
Derive the balancing condition of a Wheatstone bridge
Answer
609k+ views
Hint: First draw the circuit diagram of the Wheatstone’s bridge and then try to analyse the condition. Try to understand the concept of the bridge and obtain the required balanced condition by using the concept of current flow and voltage division.
Complete step by step answer: the Wheatstone’s bridge works on the principle that where the ratio of the resistances are equal no current flows through the galvanometer. In normal condition the galvanometer is in unbalanced condition that is current flows through the galvanometer. When no current flows through the galvanometer it is known as the balanced condition of the galvanometer.
The Wheatstone’s bridge will be in the balanced condition when the current through the galvanometer is zero.
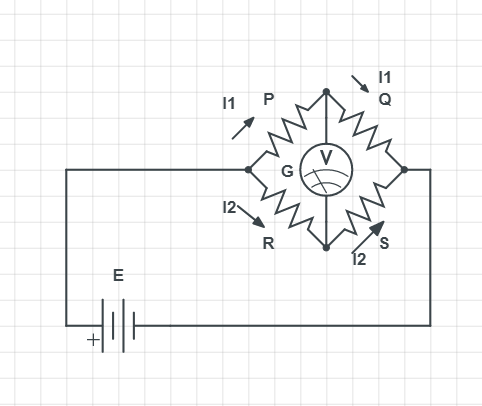
Current will divide in magnitude to ${{I}_{1}}\And {{I}_{2}}$ to go through resistors P and R.
So, ${{I}_{1}}P={{I}_{2}}R$
When no current flows through galvanometer current ${{I}_{1}}$ will go through P and Q and current ${{I}_{2}}$ will go through R and S.
So, we can write.
${{I}_{1}}=\dfrac{E}{P+Q}$ and ${{I}_{2}}=\dfrac{E}{R+S}$
By substituting these values in the above equation, we get that
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{E}{P+Q}P=\dfrac{E}{R+S}R \\
& \dfrac{P}{P+Q}=\dfrac{R}{R+S} \\
& P\left( R+S \right)=R\left( P+Q \right) \\
& PR+PS=PR+PQ \\
& PS=PQ \\
\end{align}$
This is the required condition for a balanced galvanometer.
We can also write it as,
$\dfrac{P}{R}=\dfrac{Q}{S}$
i.e. if the ratio of the resistance connected in the circuit in this way is equal then the galvanometer will be in its balanced condition.
Note: In a wheatstone bridge we have two known resistances and two unknown resistances. From these if we put one resistance with some value then we can find out what value of resistance we should put so that the bridge will be in a balanced condition.
Complete step by step answer: the Wheatstone’s bridge works on the principle that where the ratio of the resistances are equal no current flows through the galvanometer. In normal condition the galvanometer is in unbalanced condition that is current flows through the galvanometer. When no current flows through the galvanometer it is known as the balanced condition of the galvanometer.
The Wheatstone’s bridge will be in the balanced condition when the current through the galvanometer is zero.

Current will divide in magnitude to ${{I}_{1}}\And {{I}_{2}}$ to go through resistors P and R.
So, ${{I}_{1}}P={{I}_{2}}R$
When no current flows through galvanometer current ${{I}_{1}}$ will go through P and Q and current ${{I}_{2}}$ will go through R and S.
So, we can write.
${{I}_{1}}=\dfrac{E}{P+Q}$ and ${{I}_{2}}=\dfrac{E}{R+S}$
By substituting these values in the above equation, we get that
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{E}{P+Q}P=\dfrac{E}{R+S}R \\
& \dfrac{P}{P+Q}=\dfrac{R}{R+S} \\
& P\left( R+S \right)=R\left( P+Q \right) \\
& PR+PS=PR+PQ \\
& PS=PQ \\
\end{align}$
This is the required condition for a balanced galvanometer.
We can also write it as,
$\dfrac{P}{R}=\dfrac{Q}{S}$
i.e. if the ratio of the resistance connected in the circuit in this way is equal then the galvanometer will be in its balanced condition.
Note: In a wheatstone bridge we have two known resistances and two unknown resistances. From these if we put one resistance with some value then we can find out what value of resistance we should put so that the bridge will be in a balanced condition.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE

a Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode class 12 chemistry CBSE




