
Define the term principal foci of a convex lens and show them with the help of proper diagrams.
Answer
518.4k+ views
Hint: A concave lens is a lens that possesses at least one surface that curves inwards. It is a diverging lens, meaning that it spreads out light rays that have been refracted through it. A concave lens is thinner at its centre than at its edges, and is used to correct short-sightedness (myopia).
Complete answer:
Principal foci: A principal focus or focal point is a special focus- for a lens, or a spherical or parabolic mirror, it is a point onto which collimated light parallel to the axis is focused. Since light can pass through a lens in either direction, a lens has two focal points – one on each side.
A light ray can pass through a lens from either direction. Therefore, a lens has two principal foci.
For a concave lens, the first focal point is a point F1 on the principal axis of the lens such that the incident rays of light appearing to meet at it, after refraction from the lens become parallel to the principal axis of the lens.
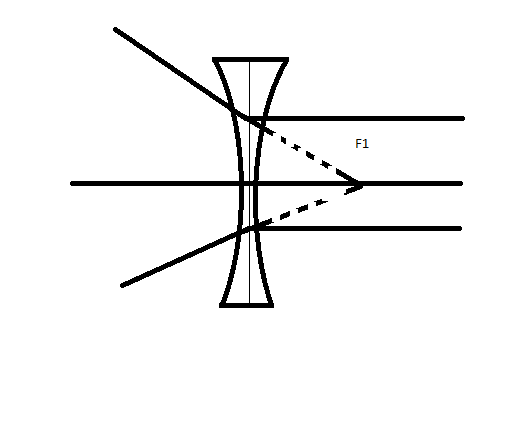
The second focal point for a concave lens is a point F2 on the principal axis of the lens such that the rays of light incident parallel to the principal axis, after refraction from the lens, appear to be diverging from this point.
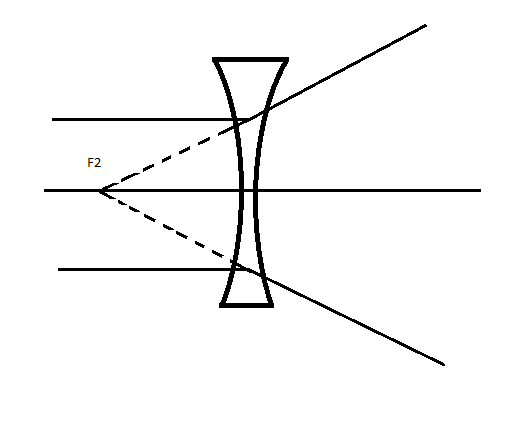
Note: The image formed by a concave lens is always virtual, which can never be captured or obtained on a screen because the incoming rays diverge after refraction. Properties of the images formed by a concave lens. ... The image formed by the concave lens is always virtual, erect, and diminished (very small).
Complete answer:
Principal foci: A principal focus or focal point is a special focus- for a lens, or a spherical or parabolic mirror, it is a point onto which collimated light parallel to the axis is focused. Since light can pass through a lens in either direction, a lens has two focal points – one on each side.
A light ray can pass through a lens from either direction. Therefore, a lens has two principal foci.
For a concave lens, the first focal point is a point F1 on the principal axis of the lens such that the incident rays of light appearing to meet at it, after refraction from the lens become parallel to the principal axis of the lens.

The second focal point for a concave lens is a point F2 on the principal axis of the lens such that the rays of light incident parallel to the principal axis, after refraction from the lens, appear to be diverging from this point.

Note: The image formed by a concave lens is always virtual, which can never be captured or obtained on a screen because the incoming rays diverge after refraction. Properties of the images formed by a concave lens. ... The image formed by the concave lens is always virtual, erect, and diminished (very small).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




