
Define the term 'cell' for plants/animals. Name the different organelles that make a cell. Explain why none of these are called the structural and function unit of life?
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: Cell organelles are not called basic and practical units of life since they are the structures present inside the phone that help it to play out its relevant capacities. These cell organelles cooperate to perform various elements of the cell.
Complete answer:
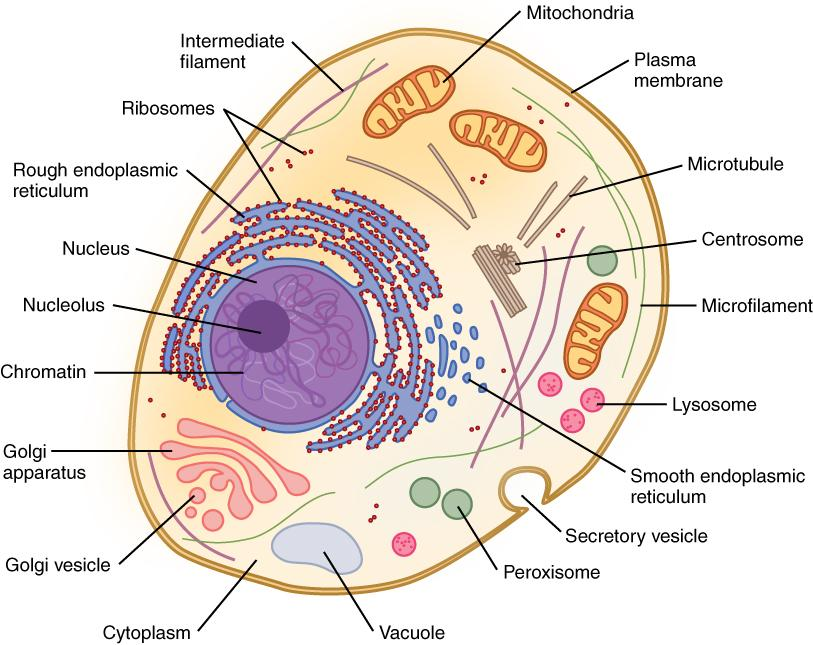
Plant animal’s cells: are both eukaryotic cells, which means they have a characterized core and layer bound organelles. They share numerous normal highlights, for example, a cell layer, core, mitochondria, Golgi contraption, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, and more. However, they have some clear contrasts. Initially, plant cells have a cell divider that encompasses the cell layer, while creature cells don't. Plant cells likewise have two organelles that creature cells need: chloroplasts and an enormous focal vacuole.
Nucleus: the nucleus is a layer bound organelle that contains hereditary material (DNA) of eukaryotic life forms. In that capacity, it serves to keep up the respectability of the cell by encouraging record and replication measures. It's the biggest organelle inside the cell taking up about a 10th of the whole cell volume.
Mitochondria: film bound cell organelles (mitochondrion, particular) that create the majority of the synthetic energy expected to control the cell's biochemical responses. Synthetic energy created by the mitochondria is put away in a little atom called adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Ribosomes: minute particles composed of RNA and related proteins that have the capacity to combine proteins. Proteins are required for some phone capacities, for example, fixing harm or coordinating substance measures.
Vacuole: A vacuole is a film bound cell organelle. In creature cells, vacuoles are commonly little and help sequester byproducts. In plant cells, vacuoles help keep up water balance. Now and then a solitary vacuole can take up the vast majority of the inside space of the plant cell.
Golgi complex: apparatus modifies proteins and lipids that it gets from the endoplasmic reticulum. These biochemical leave the Golgi by exocytosis before being conveyed to various intracellular or extracellular targets.
Endoplasmic reticulum: The huge organization of membranous sheets and cylinders is called endoplasmic reticulum. They are loaded up with liquids and conveys materials all through the phone because of which it is likewise called transport arrangement of the phone.
Note: None of them are called the structural and functional unit of life because the functions capacities and structures of cell organelle in total summarize the capacity of the cell. Nonetheless, an individual organelle is unequipped for conveying all the exercises of a cell.
Complete answer:
Plant animal’s cells: are both eukaryotic cells, which means they have a characterized core and layer bound organelles. They share numerous normal highlights, for example, a cell layer, core, mitochondria, Golgi contraption, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, and more. However, they have some clear contrasts. Initially, plant cells have a cell divider that encompasses the cell layer, while creature cells don't. Plant cells likewise have two organelles that creature cells need: chloroplasts and an enormous focal vacuole.
Nucleus: the nucleus is a layer bound organelle that contains hereditary material (DNA) of eukaryotic life forms. In that capacity, it serves to keep up the respectability of the cell by encouraging record and replication measures. It's the biggest organelle inside the cell taking up about a 10th of the whole cell volume.
Mitochondria: film bound cell organelles (mitochondrion, particular) that create the majority of the synthetic energy expected to control the cell's biochemical responses. Synthetic energy created by the mitochondria is put away in a little atom called adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Ribosomes: minute particles composed of RNA and related proteins that have the capacity to combine proteins. Proteins are required for some phone capacities, for example, fixing harm or coordinating substance measures.
Vacuole: A vacuole is a film bound cell organelle. In creature cells, vacuoles are commonly little and help sequester byproducts. In plant cells, vacuoles help keep up water balance. Now and then a solitary vacuole can take up the vast majority of the inside space of the plant cell.
Golgi complex: apparatus modifies proteins and lipids that it gets from the endoplasmic reticulum. These biochemical leave the Golgi by exocytosis before being conveyed to various intracellular or extracellular targets.
Endoplasmic reticulum: The huge organization of membranous sheets and cylinders is called endoplasmic reticulum. They are loaded up with liquids and conveys materials all through the phone because of which it is likewise called transport arrangement of the phone.

Note: None of them are called the structural and functional unit of life because the functions capacities and structures of cell organelle in total summarize the capacity of the cell. Nonetheless, an individual organelle is unequipped for conveying all the exercises of a cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




