
Define reflex arc and its component.
Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint: A reflex or reflex action is an involuntary and instantaneous movement in response to a stimulus and it is possible by neural pathways called reflex arcs. A reflex arc is the neural pathway which carries sensory information from the receptor organ to the spinal cord and then carries the response generated by the spinal cord to the organ during reflex action.
Complete answer:
The entire process of response to a peripheral nervous stimulation that occurs involuntarily and it requires the involvement of a part of the central nervous system. Reflex actions are very rapid, automatic responses in which some kind of stimulus evokes a short lived response.
There are two types of reflex arc:
• Autonomic reflex arc (affecting inner organs)
• Somatic reflex arc (affecting muscles)
The reflex arc consists of 5 components:
• Sensory receptor
• Sensory neuron
• Interneuron
• Motor or efferent neuron
•Effectors
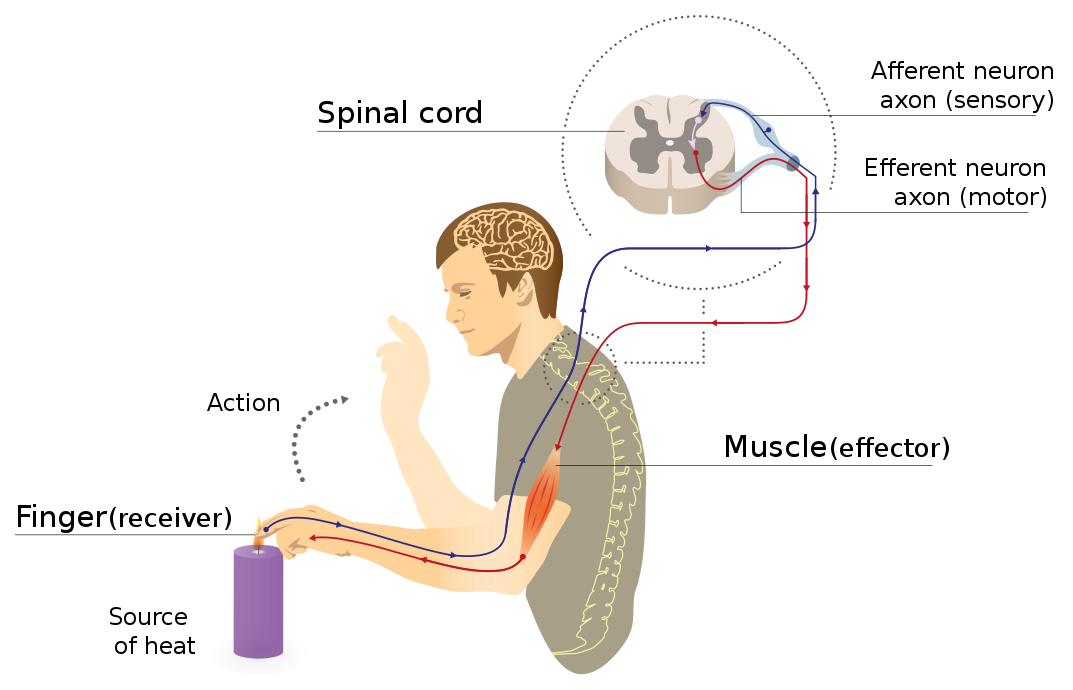
Working of the components of reflex arc:
• The stimulus is detected by sensory receptors present in the skin.
• These initiate nerve impulses in the sensory or afferent neurons leading them to the spinal cord.
• These impulses enter the spinal cord and initiate impulses in one or more interneurons.
• Interneurons initiate impulses in one or more motors or different neurons.
• The motor neurons carry these impulses to the effectors or skeletal muscles in which response will be shown.
• The muscles called flexors (bends a part towards the body) are stimulated to withdraw the body part whereas the muscles called extensors (extends a part) are inhibited to avoid the extension of the body parts. This results in the involuntary movement of the body from the irritating stimulus.
Note: The reflex pathway comprises at least one afferent neuron (coming from receptor) and one efferent neuron (going to effector) appropriately arranged in series. A reflex arc is a neural pathway that controls a reflex.
Complete answer:
The entire process of response to a peripheral nervous stimulation that occurs involuntarily and it requires the involvement of a part of the central nervous system. Reflex actions are very rapid, automatic responses in which some kind of stimulus evokes a short lived response.
There are two types of reflex arc:
• Autonomic reflex arc (affecting inner organs)
• Somatic reflex arc (affecting muscles)
The reflex arc consists of 5 components:
• Sensory receptor
• Sensory neuron
• Interneuron
• Motor or efferent neuron
•Effectors

Working of the components of reflex arc:
• The stimulus is detected by sensory receptors present in the skin.
• These initiate nerve impulses in the sensory or afferent neurons leading them to the spinal cord.
• These impulses enter the spinal cord and initiate impulses in one or more interneurons.
• Interneurons initiate impulses in one or more motors or different neurons.
• The motor neurons carry these impulses to the effectors or skeletal muscles in which response will be shown.
• The muscles called flexors (bends a part towards the body) are stimulated to withdraw the body part whereas the muscles called extensors (extends a part) are inhibited to avoid the extension of the body parts. This results in the involuntary movement of the body from the irritating stimulus.
Note: The reflex pathway comprises at least one afferent neuron (coming from receptor) and one efferent neuron (going to effector) appropriately arranged in series. A reflex arc is a neural pathway that controls a reflex.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




