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{1}}}$
Note: The efficiency of a carnot engine is independent of the nature of the working substance and dependent on the temperature of the hot and cold reservoirs. Working fluid in each cycle passes through equilibrium to non-equilibrium states (same physical state) and it consists of one and the same phase throughout the cycle .There are no entropy changes in the engine.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Carnot cycle consist of following four processes and carnot engine is an ideal reversible closed thermodynamic cycle

1) Isothermal expansion
Heat ${{Q}_{1}}$ is absorbed from the reservoir at temperature ${{T}_{1}}$ and gas is taken from ${{P}_{1}},{{V}_{1}},{{T}_{1}}$ to ${{P}_{2}},{{V}_{2}},{{T}_{2}}$. The total change in internal energy is zero and work done by the gas on the environment is equal to the heat absorbed by the gas.
Work done by the gas is given by:
${{W}_{12}}={{Q}_{1}}=\mu R{{T}_{1}}\times \ln \dfrac{{{v}_{2}}}{{{v}_{1}}}$
2) Adiabatic expansion
From ${{P}_{2}},{{V}_{2}},{{T}_{1}}$ to ${{P}_{3}},{{V}_{3}},{{T}_{2}}$ gas expands adiabatically
Work done by the gas is given by:
${{W}_{23}}=\dfrac{\mu R}{\gamma -1}({{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}})$
3) Isothermal compression:
From ${{P}_{3}},{{V}_{3}},{{T}_{2}}$ to ${{P}_{4}},{{V}_{4}},{{T}_{2}}$ gas is compressed isothermally
Work done by the gas is given by:
${{W}_{34}}=\mu R{{T}_{2}}\ln \dfrac{{{v}_{3}}}{{{v}_{4}}}$
4) Adiabatic compression
From ${{P}_{4}},{{V}_{4}},{{T}_{2}}$ to ${{P}_{1}},{{V}_{1}},{{T}_{1}}$ gas is compressed adiabatically
Work done by the gas is given by:
${{W}_{41}}=\dfrac{\mu R}{\gamma -1}({{T}_{1}}-{{T}_{2}})$
Total work done by the gas in one complete cycle is given by:
\[\begin{align}
& W={{W}_{12}}+{{W}_{23}}+{{W}_{34}}+{{W}_{41}} \\
& W=\mu R{{T}_{1}}\ln \dfrac{{{v}_{2}}}{{{v}_{1}}}-\mu R{{T}_{2}}\ln \dfrac{{{v}_{3}}}{{{v}_{4}}} \\
\end{align}\]
Net efficiency (Ne) of engine is equal to ratio of net work done by the gas to the heat absorbed by the gas
$\begin{align}
& Ne=\dfrac{W}{{{Q}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{Q}_{1}}-{{Q}_{2}}}{{{Q}_{1}}} \\
& Ne=1-\dfrac{{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{1}}}\dfrac{\ln \dfrac{{{v}_{3}}}{{{v}_{4}}}}{\ln \dfrac{{{v}_{2}}}{{{v}_{1}}}} \\
\end{align}$
(1) and (2) process is an adiabatic process
${{T}_{1}}{{V}_{2}}^{\gamma -1}={{T}_{2}}{{V}_{3}}^{\gamma -1}$
(4) And (1) process we can write
$\dfrac{{{v}_{1}}}{{{v}_{2}}}={{(\dfrac{{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{1}}})}^{\dfrac{1}{\gamma -1}}}$
Net efficiency of Carnot engine =$1-\dfrac{{{T}_{2}}}{{{T}_{1}}}$
Note: The efficiency of a carnot engine is independent of the nature of the working substance and dependent on the temperature of the hot and cold reservoirs. Working fluid in each cycle passes through equilibrium to non-equilibrium states (same physical state) and it consists of one and the same phase throughout the cycle .There are no entropy changes in the engine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




