
Define the ascent of sap. Describe in detail the mechanism of the ascent of sap.
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: The xylem tissue is involved in the ascent of sap which is the upward movement of water and minerals from the root to the crown part of the plant. It is used to transport nutrients and water to the leaves to carry out photosynthesis.
Complete answer:
-The xylem is a complex tissue consisting of both living and non-living cells.
-The conducting cells in xylem are typically non-living called tracheids and xylem vessels.
-Both of these cells have thick, lignified secondary cell walls and are dead at maturity.
-Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain the phenomenon but the cohesion-tension mechanism has been found to be most evident.
-The cohesion-tension hypothesis was proposed simultaneously by two groups of scientists Dixon and Joly in the UK and Askenasy in Germany.
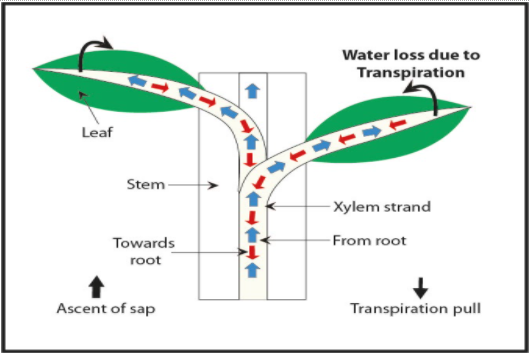
-The principle of this mechanism is that water is assumed to form a continuous column extending from the growing shoots and leaves to the roots. Evaporation from the surface of the mesophyll leaves of the leaf provides the driving force for water movement and thus increases their suction force resulting in the withdrawal of water from the dead xylem cells.
-This puts the column in strain. The xylem cells merely act as inert tubes and are of considerable importance because they prevent the collapse of the water column and also prevent the entry of bubbles.
-The column resists breaking because of the cohesive and adhesive forces between the water molecules.
-Water covers the surfaces of the mesophyll cells as a thin film, adhering to cellulose and the other hydrophilic surfaces.
-Evaporation into the leaf spaces causes the water-air interface to retreat into the small spaces between cellulose microfibrils and at the junctions of leaf mesophyll cells.
-As the water retreats, the resulting surface tension pulls water from the adjacent cells.
-Since the water column is continuous, this tension is transmitted through the column, ultimately down to the roots and soil water.
Note: -When the atmospheric pressure is reduced, air enters a wound.
-Water tends to evaporate, filling the tracheid (cavitation) followed by the release of dissolved gases in the form of bubbles of air, thus blocking the movement of water.
Complete answer:
-The xylem is a complex tissue consisting of both living and non-living cells.
-The conducting cells in xylem are typically non-living called tracheids and xylem vessels.
-Both of these cells have thick, lignified secondary cell walls and are dead at maturity.
-Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain the phenomenon but the cohesion-tension mechanism has been found to be most evident.
-The cohesion-tension hypothesis was proposed simultaneously by two groups of scientists Dixon and Joly in the UK and Askenasy in Germany.
-The principle of this mechanism is that water is assumed to form a continuous column extending from the growing shoots and leaves to the roots. Evaporation from the surface of the mesophyll leaves of the leaf provides the driving force for water movement and thus increases their suction force resulting in the withdrawal of water from the dead xylem cells.
-This puts the column in strain. The xylem cells merely act as inert tubes and are of considerable importance because they prevent the collapse of the water column and also prevent the entry of bubbles.
-The column resists breaking because of the cohesive and adhesive forces between the water molecules.
-Water covers the surfaces of the mesophyll cells as a thin film, adhering to cellulose and the other hydrophilic surfaces.
-Evaporation into the leaf spaces causes the water-air interface to retreat into the small spaces between cellulose microfibrils and at the junctions of leaf mesophyll cells.
-As the water retreats, the resulting surface tension pulls water from the adjacent cells.
-Since the water column is continuous, this tension is transmitted through the column, ultimately down to the roots and soil water.
Note: -When the atmospheric pressure is reduced, air enters a wound.
-Water tends to evaporate, filling the tracheid (cavitation) followed by the release of dissolved gases in the form of bubbles of air, thus blocking the movement of water.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




