
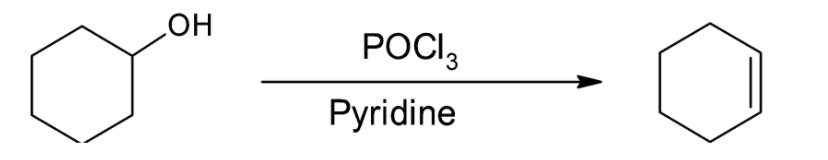
Dehydration of alcohols takes place more rapidly with $POC{l_3}$ than with ${H_2}S{O_4}$. Select the correct statements about the above dehydration reaction:
A.It does not involve carbocation
B.It involves $R - OPOC{l_2}$ with $ - OPOC{l_2}$ as a better leaving group
C.It involves the $E2$ mechanism as the pyridine base abstracts protons from the adjacent carbon at the same time at which $ - OPOC{l_2}$ is leaving.
D.It is an $E1$ reaction without formation of carbocation.

Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint:Dehydration of alcohols is a method for the preparation of alkenes from alcohols. $POC{l_3}$ is a very useful reagent for the dehydration of alcohols for the production of alkenes. It has an advantage over dehydration using ${H_2}S{O_4}$ as unlike the latter, no rearrangement occurs in the reaction with $POC{l_3}$.
Complete answer:
The dehydration reaction given is occurring in the presence of $POC{l_3}$ as initial attacking species and pyridine as base. Phosphorous oxychloride is a derivative of phosphoric acid and converts the alcohol into an alkyl chloro phosphite. The $ - OPOC{l_2}$ group formed is a strong leaving group as compared to the hydroxyl group, thus making the reaction more feasible.
Now, the base pyridine attacks the intermediate alkyl phosphate and deprotonates it. The reaction occurs by the $E2$ mechanism and no carbocation is formed. The hydrogen ion is abstracted in the same step as the chloro phosphate group leaves.
Thus, we can conclude that the correct options are A, B and C.
Note:
We know that the hydroxyl group is a very poor leaving group. This is because the bond formed between carbon and oxygen is very strong due to almost similar sizes of the atoms and thus it is difficult to cause the removal of the hydroxyl group by breaking the carbon- oxygen bond. So, to make sure that the alcohols participate in a desired substitution or elimination reaction which involves the departure of the hydroxyl group, the hydroxyl group is first modified so as to stabilize the anion formed on the cleavage of carbon- oxygen bond thus making the cleavage more feasible.
Complete answer:
The dehydration reaction given is occurring in the presence of $POC{l_3}$ as initial attacking species and pyridine as base. Phosphorous oxychloride is a derivative of phosphoric acid and converts the alcohol into an alkyl chloro phosphite. The $ - OPOC{l_2}$ group formed is a strong leaving group as compared to the hydroxyl group, thus making the reaction more feasible.
Now, the base pyridine attacks the intermediate alkyl phosphate and deprotonates it. The reaction occurs by the $E2$ mechanism and no carbocation is formed. The hydrogen ion is abstracted in the same step as the chloro phosphate group leaves.
Thus, we can conclude that the correct options are A, B and C.
Note:
We know that the hydroxyl group is a very poor leaving group. This is because the bond formed between carbon and oxygen is very strong due to almost similar sizes of the atoms and thus it is difficult to cause the removal of the hydroxyl group by breaking the carbon- oxygen bond. So, to make sure that the alcohols participate in a desired substitution or elimination reaction which involves the departure of the hydroxyl group, the hydroxyl group is first modified so as to stabilize the anion formed on the cleavage of carbon- oxygen bond thus making the cleavage more feasible.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




