
Derive Laplace’s law for a spherical membrane.
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: or a spherical liquid drop, we know that there will be a pressure difference between the inside and outside. You could first find the work done by the surface tension in causing the change in area. Then you could find the work done in terms of force and displacement, where force is further reduced into a product of pressure difference and area. Equate the above two expressions to find the required expression.
Formula used:
Area of a sphere,
$A=4\pi {{r}^{2}}$
Work done,
$W=F\times S$
Pressure,
$P=\dfrac{F}{A}$
Complete step by step answer:
We know that liquid drops and bubbles are spherical when the effect of gravity and air resistance is negligible due to the action of surface tension. Due to the same reason the inside pressure $\left( {{P}_{i}} \right)$ is greater than outside pressure $\left( {{P}_{o}} \right)$ and the excess pressure could be given by, ${{P}_{i}}-{{P}_{{{o}_{{}}}}}$
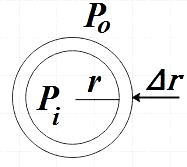
Assume that the radius of the drop is increasing from $r$ to $r+\Delta r$ where $\Delta r$ is negligibly small for the pressure inside could be thought of as constant.
Then, initial surface area,
${{A}_{1}}=4\pi {{r}^{2}}$
Final surface area,
${{A}_{2}}=4\pi {{\left( r+\Delta r \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{A}_{2}}=4\pi {{r}^{2}}+8\pi r\Delta r+4\pi \Delta {{r}^{2}}$
We could neglect $4\pi \Delta {{r}^{2}}$ as $\Delta {{r}^{2}}$ will be negligibly small.
${{A}_{2}}=4\pi {{r}^{2}}+8\pi r\Delta r$
Change in area,
$\Delta A={{A}_{2}}-{{A}_{1}}=8\pi r\Delta r$
We could express the work done in increasing the surface area as,
$dW=T\times dA=T\left( 8\pi r\Delta r \right)$ ……………………………………. (1)
But we know that work done is normally expressed as the product of force and displacement, that is,
$dW=F\times S=F\times \Delta r$ ……………………………………………. (2)
Also, $P=\dfrac{F}{A}$
Therefore, F = excess pressure × area
$F=\left( {{P}_{i}}-{{P}_{o}} \right)\times 4\pi {{r}^{2}}$
Substituting this in equation (2), we get,
$dW=\left( {{P}_{i}}-{{P}_{o}} \right)\times 4\pi {{r}^{2}}\Delta r$ …………………………………. (3)
Equating equations (2) and (3), we get,
$\left( {{P}_{i}}-{{P}_{o}} \right)\times 4\pi {{r}^{2}}\times \Delta r=T\times 8\pi r\Delta r$
$\therefore \left( {{P}_{i}}-{{P}_{o}} \right)=\dfrac{2T}{r}$
This formula thus derived is known as Laplace’s law for the spherical membrane for a liquid drop.
Additional information:
For the case of a liquid bubble, it has two free surfaces, while calculating the change in area we get,
$dA=16\pi r\Delta r$
All the other steps remain the same and hence the final expression becomes,
$\left( {{P}_{i}}-{{P}_{o}} \right)=\dfrac{4T}{r}$
Note: Rise and fall of liquid in capillary tubes could be explained by this fact of existence of pressure difference. The liquid surface is flat when the pressure difference between liquid side and vapor side is zero. For the concave surface the pressure on the vapor side is more and for the convex liquid surface the pressure on the liquid side is more.
Formula used:
Area of a sphere,
$A=4\pi {{r}^{2}}$
Work done,
$W=F\times S$
Pressure,
$P=\dfrac{F}{A}$
Complete step by step answer:
We know that liquid drops and bubbles are spherical when the effect of gravity and air resistance is negligible due to the action of surface tension. Due to the same reason the inside pressure $\left( {{P}_{i}} \right)$ is greater than outside pressure $\left( {{P}_{o}} \right)$ and the excess pressure could be given by, ${{P}_{i}}-{{P}_{{{o}_{{}}}}}$

Assume that the radius of the drop is increasing from $r$ to $r+\Delta r$ where $\Delta r$ is negligibly small for the pressure inside could be thought of as constant.
Then, initial surface area,
${{A}_{1}}=4\pi {{r}^{2}}$
Final surface area,
${{A}_{2}}=4\pi {{\left( r+\Delta r \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{A}_{2}}=4\pi {{r}^{2}}+8\pi r\Delta r+4\pi \Delta {{r}^{2}}$
We could neglect $4\pi \Delta {{r}^{2}}$ as $\Delta {{r}^{2}}$ will be negligibly small.
${{A}_{2}}=4\pi {{r}^{2}}+8\pi r\Delta r$
Change in area,
$\Delta A={{A}_{2}}-{{A}_{1}}=8\pi r\Delta r$
We could express the work done in increasing the surface area as,
$dW=T\times dA=T\left( 8\pi r\Delta r \right)$ ……………………………………. (1)
But we know that work done is normally expressed as the product of force and displacement, that is,
$dW=F\times S=F\times \Delta r$ ……………………………………………. (2)
Also, $P=\dfrac{F}{A}$
Therefore, F = excess pressure × area
$F=\left( {{P}_{i}}-{{P}_{o}} \right)\times 4\pi {{r}^{2}}$
Substituting this in equation (2), we get,
$dW=\left( {{P}_{i}}-{{P}_{o}} \right)\times 4\pi {{r}^{2}}\Delta r$ …………………………………. (3)
Equating equations (2) and (3), we get,
$\left( {{P}_{i}}-{{P}_{o}} \right)\times 4\pi {{r}^{2}}\times \Delta r=T\times 8\pi r\Delta r$
$\therefore \left( {{P}_{i}}-{{P}_{o}} \right)=\dfrac{2T}{r}$
This formula thus derived is known as Laplace’s law for the spherical membrane for a liquid drop.
Additional information:
For the case of a liquid bubble, it has two free surfaces, while calculating the change in area we get,
$dA=16\pi r\Delta r$
All the other steps remain the same and hence the final expression becomes,
$\left( {{P}_{i}}-{{P}_{o}} \right)=\dfrac{4T}{r}$
Note: Rise and fall of liquid in capillary tubes could be explained by this fact of existence of pressure difference. The liquid surface is flat when the pressure difference between liquid side and vapor side is zero. For the concave surface the pressure on the vapor side is more and for the convex liquid surface the pressure on the liquid side is more.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




