
Derive an expression related to position velocity $2as={{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}}$ using graphical method.
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: Draw a velocity time graph. Assume that the object must be moving with uniform acceleration. The distance traveled by the body moving with uniform acceleration can be calculated as the area of the trapezium that will be formed.
Formula used:
Area of trapezium=$\dfrac{1}{2}$ (sum of parallel sides + distance between parallel sides)
Complete step-by-step answer:
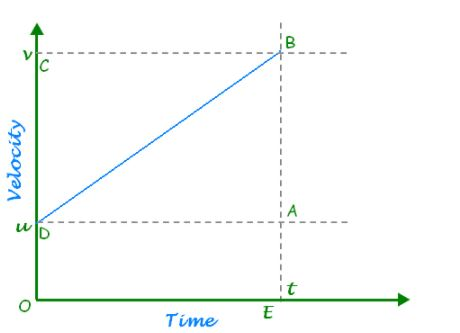
Let us assume the initial velocity of the object, final velocity of the object, acceleration of the object and distance traveled by the object as $u,v,a,S$ respectively. Let the object reach the point B after time $t$. Now, draw a line parallel to the x-axis DA from point D from where the object starts moving. Now, draw another line from point B parallel to y-axis which meets E at y-axis. Now, the distance travelled by the body with uniform velocity is given by the area of trapezium ABDO.
Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& S=\dfrac{1}{2}(DO+BE)\times OE \\
& S=\dfrac{1}{2}(u+v)\times t \\
& \\
\end{align}$
We also know that,
$\begin{align}
& a=\dfrac{v-u}{t} \\
& t=\dfrac{v-u}{a} \\
\end{align}$
Now, substitute the t value in distance equation, we get,
$\begin{align}
& S=\dfrac{1}{2}(u+v)(v-u) \\
& 2S={{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}} \\
& \\
\end{align}$
Hence proved.
Additional Information: We know, velocity is directly proportional to time when acceleration is constant and displacement is directly proportional to time squared, when acceleration is constant. If we combine the above two equations, we get an equation that is independent of time. Displacement is proportional to velocity squared when acceleration is constant. This equation is useful in driving safety. If we double the speed, the distance travelled by the vehicle before it stops will be quadrupled. This equation is the third equation of motion.
Note: For deriving the newton’s one-dimensional equations of laws of motion, the acceleration must be constant. The equations of motions are valid when the acceleration is constant and the path is considered a straight line. In this equation, the distance traveled by the body is calculated as the area of the trapezium.
Formula used:
Area of trapezium=$\dfrac{1}{2}$ (sum of parallel sides + distance between parallel sides)
Complete step-by-step answer:

Let us assume the initial velocity of the object, final velocity of the object, acceleration of the object and distance traveled by the object as $u,v,a,S$ respectively. Let the object reach the point B after time $t$. Now, draw a line parallel to the x-axis DA from point D from where the object starts moving. Now, draw another line from point B parallel to y-axis which meets E at y-axis. Now, the distance travelled by the body with uniform velocity is given by the area of trapezium ABDO.
Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& S=\dfrac{1}{2}(DO+BE)\times OE \\
& S=\dfrac{1}{2}(u+v)\times t \\
& \\
\end{align}$
We also know that,
$\begin{align}
& a=\dfrac{v-u}{t} \\
& t=\dfrac{v-u}{a} \\
\end{align}$
Now, substitute the t value in distance equation, we get,
$\begin{align}
& S=\dfrac{1}{2}(u+v)(v-u) \\
& 2S={{v}^{2}}-{{u}^{2}} \\
& \\
\end{align}$
Hence proved.
Additional Information: We know, velocity is directly proportional to time when acceleration is constant and displacement is directly proportional to time squared, when acceleration is constant. If we combine the above two equations, we get an equation that is independent of time. Displacement is proportional to velocity squared when acceleration is constant. This equation is useful in driving safety. If we double the speed, the distance travelled by the vehicle before it stops will be quadrupled. This equation is the third equation of motion.
Note: For deriving the newton’s one-dimensional equations of laws of motion, the acceleration must be constant. The equations of motions are valid when the acceleration is constant and the path is considered a straight line. In this equation, the distance traveled by the body is calculated as the area of the trapezium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




