
Derive an expression for a one-dimensional simple harmonic progressive wave travelling in the direction of the positive x-axis. Express it in terms of $A,\lambda ,\nu ,t(and)x$.
Answer
513k+ views
Hint:In physics, when a wave is moving in space but linearly in only one direction continuously then the mathematical representation of travelling wave in the function of sine and cosine forms of simple harmonic motion is known as simple harmonic travelling progressive wave of one dimension.
Formula used:
A simple harmonic wave is simple written in sine form as,
$y = A\sin \omega t$
where $y$ is the displacement of a wave at time $t$ with maximum amplitude $A$.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us suppose a progressive simple harmonic wave is travelling in positive x axis and let $\delta $ is the path difference of the wave and $y$ is the displacement of wave at time $t$ with maximum amplitude $A$ then using $y = A\sin \omega t$ we can write travelling wave as $y = A\sin (\omega t - \delta )$. Wave is represented as,
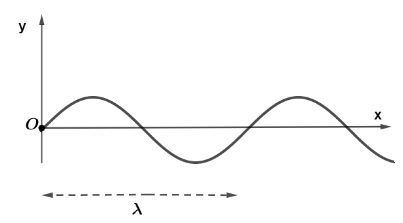
And path difference is calculated by the formula,
$\delta = \dfrac{{2\pi x}}{\lambda }$
Where, $x,\lambda $ are the position of the wave on the x-axis and the wavelength of the wave.
So,
$y = A\sin (\omega t - \dfrac{{2\pi x}}{\lambda })$
Now, angular frequency is written as
$\omega = 2\pi \nu $ Where $\nu $ is the frequency of the wave.
So we get,
$y = A\sin (2\pi \nu t - \dfrac{{2\pi x}}{\lambda })$
Take $2\pi $from the sine function
$\therefore y = A\sin 2\pi (\nu t - \dfrac{x}{\lambda })$
Hence, a simple harmonic progressive travelling wave on the positive X-axis can be written mathematically as $y = A\sin 2\pi (\nu t - \dfrac{x}{\lambda })$.
Note:It should be remembered that if the travelling wave was moving in negative x-axis the wave equation will therefore be written as $y = A\sin 2\pi (\nu t + \dfrac{x}{\lambda })$ the travelling waves when bound between two points and when they form new wave by incident and reflected wave superimposed on each other are known as standing waves.
Formula used:
A simple harmonic wave is simple written in sine form as,
$y = A\sin \omega t$
where $y$ is the displacement of a wave at time $t$ with maximum amplitude $A$.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us suppose a progressive simple harmonic wave is travelling in positive x axis and let $\delta $ is the path difference of the wave and $y$ is the displacement of wave at time $t$ with maximum amplitude $A$ then using $y = A\sin \omega t$ we can write travelling wave as $y = A\sin (\omega t - \delta )$. Wave is represented as,

And path difference is calculated by the formula,
$\delta = \dfrac{{2\pi x}}{\lambda }$
Where, $x,\lambda $ are the position of the wave on the x-axis and the wavelength of the wave.
So,
$y = A\sin (\omega t - \dfrac{{2\pi x}}{\lambda })$
Now, angular frequency is written as
$\omega = 2\pi \nu $ Where $\nu $ is the frequency of the wave.
So we get,
$y = A\sin (2\pi \nu t - \dfrac{{2\pi x}}{\lambda })$
Take $2\pi $from the sine function
$\therefore y = A\sin 2\pi (\nu t - \dfrac{x}{\lambda })$
Hence, a simple harmonic progressive travelling wave on the positive X-axis can be written mathematically as $y = A\sin 2\pi (\nu t - \dfrac{x}{\lambda })$.
Note:It should be remembered that if the travelling wave was moving in negative x-axis the wave equation will therefore be written as $y = A\sin 2\pi (\nu t + \dfrac{x}{\lambda })$ the travelling waves when bound between two points and when they form new wave by incident and reflected wave superimposed on each other are known as standing waves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




